spektro IR
advertisement

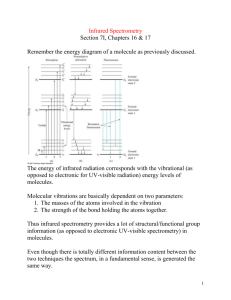
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY Pn. Suryati Bt. Syafri En. Maywan Hariono 2009 What is IR light? Is a kind of electromagnetic radiation which has wave region longer than visible light, but shorter than radio wave. Low energy What is IR region? The wavelength region is 2.5-25 µm The unit commonly used is wavenumbers (cm-1 ) i.e. 4000-400 cm-1 Remember that Wavenumber is proportional with energy (E) and frequency (v), but reciprocal with wavelength. Light & Electromagnetic Spectrum IR Application - Broadly applied in several area sort of : Army Fire man Veterinary Pharmacy Electronic devices Remote sensing IR spectrum Divided into 3 regions 1. Near Infrared 2. Middle Infrared 3. Far Infrared Spektrum IM Ranges Far Infrared Middle Infrared Near Infrared Wavelength 50-1000µm 2.5-50µm range 0.8-2.5µm Wavelength 200-10cm-1 4000number 200cm-1 125004000 cm-1 Energy range 1.55-0.5eV 0.0250.0012eV 0.50.025eV Principles When the certain molecules are exposed to IR light, it will absorb the energy to make the atoms of molecules vibrating The vibration frequency depend on the amount of atoms and the length and the strength of atomic bonding Molecule vibration is stimulated by absorption radiation in the same frequency with the frequency of its origin vibrations Energy Trends Energy follows vibration frequency of atoms -light atoms vibrate more rapidly: -CH, NH, OH vibrations . 2800 cm-1 Multiple bonds vibrate more rapidly: triple bonds : C≡C (2100-2200), C≡N (2240- 2280) Double bonds : C=O (1680-1750), C=C (1620-1680) Single bond : C-O (1025-1200) Intensity Trends Follows change in dipole caused by vibrating atoms – Polar bonds (strong bond dipoles) absorb strongly O-H C=O, C=N C-O – Nonpolar bonds absorb weakly C=C, C≡C Follows overlapping bands – CH bands tend to overlap – Molecules contain many CH – CH absorptions tend to be strong PRINCIPLES For each molecules, there is a various kind of vibration occurs What kind of sample be able to absorb IR radiation? Only vibration which alters molecule dipole moment (electron Hanya getaran yang meyebabkan perubahan dipole molekul (the magnitude of positive and negative charge between two bonded atoms) and having the IR absorption frequency in the IR region Gas molecules such as O2, H2 and Cl2 don’t have a dipole moment, means no IR absorption occurs SO2 dan CO2 have a dipole moment so it will give IR absorption Every functional group has their own IR absorption The more complex in molecule structure, the more complex in IR absorption It is used to identify any functional group presents in a molecule structure IR Spectrum Distribution 1. 4000-2500 cm-1, absorption of atom which is bond to H atom, ex: C-H, O-H dan N-H 2. 2500-2000 cm-1, triple bond, ex: C≡C , C≡N 3. 2000-1500 cm-1, double bond, ex: C=O, C=C, C=N 4. 1500-400 cm-1, an absorption that involves the deformation of other bondings Fingerprint region (<1500 cm-1) Many bands & many overlaps – Heavy atom stretches – All bends, etc. – Should have simple molecule (or other evidence or structure) before intepreting bands in this region Overall pattern reflects molecular structure – Pattern from 1400-600 = molecular fingerprints Prosedure IR light is passed through the sample, and the amount of energy which is absorbed by the sample per cm wavelength will be recorded . The IR light desired will be selected by monochromator before exposed to the sample’ Interferometer is used for measuring all wavelength in one running time. The data will be translated into the graph which is plotted as wavelength vs transmision The graph might be compared to known standard reference Instrumentation Conventional method(dispersive instrument) – The monochromator being used to select frequency of one radiation in one time through the sample. Peralatan Spektrometer FTIR (Fourir Transform IR) – Semua frekuensi yang diperlukan melalui instrument sekaligus – Menggunakan interferometer contohnya Michelson Interferometer – Teknik cepat dan pantas – Digunakan dikebanyakan makmal kimia Animation of FTIR IR Components A. IR Resources – Quartz halogen Nernst Glower lamp (run at 2000oC) – Globar (made from Carbide silicon, run at 1100oC) IR Components B. sample 1. solids – A. Nujol mull The sample is ground using a mortar and pestle to give a very fine powder A small amount is then mixed with nujol (liquid paraffin) togive a paste Several drops of this paste are then applied between two sodium chloride plates (these do not absorb infrared in the region of interest) The plates are then place in the instrument sample holder ready for scanning IR Components B. Potassium Bromide disk – A verry small amount of the solid (approximately 1-2 mg) is added to pure potassium bromide powder (approximately 200 mg) and ground up as fine as possible – This is then placed in a small die and put under pressure mechanically. The pressure is maintained for several minutes before removing the die and the KBr disk formed – The disk is then placed in a sample holder ready scanning Sample preparation Sample preparation 2. thin films – The infrared spectrum of thin film can be easily obtained by placing a sample in a suitable holder, such as a card with a slot cut for the sample window – This method is often used for checking the calibration of an instrument with a polystrirene sample as the band produced by this material are accurately known 3. liquids – This is possibly the simplest and the common method for sample preparation – A drop of the sample is placed between two potassium bromide or sodium chloride circular plates to produce a thin capillary film – The plates are then placed in a holder ready for analysis Sample preparation 4. gases – To obtaine an infrared spectrum of a gas requires the use of a cylindrical gas cell with windows at each end composed of an infrared inactive material such as KBr, NaCl or CaF2 – The cell usually has an inlet and outlet port with atap to enable the cell to be easilly filled with the gas to be analyzed instrumentation C. monochromator/interferometer – Break down the radiation of light to the different wave region in one time running process. D. detector – CCD (charge couple device) – InGaAs (Indium Gallium Arsen) – Pbs (Lead sulfide) Instrumentation Display – Exhibit the collected data – Translate the data to the graph – The graph is plotted as transmision vs frequnecy (wavenumbers) Advantages Provide the fingerprint for the sample being analyzed The installation of instrument to the computer allows the comparison of sample spectrum and standard reference can be run simultaneously Disadvantages Rarely used for quantitative purpose since the spectrum produced is too complicated to determine one by one The sample preaparation is quite difficult, needs the skill to handle it. aniline phenol Salycilic acid ethanol Contoh spektrum allopurinol phenytoin References David G. watson (2005). Pharmaceuthical Analysis. Second edition. Pp:115-128 http://en. Wikipedia.org./wiki/Infrared spectroscopy http://www.chem.ualberta.ca/~orgla bs/procedures/Infrared Spectroscopy/ir/IR%20Main.html