Carboxylic Acids
advertisement
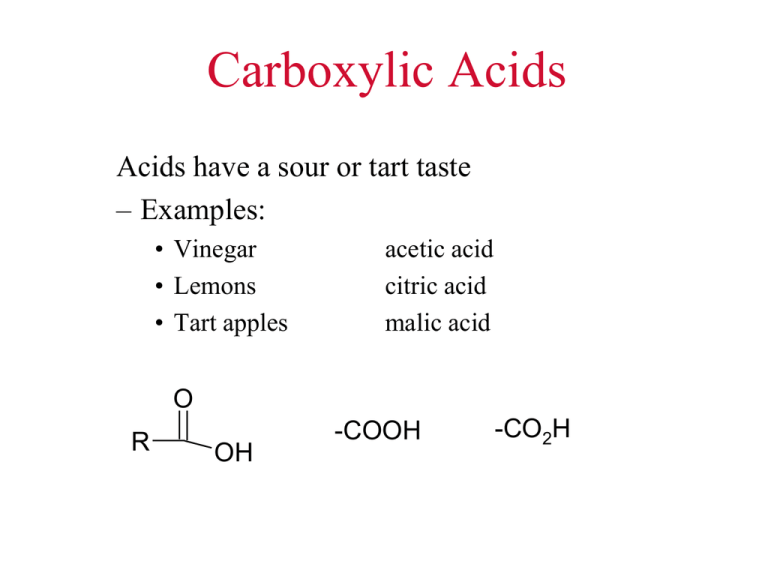
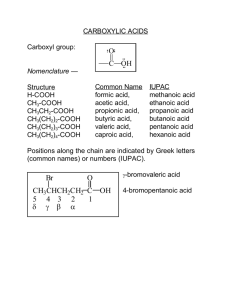
Carboxylic Acids Acids have a sour or tart taste – Examples: • Vinegar • Lemons • Tart apples acetic acid citric acid malic acid O R OH -COOH -CO2H Nomenclature • • Drop the e and ad oic acid If two acid groups in a molecule – keep the e and say dioic acid – – Carbonyl C is always is number 1 carbon Also called an “acyl” group C OH O Practice some on the board Nomenclature #C Common Name IUPAC Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 Formic acid Acetic acid Propionic acid Butyric acid Valeric acid Caproic acid Methanoic acid Ethanoic acid Propanoic acid Butanoic acid Pentanoic acid Hexanoic acid http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AntCzWw-28s Remembering Nomenclature • • • • • Formic acid… Acetic acid……. Butyric acid…….. Caproic acid………. Unbranched 3-10……. “ant acid” “acetum” (Latin=vinegar) “butter acid” “goat acid” “fatty acids” Physical Properties Increasing BP • Highest bp of compounds studied so far! Carboxylic acids Alcohols Ethers/Aldehydes/Ketones Alkyl halides Alkanes Physical Properties • Higher boil points due to hydrogen bonding and • Carboxylic acid dimers – Two identical units O H R O C C O H O R Physical Properties – Foul odors • butyric acid stale perspiration locker room odor, rancid butter • valeric acid smells worse (goat smell) From Yahoo Images Solubility of Organics • One electronegative group per four carbons will make a compound dissolve in water Fatty Acids • • • • • • Long un-branched carboxylic acids Most have between 12 and 20 carbons Derived from the hydrolysis of fats Most have an even number of C’s If unsaturated, the cis isomer predominates Unsaturated have lower melt points than saturated Melting Points Saturated have higher melting points than unsaturated fatty acids Soap • Soap is made by adding NaOH to a fat • This reaction is called soponification • This cleaves each of the fatty acids producing the solid fatty acid salt (soap) • The other product is glycerol soap O H 3 Na O H C O C O H C O C O H C O C H fat or oil + 3 NaOH + O C + H H OH H OH H OH H glycerol Soap O soap + Na O C polar non polar Soap Micelles O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O O Modern Detergents CH2(CH2)10CH2 Dodecylbenzene H2SO4 NaOH CH2(CH2)10CH2 SO3-Na+ Sodium 4dodecylbenzenesulfonate Acidity due to Electron Withdrawing Groups H H O OH H PKa = 4.76 H H Cl O Cl OH Pka = 2.86 Cl Cl O OH PKa = 0.70 Carboxylic Acid Reactions React as an acid with a base O O OH + LiOH O O Li O OH + NH3 O NH4+ + + H2O Separation using soluble salts Reduction To an Alcohol Reduction is difficult for acids, but Lithium Aluminum Hydride will do it O LiAlH4 Ether OH H2O CH2OH + LiOH + Al(OH)3 Fischer Esterification O OH + OH H2 SO4 O O + H2O Decarboxylation O Heat OH + CO2