Where were we last year???
advertisement

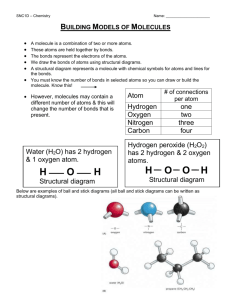
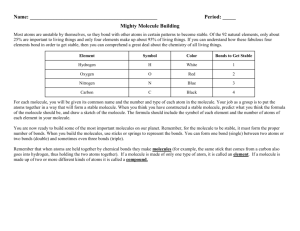
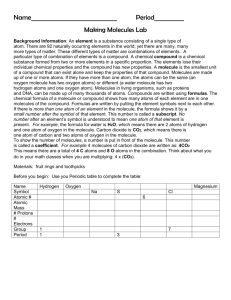
1. Functional Groups: are structural features that show up repeatedly in molecules and seem to account for some of their chemical properties (ex: smell). What are the main functional groups? O C KETONE (carbon double-bonded to an oxygen) What are the main functional groups? O C O C ESTER (carbon double-bonded to an oxygen & attached to another oxygen atom which is attached to another carbon) What are the main functional groups? O C O H CARBOXYLIC ACID (carbon double-bonded to an oxygen & attached to another oxygen atom which is attached to a hydrogen) What are the main functional groups? C N AMINE (carbon bonded to a nitrogen atom) What are the main functional groups? ALCOHOL (carbon bonded to an oxygen bonded to a hydrogen atom) What functional group is present in this molecule? H H H H H H C C C H H C H C H H C H C C H C H H H O H ketone C H What functional group is present in this molecule? H H O C C H O H H C C H H ester H What functional group is present in this molecule? O H H H H C C C H C O H H C H H carboxylic acid H What functional group is present in this molecule? H H H H H H C C C H H C H C H H C H C H C H H C H H H O H Alcohol C H What functional group is present in this molecule? H H C N H H H O C C C C C H amine H H C C H H H 4. Structural Formula: A drawing or diagram that a chemist uses to show how the atoms in a molecule are connected. It is a 2D picture of the molecule. Structural formulas show how the atoms in a molecule are put together. #3 5 (how many?) on this page shows _____ structural formulas. 5. Molecular Formula: The shorthand notation a chemist uses to show how many atoms of each element are present in a particular molecule or the ratio of ions in an ionic formula. Ex: H2O 6. Bond: A connection between atoms in a molecule. In structural formulas, the covalent bonds are represented as lines _______________. Double bond = 2 lines together. How many lines would you need 3 for a triple bond? ______. **Question to ponder: Can molecules have the same molecular formula and smell differently? Answer: _________ yes We saw this in the smell lab—2 substances had the formula C4H8O2 but one smelled putrid & the other smelled sweet! A. Examine the following molecules. What patterns do you see in the bonding of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon & nitrogen? H H H H H H H H H C C C N C C C H C H H C H H H H H H C H H H C H H H C H C C C H H C H H H O Vial K—Fishy, diisobutylamine C H C H H H C H H H Vial E—Minty, menthone a. How many bonds (lines) do carbons always 4 b. How about have around them? ___ 3 c. How about hydrogen nitrogen atoms? ___ 1 d. How about oxygen atoms? ___ 2 atoms? ___ What do you think the rule HONC—1234 means? HONC 1234 H = 1 bond O = 2 bonds N = 3 bonds C = 4 bonds (H-1) (O-2) (N-3) (C-4) How it’s done 1. Start with the carbon atoms. Connect them together. 2. Now insert the nitrogen, oxygen, or other atoms. Remember, they may connect on the ends of the carbon chain, or somewhere in the middle. 3. Fill in with the hydrogen atoms. 4. Problem-solve until you have the correct number of bonds for each element. ***Tip: things that can form more bonds are more likely to show up in the middle of the structure*** You try D. Draw each of the following molecules: a. CH4 b. CH4O c. CH5N E. Draw C4H10 correctly, but in two different ways! Isomer: two or more molecules that are composed of the same elements in the same proportions (in other words, they have the same molecular formula) (ex: C4H10 above) but differ in properties because of differences in structural formulas.