( ) ) ( )(

4-6. (a) f = !
b nt (Equation 4-5)
For Au, n
=
.
"
28 foil t
=
2 0 µ m
= "
!
6 m .
b = kq Q
!
2 cot
"
2
=
( )( ) ke 2
2 K
!
3 (see Example 4-2) and for this cot
90
2
=
( )( )( eV nm )
( .
#
6 eV )
=
!
5 nm =
!
14 m f = !
(
#
" 14 m
2
) (
#
28 / m 3 )(
#
" 6 m )
= #
" 5
(b) For !
= °
For !
= °
= #
Therefore,
" f
( ) b ( 90 ° )( cot
° ) ( /
=
= b ( 90 ° )( tan
° ) ( /
#
" 5 nm
= #
" 14 m f ( ) # f ( ) #
" 4
( ) b ( 90
° )( tan
° ) ( /
" 4
" 5 nm = # " 14 m
( 45
° !
75 ) #
!
4
!
.
#
!
4
=
.
)
)
)
#
!
4
(Problem 4-6 continued)
(c) Assuming the Au atom to be a sphere of radius r ,
4
3
!
r 3
=
M
N
A
"
=
( .
#
23
197
)( 19 3 / 3 )
4-7. r =
"
$
3
4 !
(
& r = " !
3 cm =
23
197
"
)( 19 3 / 3 )
#
%
!
10 m = 16 2 nm
1 sin 4 ( !
/ 2 )
=
A sin 4 ( !
/ 2 )
(From Equation 4-6), where A is the product of the two
quantities in parentheses in Equation 4-6.
(a)
" N
" N ( )
=
A / sin 4
A
( ° )
/ sin 4 ( / )
= sin 4 ( .
° ) sin 4
=
(b)
"
N ( 30
° )
"
N ( )
= sin 4 ( .
° ) sin 4
= #
!
6
# !
4
4-9.
For E k !
r d
=
=
( ) m v
!
2
MeV : r d
= ke 2 2 79
(Equation 4-11)
E k !
=
( 1 44 MeV fm
MeV
=
For E k !
=
MeV : r d
= fm
For E k !
= 12 MeV : r d
= fm fm
4-11. x rms
= N 10 n
=
" t t
=
10 !
6 m
10 !
10 m
=
° = N ( ° ) " N = ( ° )
2
° =
10 4 atomic layers is not enough to produce a deflection of 10 ° , assuming 1 collision/layer.
4-13. (a) r n
=
Z
0 (Equation 4-18) r
6
=
( nm )
1
= nm
(b) ( )
=
( nm )
2
= nm
4-15.
1
!
=
"
% n
1 1
2 f
$ n i
2
(Problem 4-15 continued)
#
&
(Equation 4-22)
1
!
ni
=
R
"
%
'
1
1 1
2
$ n i
2
#
=R
"
& %
( ' n i
2
$ 1 n i
2
#
&
(
!
ni
=
( n i
2 i
2
&
=
) ( .
' n
1 1 0968 10 7 i
2 m )( n i
2
&
1 )
= ( nm )
"
$
( n i
2 n i
2
& 1
#
%
)
!
2
=
4
3
( nm ) =
121 57 nm !
3
=
9
8
( nm ) =
!
4
( nm ) = 97 25 nm !
"
=
None of these are in the visible; all are in the ultraviolet.
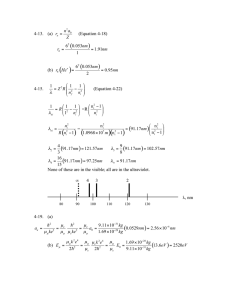
4-19. (a)
=
16
15
80
∞
90
4 3
100 110
2
120 nm
130 nm a u
=
µ
µ h 2 ke 2
=
µ e
µ
µ
µ h 2 e ke 2
=
µ e
µ
µ a
0
=
"
"
!
31 kg
!
28 kg
( nm ) = "
!
4 nm
λ , nm
(b) E
µ
=
µ
µ
2 h 2
=
µ
µ
µ e
µ e
2 h 2
=
µ
µ
µ e
E
0
=
"
"
!
28 kg
!
31 kg
( eV ) = 2520 eV
(Problem 4-19 continued)
(c) The shortest wavelength in the Lyman series is the series limit
( n i
= !
, n f
= 1 ). The photon energy is equal in magnitude to the ground state energy !
E
µ
.
!
"
= hc
E
µ
=
1240 eV nm
2520 eV
= nm
(The reduced masses have been used in this solution.)
4-21.
Energy (eV)
0
-2 (d) n= ∞ n=4 n=3 n=2
-4 (b) (c)
-6
-8
(a) Lyman limit, (b) H
!
line, (c) H
!
line, (d) longest wavelength line of Paschen series
4-24. (a) The reduced mass correction to the Rydberg constant is important in this case.
R
=
R
"
#
(
1
+
1
E n
= !
$
)
=
R
"
=
.
%
6 m !
1 (from Equation 4-26)
2 (from Equations 4-23 and 4-24)
E
1
= !
( 1240 eV nm ) (
"
6 m !
1 )( 10 !
9
Similarly, E
2
= !
1 701 eV and E
3
= !
eV
/ ) / ( )
2
= !
eV
(b) Lyman α is the n
=
2
!
n
=
1 transition. hc
"
= E
2
# E
1
$ "
!
= hc
E
2
# E
1
=
#
1240 eV nm eV
Lyman β is the n = 3 !
n = 1 transition.
"
!
= hc
E
3
#
E
1
=
#
1240 eV nm eV eV )
=
205 nm
4-26. (a)
1
!
= ( $
1 )
2
"
%
' n
1 1
1
2
$ n 2
2
#
&
(
!
3
=
#
*
.
( .
'
7 m " 1 ) ( )
2 %
,
1
1 1
2
"
3 2
& $
-
+
/
" 1
= ' eV )
= 243 nm
" 11 m
= nm
!
4
=
(b) !
lim it
#
*
.
(
=
#
*
.
(
.
'
7 m " 1 ) (
.
'
7 m " 1 ) (
)
2 %
(
,
1
1 1
2
"
4 2
)
2 %
,
1
1 2
&
)
-
$
+
/
" 1
" 0
& $
-
+
/
" 1
=
=
'
'
" 11 m = 0 0578 nm
" 11 m = 0 0542 nm
4-27.
1
"
= ( %
1 )
2
#
&
( n
1 1
1
2
% n 2
2
$
'
)
=
Z
"
1
= %
%
#
%
!
R
1
'
1 "
1
4
(
/
&
&
$
&
Z
!
=
#
%
(
( %
1 )
2 #
(
1
1 1
2
%
2 2
$
)
for K
!
nm ) (
1
) " 2 / nm ) ( )
$
&
4-29. r n
=
0 (Equation 4-18)
Z
The n =1 electrons “see” a nuclear charge of approximately Z !
1 , or 78 for Au. r
1
= 0 0529 nm / = .
" !
4 nm ( 10 !
9 )( 10 15 )
= 680 fm , or about 100 times the radius of the Au nucleus.
4-36. E hc
" = =
!
1240 eV nm
790 nm
= eV .
The first decrease in current will occur when the voltage reaches 1.61
V .
4-40. Those scattered at !
=
180
°
obeyed the Rutherford formula. This is a head-on collision where the α comes instantaneously to rest before reversing direction. At that point its kinetic energy has been converted entirely to electrostatic potential energy, so
1
2 m v
!
2
=
MeV
=
( )( 79 e )
where r = upper limit of the nuclear radius. r r
= k ( )( ) e 2
=
( )(
MeV
MeV fm )
MeV
= fm
4-43. !
=
#
(
R
%
* n
1 1
2 f
" n i
2
& $
+ )
)
" 1
' !
= d d
!
µ
' µ =
(
" R " 2 )
%
*
&
+
" 1 n
1 1
2 f
" n i
2 dR d µ
' µ
Because R % µ
, /
µ = R µ !
µ
H
= m m p m e
+ m p
µ
D
= m m d m e
+ m d
( R " 2 )
#
( n
1 1
2 f
" n i
2
$
)
" 1
( R /
µ ) & µ = " !
( & µ µ )
" µ
µ
=
µ
D
µ
!
H
µ
H
=
µ
µ
D
H
!
1
= m m d
/ ( m e
+ m d m m p
/ ( m e
+ m p
)
)
!
1
= m d
/ ( m e
+ m d
) m p
/ ( m e
+ m p
)
!
1
=
If we approximate m d
= 2 m p
and m e m d
, then
!
µ
µ
" m e
2 m p
and
( d
!
m
( e
+ m d p
)
)
" !
= # !
( "
/ ) = # ( nm )
(
0 511 MeV
MeV )
= #
4-45. (a) E n
= !
E Z 2 / n 2 (Equation 4-20)
For Li ++ , Z = 3 and E n
= !
13 6 eV ( ) / n 2
= !
nm
The first three Li
(Problem 4-45 continued)
++ levels that have the same (nearly) energy as H are: n
=
E
3
= !
13 6 eV n
=
, E
6
= !
3 4 eV n
=
, E
9
= !
eV
Lyman α corresponds to the n = 6 → n = 3 Li ++ transitions. Lyman β corresponds
to the n = 9 → n = 3 Li ++ transition.
(b) ( ) =
R
"
(
( ) = R
"
(
For Lyman α :
(
(
+
MeV / 938 8 MeV ) )
=
+ MeV / 6535 MeV ) ) =
.
#
7 m !
1
.
#
7 m !
1
1
!
=
#
1
"
1
2 2
$
*
= %
7 m " 1 ( 10 " 9 ) ( 3 4 ) &
.
nm
For Li ++ equivalent:
1
!
=
#
&
(
3
1 1
2
"
6 2
$
'
)
Z 2
= .
%
7 m " 1
!
= 121 512 nm " !
= 0 056 nm
( 10 " 9
4-50. For He: E n
= !
eV Z 2 / n 2
= !
2 (Equation 4-20)
)
#
&
(
1 1
9 36
$
'
)
( )
2
(a)
Energy (eV)
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
∞
5
4
3
2
1
(b) Ionization energy is 54.5eV.
E
1
= -54.4 eV
E
2
= -13.6 eV
E
3
= -6.04 eV
E
4
= -3.04 eV
E
5
= -2.18 eV
E
∞
= 0 eV
(c) H Lyman α : !
= hc / " = 1240 eV nm / ( 13 6 eV #
H Lyman β : !
= hc / " = 1240 eV nm / ( 13 6 eV
He + Balmer α : !
= hc / " E = 1240 eV nm / ( 13 6
# eV
He + Balmer β : !
= hc / " E = 1240 eV nm / ( 13 6 eV
# !
= 42 4 nm # " = nm
#
# eV ) = eV ) eV eV
=
)
) =
= nm nm nm nm
(The reduced mass correction factor does not change the energies calculated above to three significant figures.)
(d) E n
= !
eV Z 2 / n 2 because for He + , Z = 2, then Z 2 = 2 2 . Every time n is an even number a 2 2 can be factored out of n 2 and cancelled with the Z 2 = 2 2 in the numerator; e.g., for He + ,
(Problem 4-50 continued)
E
2
E
4
E
6
= !
= !
= !
.
eV /
.
eV /
.
eV / 2
2
2
= !
13 6 eV (H ground state)
= !
.
eV / !
= !
.
eV / !
M etc.
Thus, all of the H energy level values are to be found within the He + energy levels, so
He + will have within its spectrum lines that match (nearly) a line in the H spectrum.
4-53. kZe 2 mv r
= r
2
" kZe 2 r 2
=
( !
mv )
2 mr
(from Equation 4-12)
!
v
=
#
%
( kZe 2 mr
$
&
)
= v
1 ' "
2
1 c 2
!
2
* !
2
=
$
(
+ kZe 2 mr
%
)
,
Therefore, !
2
&
-
" c 2
+
$
(
+ kZe 2 mr
% # $
)
=
(
,
'
.
+ kZe 2 mr
%
)
,
(Problem 4-53 continued)
!
2
$ c
1
2
"
'
) kZe ma o
2
#
(
*
% !
=
0 0075 Z
% v
= cZ
=
.
&
6
E
= %
/
= mc 2 ( !
%
1 ) % kZe 2 r
= mc 2
#
&
1
1 % "
2
1
$
% ' % kZe 2 r
And substituting !
= 0 0075 and r = a o
&
E = %
3 eV
#
'
!
#
1
1 & ( 0 0075
= 14 4 eV !
28 8 Z eV = !
)
2
& 1
"
$
$
& 28 8 Z eV
Z eV