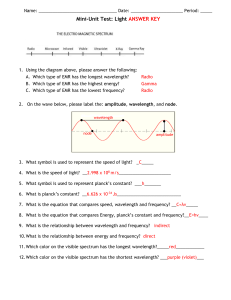
EM Spectrum - A Calculation Investigation
advertisement

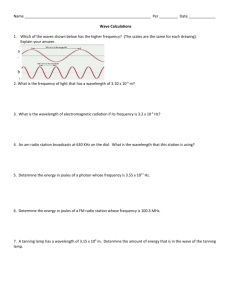
HON 203 Lab 2 EM Spectrum - A Calculation Investigation You are given the following two equations that express the relationships between the speed, the wavelength, the energy and the frequency of light: c=ln speed = wavelength x frequency E = hn energy = Planck's constant x frequency 1. Check the equations above and show that the units match on each side of the equations. 2. Manipulate both equations to solve for energy (E) as a function of wavelength (l) and fundamental constants. Show each step. Show that the units match on each side of the resulting equations. 3. Given a photon's wavelength, frequency or energy in the chart below, use the above equations to solve for the other two (in the units indicated). Use the useful constants page if you need to. 4. Summarize what you have learned about light and the relationship between its energy, frequency and wavelength. Wavelength (m) Frequency (Hz) Energy (J) 0.001 7.0 x 1013 5.0 x 10-7 2.0 x 10-15 1.2 x 1022 Electromagnetic Radiation Range Useful Constants speed of light (c) = 3.0 x 108 m/s Planck's Constant (h) = 6.626 x 10-34 Joules second Charge of an electron (q) = 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs Useful Units frequency = cycles/second (Hz) wavelength = length (m) volt = a unit of potential of electric field, such that that it takes 1 Joule to push a charge of 1 Coulomb across 1 volt Conversion Factors 1 angstrom (A) = 1 x 10-10 meters (often used for the optical region of the spectrum) 1 KeV = 1,000 eV = 1.6 x 10-16 Joules