DETERMINATION OF ASCORBIC ACID IN VITAMIN TABLETS

N8.
DETERMINATION OF ASCORBIC ACID IN VITAMIN
TABLETS
PREWORK
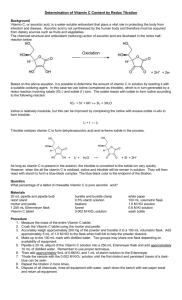
• Write balanced equations for the reaction of iodine with ascorbic acid, and iodine with thiosulfate
• What is a back titration?
PROCEDURE
1.
Place a soluble (no added colour if possible) Vitamin C tablet in a beaker and add about 150 mL of purified water. Allow the tablet to dissolve and the effervescence to cease.
2.
Quantitatively transfer to a 250 mL volumetric flask and make up to the mark.
3.
Pipette 50 mL aliquots into three conical flasks
4.
If the sample is coloured, pour about 25 mL of sample and 25 mL of water into a fourth flask, to serve as a reference. Do not carry out steps 5 and 6 on this flask
5.
Add, by pipette, 25 mL of standardised 0.1M iodine solution to the first three flasks. Swirl for a few minutes. Place a watch glass over the neck of the flasks until you are ready to titrate
6.
Titrate with standardised 0.1M sodium thiosulfate until the solution loses most of the iodine colour. Make sure that the colour does not return back to that of the reference tablet solution. Add a few drops of starch indicator and continue titrating until the blue colour disappears.
Alterations if a powdered sample is supplied
Step 1 Take 1 teaspoon of Vitamin C powder, dissolve in approximately 150 mL of purified water.
Step 2a. Quantitatively transfer to a 250 mL flask and make up to the mark
Step 2b. Make a 5 times dilution by taking 50 mL up to 250 mL
Complete as per the original method
CALCULATIONS
1.
Use the equations determined in the prework
2.
Calculate the moles of iodine added in the 25 mL aliquot
3.
Average the titration values
4.
Calculate the moles of thiosulfate used in the titration
5.
Calculate the moles of iodine that reacted with the thiosulfate in the titration
6.
Calculate the moles of iodine that reacted with the ascorbic acid
7.
Calculate the moles of ascorbic acid in the titrated sample
8.
Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid in the titrated sample
9.
Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid per tablet
DISCUSSION
• Explain why a back titration is used in the analysis of ascorbic acid
• Explain why a watch glass is placed over the mouth of the flasks
• Discuss the use of iodine as a standardised solution and titrant
• How reliable is your result in relation to the entire packet or bottle of tablets
QUESTIONS
1.
Chewable Vitamin C tablets cannot be analysed by the method used in this experiment due to the use of starch as a binder to hold the tablets together. Explain why this would be a problem
2.
What health problems does Vitamin C deficiency cause?
3.
Give the structure of two other vitamins and describe the health effects of these vitamins