Physical Science
Molecular Models
Lab
Introduction
Covalent bonds form between nonmetals. The number of valence electrons that are shared between
the atoms depends on how many electrons are needed to fill each atom’s outermost energy level. The
covalent bonds can be represented by several different types of molecular models, including electrondot diagrams, space-filling models, and structural formulas.
Objectives
Draw electron-dot diagrams, space-filling models, and structural formulas of various covalent
molecules
Use structural formulas to determine bond angles
Procedures
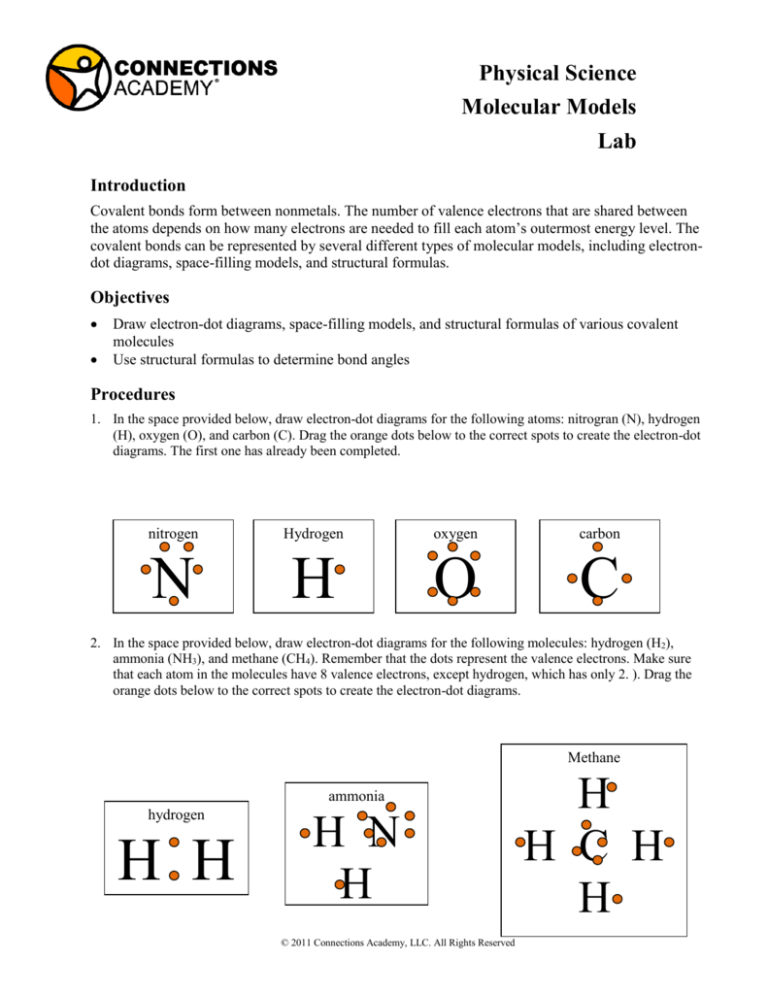
1. In the space provided below, draw electron-dot diagrams for the following atoms: nitrogran (N), hydrogen
(H), oxygen (O), and carbon (C). Drag the orange dots below to the correct spots to create the electron-dot
diagrams. The first one has already been completed.
2.
nitrogen
Hydrogen
oxygen
carbon
3.
N
H
O
C
4.
2. In the space provided below, draw electron-dot diagrams for the following molecules: hydrogen (H2),
ammonia (NH3), and methane (CH4). Remember that the dots represent the valence electrons. Make sure
that each atom in the molecules have 8 valence electrons, except hydrogen, which has only 2. ). Drag the
orange dots below to the correct spots to create the electron-dot diagrams.
Methane
ammonia
hydrogen
H H
H N
H
H
© 2011 Connections Academy, LLC. All Rights Reserved
H
H C H
H
3.
a. Draw the structural formula for a hydrogen molecule (H2) and an oxygen molecule (O2).
Remember that each line represents an electron pair being shared. Drag the correct set of lines to the
left over to the correct spots to show the correct structural formulas. See page 166 in book.
Single bond
hydrogen
Double bond
oxygen
H H
Triple bond
O O
b. The oxygen atoms in carbon dioxide (CO2) form double bonds with the carbon atom,
forming a linear molecule. Draw the structural formula for carbon dioxide by dragging the lins
above.
Carbon dioxide
O C O
4. Sketch space-filling models of a hydrogen molecule (H2) and carbon dioxide (CO2)..Drag the
space-filled models below into the correct boxes.
hydrogen
Carbon dioxide
Analysis -Use the table below to answer questions #1-3. This is from page 3 of your lesson
1. What is the bond angle between the hydrogen atoms in an ammonia (NH3) molecule (trigonal
planar)? 120
2. What is the bond angle between the oxygen atoms in the carbon dioxide molecule (linear)?
180
3. What is the molecular shape of a methane (CH4) molecule? 109.5
Shape
Number of particles
bonded to central Atom
Linear
Trigonal Planar
Tetrahedral
© 2011 Connections Academy, LLC. All Rights Reserved
2
3
4
Bond Angle
180º
120º
109.5º