Properties of Water
advertisement

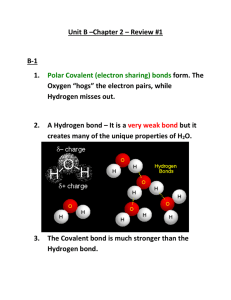
Properties of Water Practice Quiz 1. What two elements make up water? Hydrogen (H) & Oxygen (O) 2. Write the chemical formula for water. H2O 3. Is water an element, compound, or mixture? Compound 4. Define the term compound. A substance with two or more elements chemically combined in definite proportions. 5. What kind of chemical bond exists between a hydrogen and oxygen atom in a water molecule? A covalent bond 6. Draw a model of a water molecule. (+) (-) (+) The parentheses mean ‘partial.’ (-) 7. Draw partial (+) and partial (-) charges on the water molecule you drew above. This symbol also means partial → δ+ 8. Which of the following molecules are polar? (+) (-) (+) (-) (-) (+) (-) (-) water (-) (+) (-) carbon dioxide (+) (+) ammonia (+) (+) (-) (+) (-) Hydrogen chloride (-) (-) (+) formaldehyde (+) (+) methane (+) 9. Draw two water molecules and a hydrogen bond. 1 The use of dashed lines show that hydrogen bonds are relatively weak. (-) Hydrogen bond (+) 4 2 3 10. How many hydrogen bonds can a water molecule form with other water molecules? Four 11. What term describes the attraction between molecules of the same substance? Cohesion B A No 12. Without a hydrogen bond, when molecule A moves to the right, will it be able to drag molecule B along with it? 13. With a hydrogen bond between them, will molecule A be able to drag molecule B along with it? B A Yes 14. What are some examples of water cohesion? Surface tension Drops on a penny Insect trapped in water A proboscis keeps this bee at a safe distance 15. What are some examples where surface tension breaks down? “Scaring” pepper Bread clip motor boat 16. What term describes the attraction between molecules of different substances? Adhesion (+) (+) (-) (+) (+) (+) glass Water drop on glass slide 17. What will happen when a charged rod or balloon is brought up close to a stream of water? The water will be attracted toward the rod 18. What are some examples of water adhesion? A meniscus that water forms in a glass tube. Capillary action 19. What are some examples of anti-adhesion? Scotchgard ® carpet Water on wax paper Wax-layer on leaves Duck feathers repel water New: Researchers have made an omniphobic material that repels both water and oil. Nature has never made this type of material. 20. What is the term which describes the amount of heat energy needed to increase a substance’s temperature? Heat Capacity of Various Materials [cal/(g·°C)] Heat Capacity [cal/(g·°C)] 1.20 1.00 1.00 Heat Capacity 0.80 0.60 0.54 0.42 0.40 0.21 0.20 0.20 0.19 0.12 0.09 0.03 0.00 0.02 21. Which substance in the chart is able to absorb the most heat for a given change in temperature? Heat Capacity of Various Materials [cal/(g·°C)] Heat Capacity [cal/(g·°C)] 1.20 1.00 1.00 Water 0.80 0.60 0.54 0.42 0.40 0.21 0.20 0.20 0.19 0.12 0.09 0.03 0.00 0.02 22. Which substance in the chart is able to absorb the least amount of heat for a given change in temperature? Heat Capacity of Various Materials [cal/(g·°C)] Heat Capacity [cal/(g·°C)] 1.20 1.00 1.00 Air 0.80 0.60 0.54 0.42 0.40 0.21 0.20 0.20 0.19 0.12 0.09 0.03 0.00 0.02 23. What example in the Properties of Water lab demonstrated a low heat capacity for air and a high heat capacity for water? Air-filled balloon Water-filled balloon 24. What is a mixture? A substance made up of elements or compounds that are combined but not chemically bonded together. 25. What are some examples of mixtures? water sugar corn syrup CO2 caramel caffeine citric acid Beef Onion Tomato Lettuce Cheese Ketchup Mustard bread copper zinc 26. What are two kinds of mixtures made with water? Solutions and suspensions 27. Compare solvent, solute, and solution. water Sugar cubes Sugar water solvent solute solution what does the dissolving what is being dissolved 28. Define a solution? A mixture in which the molecules of the mixed substances are evenly spread out. 29. Which substance(s) below dissolve in water? Magnesium iodine sulfate polar Non polar salt paraffin wax oil polar Non polar Non polar 30. What is a suspension? A mixture from which some of the nondissolved particles settle out slowly upon standing. 31. What some examples of suspensions? Chocolate milk Paint Blood 32. When water breaks apart, what kind of ions are formed? Hydrogen (H+) ions and hydroxide (OH-) ions (+) (-) 33. What does the pH scale indicate? It indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. 34. What is the range of the pH scale? 0 to 14 35. What is the pH of a substance that has an equal number of H+ and OH- ions? 7 Acids 36. Substances with a pH below 7 are ________ while those above 7 are _________? Bases H+ OH- ions? 37. Acids have more ____ions than _____ lower 38. The _______the pH, the greater the acidity. Bases have more OH- ions than H+ ions? 39. _______ 40. Place the 5 substances listed below on the scale to the right. Oven cleaner Soap Lemon juice Oven cleaner Human blood Soap Pure water Human blood Pure water Click for answer Lemon juice 41. The pH in most cells in the human body must 6.5 and______ 7.5 ? stay between _______ Buffers are weak acids or bases that can 42. __________ react with strong acids or bases to stop sharp, sudden changes in pH. 43. Buffers play an important role in the process of homeostasis ______________, where living things are able to maintain a stable, internal environment.