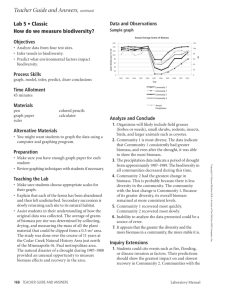
Ratio Formula to Determine Concentration (mg/ml):
advertisement

Determining Vitamin C Concentration Lab Spring 2006 Introduction Vitamins are organic compounds that must be present in small amounts in order for normal metabolic processes to occur. They cannot be synthesized by the body in adequate amounts, so these required nutrients must be obtained through food or, more recently, supplements such as vitamin tablets. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid, VC) is a water soluble vitamin which is unstable and can be destroyed by oxidation, heat, light and alkalis. Its functions are not all fully understood, although it is known to be necessary for the production of collagen, essential for healthy teeth and gums, and vital for such connective tissues as bone, cartilage, and the fibrous connective tissue of skin. It also promotes the absorption of iron and aids in resistance to infection. There is debate over how much VC is needed, but 10 mg per day is enough to prevent deficiency symptoms such as scurvy, tooth decay, soft and bleeding gums, swollen or painful joints, slow healing wounds, bruising and nosebleeds. The Recommended Daily Allowance, or RDA, for the average adult is 60 mg per day. The body will excrete or oxidize excess VC, although too much may cause nausea, stomach cramps and diarrhea. VC is naturally found in many plants, with the highest concentrations being found in citrus fruits, citrus juices, broccoli, tomatoes, and cabbage. It is also found in other green leafy vegetables and fresh fruits but in lesser amounts. Method This laboratory experiment uses a color indicator to indirectly measure the VC concentration in a solution. Normally iodine reacts with starch solution and turns it into a blue/black color. Ascorbic acid (VC) is a very strong reducing agent and will bleach the color from the iodine added to the solution. When the ascorbic acid is used up, the added iodine solution will then react with the starch in the solution, turning the solution blue/black. With a control sample of known VC concentration, you can calculate VC concentrations of unknown samples. Materials On each bench, each group will find: 2 5 ml syringes 1 1 ml transfer pipette 4 stirring rods 6 50 ml disposable beakers, labeled and pre-poured: 10 ml starch solution 20 ml iodine solution 25 ml control VC solution 25 ml sample 1 25 ml sample 2 25 ml sample 3 paper towels, beach covers etc. You need to put on a bench apron or a lab coat when you walk into the lab. Procedures A. Determine the Baseline: 1. Using transfer pipette, add 1 ml of starch solution to the control VC solution 2. Stir with a stirring rod till mix 3. Draw 5 ml iodine solution into the syringe 4. Slowly add the iodine solution to the control beaker, drop by drop, stirring the liquid between each drop, taking care not allow the tip of the syringe touching the liquid in the beaker or spill the liquid from the beaker. Continue adding and counting the drops until the liquid in the beaker turns blue/black. This process is called “Titration”. 5. Record in your data sheet, the amount of iodine left in your syringe and the number of iodine drops used in the titration. 6. Push the remaining iodine back into the iodine beaker. Now you complete the baseline measurement. B. Determine Unknown Samples: Repeat step 1-6 for sample 1, then sample 2, then sample 3. Use fresh stirring rod for each sample. (Suggestion for the group, everyone would watch and help one member to perform the baseline measurement, then take turns to measure samples 1-3, in sequence or simultaneously. Report to the group and complete the data sheet). Data Analysis A. The Concept of Concentration: Concentration of a Material in a solution is defined as the Weight of the material (e.g., in kilogram, gram, milligram) per Volume of the solution (in liter, deciliter, milliliter). It is expressed as Concentration = Weight/Volume [Material] in unit of mg/ml, g/dl, kg/l B. Determine Sample Vitamin C concentration [VC]s based on VC concentration of the Control [VC]c: Ratio Formula to Determine Concentration: [VC]c_________ # Titration Drops for Control = [VC]s_________ # Titration Drops for Sample Your control solution contains 1 mg/ml of Vitamin C, therefore Vitamin C concentration of your sample, [VC]s (in mg/ml) = 1 # TD for Control x # TD for Sample = C. Translating Lab Data to Daily VC Intake: Recommended Daily Allowance of VC is 60 mg per day, calculate the volume of the sample you need to drink to meet the RDA of 60 mg using the formula: Volume = Weight/Concentration Volume (ml) = 60 mg [VC]s mg/ml = Translate that volume into food serves, e.g., cups or fluid ounces: (1 ml = 0.034 fl.oz = 0.004 cup) Calculate the volume of juice you need to drink to meet RDA of Vitamin C for other samples: (hint, you need first to calculate their [VC].