Answer key: Homework 7
advertisement

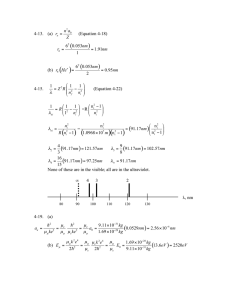
Physics 200 Homework #7 Due: November 9, 2005 1.(4 points) What is the energy of an electron in the innermost shell (n = 1) of a hydrogen atom? E 2 2 mk 2 e 4 13.6eV Hint: En = 21 2 2 n h n n2 2 2 E = -13.6eV / n = = -13.6eV / 1 = - 13.6eV 2. (4 points) What is the energy of an electron in the second shell (n = 2) of a hydrogen atom? E = -13.6eV / n2 = = -13.6eV / 22 = -13.6eV/4 = - 3.4 eV 3. (4 points) What is the energy of a photon emitted from the transition between these states? Hint: Ephoton emitted = Efinal shell – Einitial shell If a photon is EMITTED, the electron (really the entire atom) loses energy. The atom goes from a less negative energy to a more negative energy. The initial state for this specific example must be -3.1 eV and the final state must be -13.6 eV. Ephoton emitted = Efinal shell – Einitial shel = - 3.4 eV – (-13.6eV) = 10.2 eV 4. (4 points) What is the wavelength of this photon? Hint: E = hc/ E = hc/ so 5. (8 points) Using the Ritz-Rydberg formula, find the wavelength AND energy of a photon emitted from the transition from the 4th shell (n = 4) to the 2nd shell (m = 2) of a hydrogen atom. Hint: 1/ = R(1/m2 - 1/n2 ), where R = 1.097x 10-2 / nm (note: when you see it written nm-1, that just means divide by nm) Part A: 1/ = (1.097x 10-2 / nm) (1/m2 - 1/n2 ) = (1.097x 10-2 / nm)(1/ 22 - 1/ 42) = 1/ = (1.097x 10-2 / nm)(1/ 4 - 1/ 16) = (1.097x 10-2 / nm)(0.1875) = 0.00206 /nm So = 1 / (0.00206/nm) = 486 nm is in units of nm so this works out. It’s a little tricky to keep track of where the nm ends up, that’s why R is sometime written as 1.097x 10-2 nm-1 . The unit nm-1 just means 1/nm. You can say nm-1 = 1/nm. You can also say 1/nm-1 = nm. When you have a funny looking fraction like 1/(0.00206/nm) you can write is as 1/(0.00206 nm-1) = 486/(nm-1) = 486 nm. This may be a more clear way to keep track of the units once you’re used to it. Part B: E = hc/ = hc (1/) = (1240eVnm) (0.00206 /nm) = 2.55 eV 6. (4 points) What 3 principle observations led people to the “planetary model” of the atom (also known as the “Bohr model”)? The planetary model of the atom has electrons orbiting around a small, dense nucleus. The 3 principle observations that led people to this model are: 1. J.J. Thomson’s discovery of the electron in 1897 2. J.J. Balmer’s formula on the specific energies of light which are emitted by a hydrogen atom, 1885. 3. Rutherford scattering off the nucleus, 1909. Before that, there was debate as the the density of the atom. E. Rutherford and his students observed that most particles shot at an atom pass through, but a few came right back at them, as if they hit a very small, very dense thing. This was the discovery of the nucleus! Rutherford himself said "It was quite the most incredible event that ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you had fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you." 7 If you could ask any physics question to be answered in class, what would it be? I’ll try to answer some of these in class. Some questions asked are: Should you stay away from your microwave oven? Explain string theory. Explain relativity. Explain E=mc2