Name Quantum Theory Problems
advertisement
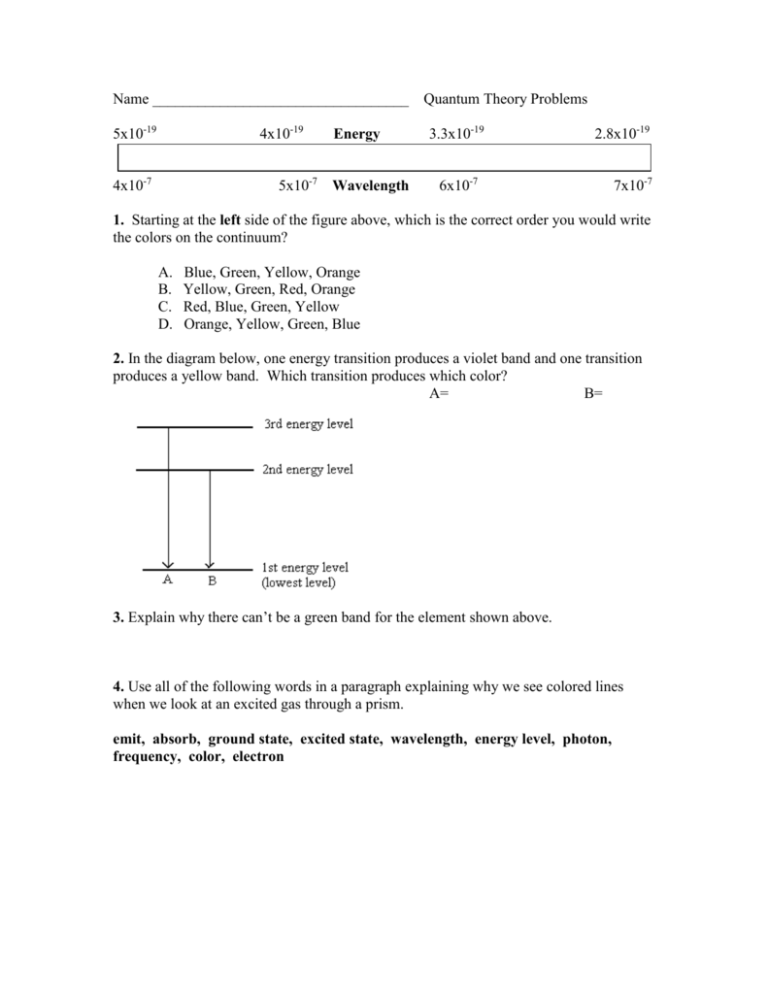
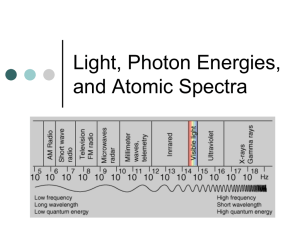
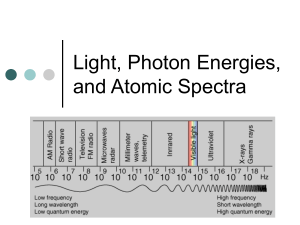
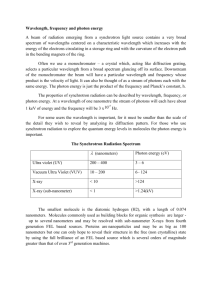
Name __________________________________ 5x10-19 4x10-19 4x10-7 5x10-7 Energy Wavelength Quantum Theory Problems 3.3x10-19 2.8x10-19 6x10-7 7x10-7 1. Starting at the left side of the figure above, which is the correct order you would write the colors on the continuum? A. B. C. D. Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange Yellow, Green, Red, Orange Red, Blue, Green, Yellow Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue 2. In the diagram below, one energy transition produces a violet band and one transition produces a yellow band. Which transition produces which color? A= B= 3. Explain why there can’t be a green band for the element shown above. 4. Use all of the following words in a paragraph explaining why we see colored lines when we look at an excited gas through a prism. emit, absorb, ground state, excited state, wavelength, energy level, photon, frequency, color, electron 5. Six energy transitions for a hypothetical element are shown in the diagram below. One produces an infrared frequency, two produce visible frequencies, and three produce ultraviolet frequencies. Label each transition as either visible, infrared, or ultraviolet. 6. Of the two visible frequencies produced above, one is orange and the other is green. Label the orange and green transitions in the diagram above. 7. The energy transitions for hydrogen are shown below. The wavelength of light produced by each transition is given in nanometers (nm). When hydrogen is excited and the light is separated by a prism, four visible bands (red, green, blue, and violet) are observed. 8. Which color is produced by the transition from n=6 to n=2? 9. Which color is produced by the transition from n=5 to n=2 (434 nm)? 10. Which color is produced by the transition from n=4 to n=2 (486 nm)? 11. Which color is produced by the transition from n=6 to n=3? Use the energy transition diagram below for a hypothetical element to answer the questions which follow. 12. Which energy transition above will produce light with the lowest frequency? 13. Which energy transition above will produce light of the longest wavelength? 14. Which energy transition will produce light with the greatest amount of energy? 15. The emission spectrum for the hypothetical element above is shown in the diagram below. Match the letters of the energy transitions above with the correct spectral bands below. 16. Which emission lines above have wavelengths that are too long for the human eye to see? Which have wavelengths that are too short to see? 17. If one of the two visible lines above is yellow and one is green, which spectral line is yellow? 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 E = hv E is the energy of the light in Joules (J), h is a constant which is 6.626 X 10-34 J·s, and v is the frequency of the light in s-1 or waves/s (also called Hertz (Hz). Use the formula above and the table below to answer the questions which follow. Frequency, 7.1 X 1014 s-1 or (1/s) Wavelength, 422 nm Color violet 6.4 X 1014 5.7 X 1014 5.2 X 1014 4.8 X 1014 4.3 X 1014 469 526 577 625 698 blue green yellow orange red 18. What is the frequency of a photon of light if it has an energy of 6.4 X10-19 Joules? 19. When calcium salt is heated in a flame, a photon of light with an energy of 3.2 X 10-19 Joules is emitted. What color would be expected for the calcium flame? 20. A photon of light has a wavelength of 698 nm. How much energy does it have in Joules? 21. What is the frequency of light if it has an energy of 3.18 X 10-19 Joules? 22. What is the color of a photon of light with an energy of 3.8 X 10-19 J? 23. How much energy does a violet photon have? 24. The longer the wavelength the __________________ the frequency. 25. The longer the wavelength the _______________ the energy.