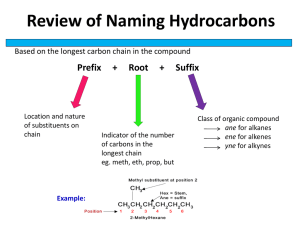
Nomenclature
advertisement

1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. Oral exam, 1st semester Classification of organic transformations. Electron configuration of carbon. The sp3 hybridization. Nomenclature of alkanes. Homologous series of alkanes, physical properties. Synthesis of alkanes. Conformation of alkanes: ethane, butane. Conformation of cycloalkanes. Isomerism of cycloalkanes. Isomerism in organic chemistry: definition, types, classification. Alkanes and cycloalkanes: chemical properties. Optical isomerism. Specific rotation, symmetry properties, chirality, types of chirality: central chirality, molecular asymmetry. Structure, naming and representation of chiral compounds. Relative and absolute configuration. Molecules with more than one chiral carbon. Separation of racemic mixtures. Preparation of optically pure compounds. Stereochemical characteristics of chemical transformations. Bond polarization: inductive and mesomeric effects, conjugation. Mesomeric structures. The sp2 hybridization. Nomenclature of alkenes. Isomerism of alkenes. Synthesis of alkenes. Chemical properties I – hydrogenation, oxidation. Alkenes: chemical properties II – electrophilic additions. Mechanism of electrophilic additions. Markovnikov’s rule. Polymerization. Dienes: types, addition reactions. Polymerization. The sp hybridization. Structure of the acetylenic bond. Synthesis, chemical properties. Structure of benzene, aromaticity. Synthesis of aromatic hydrocarbons. Addition and oxidation reactions of aromatics. Aromatic hydrocarbons: chemical properties. Aromatic electrophilic substitution. Substituent effects in aromatic SE reactions: reactivity and orientation. Polycyclic aromatic compounds. Organic halides: nomenclature, synthesis. Organic halides: chemical properties I – nucleophilic substitution. Classification of organic halides based on their reactivity. Organic halides: chemical properties II – elimination, reactions with metals. Hydroxy compounds and thio analogs: classification, nomenclature. Synthesis of compounds containing OH/SH group. Acidity of alcohols, phenols and their thio analogs. Acidity of sulfonic acids. Alcohols, phenols and thio analogs: physical properties (hydrogen bonding) and chemical properties. Ethers and sulfides: classification, nomenclature, structure, synthesis. Chemical properties. Cyclic ethers, crown ethers. Nitro compounds. Amines: classification, nomenclature, physical properties (hydrogen bonding), synthesis. Chirality of amines. Amines: chemical properties. Basicity of amines. Diazomethane. Diazonium compounds. Azo compounds. Carbonyl compounds: classification, nomenclature, structure, synthesis. General reactivity in nucleophilic additions. Reversibility. Carbonyl compounds: chemical properties I – nucleophilic additions. Carbonyl compounds: chemical properties II – enolization, acidity of enols, reactions of the enolate anion; oxidations and reductions. Carboxylic acids and derivatives: classification, nomenclature. Structure of the carboxyl group. Acidity of carboxylic and dicarboxylic acids. Chemical properties: decarboxylation, reduction. Carboxylic acids and derivatives: physical properties, synthesis. General reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives. Carboxylic acids: chemical properties – nucleophilic acyl substitutions. Substituted carboxylic acids: dicarboxylic acids, hydroxycarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids. Carbonic acid derivatives. Carbocations: types, stability; role in organic transformations. Exam test, 1st semester Nomenclature Draw the structure of the following compounds! styrene, Z-but-2-ene, allene, isoprene biphenyl, tropylium ion, ortho/para-xylene, 9,10-dihydroanthracene, cyclopentadienide ion, phenanthrene, tetralin methylene chloride, isobutyl chloride, benzyl chloride, sec-butyl chloride, vicinal dihalogen primary alcohol, allyl alcohol, ethylene oxide, ortho/para-cresol, anisole, tetrahydrofuran, glycerol, cis/trans-2,3-dimethyloxirane, ethoxy group, ethylene glycol, enol, geminal diol tosyl group, para-toluenesulfonic acid, dimethyl sulfoxide, diethyl disulfide, sulfanilamide benzenediazonium chloride, secondary amine, tertiary amine, N,N-dimethylpentanamine, azobenzene, nitronic acid, imine acetaldol, benzaldehyd cyanohydrin, acetal N,N-dimethylformamide, acetanilide, meso-tartaric acid, acetyl chloride, ethyl acetoacetate, aspirin, acetic anhydride, ketene, acetonitrile, lactol, lactone, lactam, malonic acid, diethyl malonate, salicylic acid, acetoacetic acid, maleic anhydride, alkyl carbamate/urethane, phosgene, isocyanic acid, urea, guanidine Stereochemistry Determine the absolute configuration CH2Br COOH OH OH CH2 CH2 CD2 OH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 Me C NH2 Br C NH2 ClCH2 C H CH3CH2 C CH2SH CH2 CH2 CDH CH2 CH2 CH2OH CH2OH OH OCH3 OMe CH2 CH C CCl3 Me C H CH2 CH3 Draw the equilibrium chair conformations of cis-1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane/ trans-1-chloro-2methylcyclohexane, interpret E2 elimination, and the draw the structure of the product(s)! Draw the energy diagram of SN2/SN1/E2/E1 reactions and insert structure/formula of the corresponding starting materials/products/intermediates/transition states. Indicate the activation energy of the process and interpret molecularity. Draw the energy diagram of the reaction of buta-1,3-diene with HBr. Insert structure/formula of the corresponding starting material/products/intermediate/transition states. Draw the structure of the leaving groups formed in the nucleophilic substitution of the following compounds and the corresponding conjugate acids. Rank the leaving groups according to their leaving ability. O R O H R O S R' O R NH2 R F + R N N R Br + H R O H + R NH3 R Cl R I R S H Interpret the acidity of alcohols/phenols/enols/carboxylic acids/sulfonic acids on the basis of groundstate polarization and the stability of the corresponding anions (indicate bond polarization and draw resonance structures)! Definitions conformation, conformer, chiral compound, chiral center, prochiral compound, racemic mixture, meso compound, configuration, retention, inversion, racemization, resolution, enantiomer, asymmetric synthesis, molecular asymmetry, diastereomerism, nucleophile, electrophile, degree of oxidation, primary / secondary / tertiary carbon, addition, elimination, substitution, functional group, isomerism, homologous series, atomic orbital, angular (Baeyer) strain, torsional (Pitzer) strain, tautomerization, molecularity Reactions: 1–92 Nomenclature Name the following compounds/groups! (substitution names, functional group or common names) COOH H C OH H C OH O CH CH2 Me COOH O O meso tartaric acid styrene 9,10-anthraquinone R .. cyclopentadienide ion 9,10-dihydro-phenanthrene tetralin trans-2,3-dimethyloxirane N R"(H) C R' :CH2 N O tropylium ion Me O ethylene oxide tetrahydrofuran oxirane imine SO2 CH3 NH2 CH3 SO2OH SO2NH2 Br diazomethane Cl CH2 N OCH3 CH3 SO2 mesyl group tosyl group para-toluenesulfonic acid CH3 CH2 C C O Me2N CH2CH2CH2CH3 H CH3 isoprene bromobenzene benzyl chloride CH3 H C CH CH2 sulfanilamide E-but-2-ene CH3 C N NHOCCH3 N N N N Cl acetanilide benzenediazonium chloride azobenzene CH3 Cl C OH para-cresol enol CH3 resorcinol benzol-1,3-diol CH3CHCH3 CH3CHCH2 Cl CH3CH2CH2CH2 OH Cl CH3CH2CHCH3 O O 4-hydroxybutanoic acid lactone Ac2O O CH3CH2CH2 O CH3 O methoxy group propoxy group CH2 CH Cl CH3CH2CHCH3 vinyl chloride C O H2N alkyl carbamate urethane CH3CCH2CH2 O CH3CHCH2C CH3CCH2COOH H OH butan-2-ol 3-hydroxybutanal sec-butyl alcohol CH3CCH2COOEt O ethyl acetoacetate O acetoacetic acid 3-oxobutanoic acid NH C N H O 5-amino-pentanoic acid lactam O C O maleic anhydride OH O 4-hydroxybutan-2-one O COOH malonic acid RO C O OH sec-butyl chloride O aniline acetic anhydride ethyl chloroformate COOH CH2 CH3C allyl chloride Cl butyl chloride H hydroquinone benzol-1,4-diol CH2 CH CH2 Cl Br isobutyl chloride isopropyl bromide O C CN EtO OH R phosgene CH3C benzaldehyde cyanohydrin HC OH C O Cl OH OH R' Cl H C NMe2 acetonitrile N,N-dimethylformamide OH NH2 N,N-dimethylbutanamine anisole H2N C NH2 guanidine Grading Nomenclature (10 names+5 structures, 15=3 pts, 14=2 pts, 13=1 pts, 12=0.5 p) Stereochemistry (2 questions) 16 reactions (16 x 1 pt) 2 general questions (energy diagram–2pts, leaving groups–1 pt, acidity–1 pt) 10 definitions (10 correct answers = 3 pt, 9 = 2 pts, 8 = 1 pt) 3 pts 2 pts 16 pts 3 pts 3 pt 27 pts 27/26 pts = 5 25 pts = 4,5 24 pts = 4 23 pts = 3,5 22/21 pts = 3 20/19 pts = 2,5 18–16 pts = 2 15.5 pts and less = failed 1. Everybody qualified for exemption from the written test (12 mark points or higher for the 3 tests) must write a simple test including questions of nomenclature, stereochemistry and definitions (3+2+3 points). Requirement: at least 5 points but with at least 1 point for each type of question. 2. Anybody having a successful written test but with 0 point for nomenclature (less than 11 correct answers for 15 names/structures) and/or definitions (less than 8 correct answer out of 10) has to write the nomenclature question and/or definitions to be eligible for oral exam (nomenclature: at least 11 correct answers for 15 names/structures; definitions: at least 8 correct answers out of 10). 3. In the case when a successful written test is followed by a failed exam, the written test remains valid for all oral exams but it can be retaken once.