Prepared By:*
advertisement

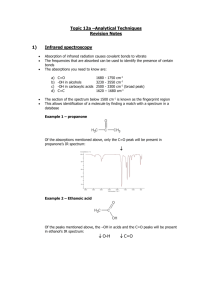
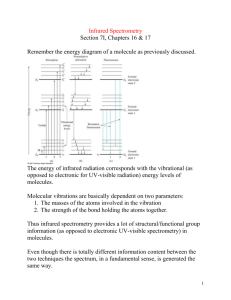
GENERAL TESTING PROCEDURE TITLE: INFRARED SPECTROPHOTOMETRY GTP No. GTP007-00 Effective Date Reference USP/Ph. Eur. Page No. 1. 1 of 2 PRINCIPLE: Spectrophotometric tests are commonly used in the Identification of chemical substances and quantification of polymorphic forms. The test procedures are applicable to substances that absorb IR radiation. The IR absorption spectrum of a substance compared with that obtained concomitantly for the corresponding reference standard / reference substance provide conclusive evidence of the identity of the substance being tested. Method -1: Recording Infrared spectrum of a solid as a disc: (USP ‹197K› and Ph.Eur.2.2.24 B) Note: Dry the Potassium Bromide at 250°C for 2 hours on the day of use. 1. Triturate about 1 to 2 mg of the substance to be examined with 300 to 400 mg, unless otherwise specified, of finely powdered and dried potassium bromide. If the substance is a hydrochloride it is preferable to use potassium chloride. 2. Carefully grind the mixture and spread it uniformly in a suitable die. 3. Submit it to the pressure of about 10000 mPa (10 tons/cm2). 4. Examine the disc visually and if any lack of uniform transparency is observed, reject the disc and prepare again. 5. Record the spectrum between 4000 to 650 cm-1 unless otherwise specified in individual standard test procedure. 6. When sample and standard are measured for concordance, the transmittance obtained at the start of the scan range, should not deviate by more than 10% between them (For eg. If the standard shows a transmittance of 75%, the sample transmittance can be between 65% and 85%). Method -2: Recording Infrared spectrum of a solid as a mull: (USP ‹197M› and Ph.Eur.2.2.24 A) 1. Triturate 5 to 10 mg of the substance to be examined with minimum quantity of liquid paraffin (mineral oil). 2. Compress the mull between two plates transparent to infrared radiation (Sodium chloride cells or Potassium bromide discs). 3. Mount the discs in a suitable holder and record the spectrum between 4000 to 650 cm1 unless otherwise specified in individual standard test procedure. Method -3: Recording Infrared spectrum of a liquid: (USP ‹197F› and Ph.Eur.2.2.24) 1. Examine the liquid in the form of a film between two plates transparent to infrared radiation (Sodium chloride cells or Potassium bromide cells). GENERAL TESTING PROCEDURE TITLE: INFRARED SPECTROPHOTOMETRY GTP No. GTP007-00 Effective Date Reference USP/Ph. Eur. Page No. 2 of 2 2. Record the spectrum between 4000 to 650 cm-1 unless otherwise specified in individual standard test procedure. Method -4: Recording Infrared spectrum of a liquids or solids in solution: (USP ‹197S› and Ph.Eur.2.2.24.) 1. Prepare a solution of the sample to be examined having a concentration of 10 to 100g per liter. 2. Select a liquid cell with a path length of 0.5 to 1 mm. 3. Fill the cell with sample solution ensuring that there are no air bubbles in the light path.. 4. Record the spectrum between 4000 to 650 cm-1 unless otherwise specified in individual Standard test procedure. 5. Subtract the absorption due to solvent by placing a similar cell containing the solvent in the reference beam. 2. PROCEDURE: 1. Prepare the sample in a suitable manner as explained above. 2. Record the spectra of the substance to be examined and the reference spectra under the same operational conditions. Acceptance criteria: a. The spectrum obtained with the test specimen exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of the similar preparation of the Reference Standard/ substance/Working standard/substance. b. When the spectra obtained with sample and standard is over layered, all absorption maxima in the spectrum obtained with sample shall be concordant with that obtained with standard, in their positions, throughout the scan range. c. If a difference appears in the IR spectra of the sample and standard, dissolve equal portions of the sample and the standard in equal volumes of a suitable solvent, evaporate the solution to dryness in similar containers under identical conditions and repeat the test on the residues.