Appendix_figure_files
advertisement
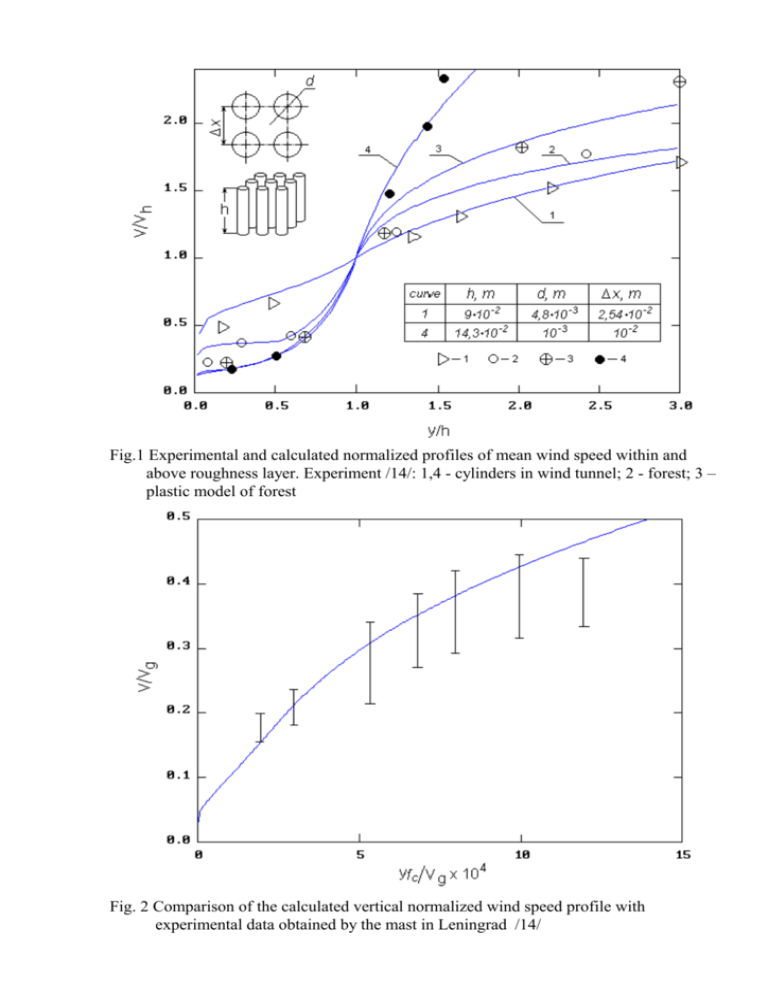
Fig.1 Experimental and calculated normalized profiles of mean wind speed within and above roughness layer. Experiment /14/: 1,4 - cylinders in wind tunnel; 2 - forest; 3 – plastic model of forest Fig. 2 Comparison of the calculated vertical normalized wind speed profile with experimental data obtained by the mast in Leningrad /14/ Fig. 3 Comparison of the calculated vertical normalized wind speed profile in pine forest with experimental data /15/ Fig. 4 Comparison of the calculated vertical normalized turbulent kinetic energy profile in fir-tree forest with experimental data /16/ Fig. 5 Comparison of the vertical air temperature profiles with experimental data within a crop /18/ (figures above the curves denote the local time, hr) Fig. 6 Calculated vertical mean wind speed profile in the atmospheric boundary layer depending upon atmospheric stability Fig. 7 Vertical turbulent kinetic energy profile in the surface layer depending upon atmospheric stability (same notation as shown in pic. 6) Fig. 8 Calculated vertical air and roughness element temperature profiles within porosity layer and above one depending upon atmospheric stability (A - denotes temperature of the roughness element surface) Fig. 9 Calculated vertical normalized mean wind speed profile within the roughness layer depending upon porosity layer dispersity under neutral atmospheric conditions Fig. 10 Calculated vertical normalized eddy viscosity coefficient profile within the roughness layer and above one depending upon porosity layer dispersity under neutral atmospheric conditions (same notation as shown in pic. 9) Fig. 11 Calculated vertical relative mean wind direction shear profile within roughness layer depending upon porosity layer dispersity under neutral atmospheric conditions (same notation as shown in pic. 9) Fig. 12 Calculated vertical eddy viscosity coefficient profile in the atmospheric boundary layer depending upon urban heat source strength within the roughness layer (Vg=5 м/с) 11 15 m/s D = 0.9, h = 10 m ; D = 0.9, h = 5 m ; D = 0.4, h = 5 m. 10 9 8 U10 , m / s 7 6 7 m/s 5 4 3 2 2 m/s 1 0 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 Lg (N) Fig. 13 Wind speed at 10 m height above ground within the roughness layer with constant porosity depending upon porosity layer dispersity under neutral atmosphere (figures denote geostrophic wind speed values) 2,2 D = 0.9 ; D = 0.6. 2,0 u 1,8 u (T)10 , m2/s 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,0 n n 0,8 s 0,6 s 5 10 15 20 25 30 h, m Fig. 14 Eddy viscosity coefficient at 10 m height above ground within the roughness layer with constant porosity depending upon the layer height under Vg=7 m/s, N=10-3 m-2 (s - stable atmosphere; n - neutral one; u - unstable one) 4,5 D = 0.9 ; D = 0.6 ; without built-up. 4,0 3,5 (T)10 , m2/s 3,0 2,5 2,0 u 1,5 1,0 0,5 n s 0,0 0 5 10 15 20 Ug, m / s Fig. 15 Eddy viscosity coefficient at 10 m height above ground within the roughness layer with constant porosity depending upon geostrophic wind speed under N=10-3 m-2, H=10 m (same notation as shown in pic. 14)