Med-surg glossary
advertisement

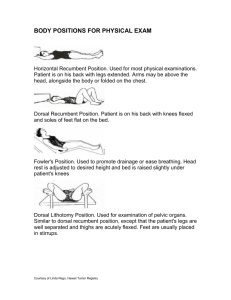
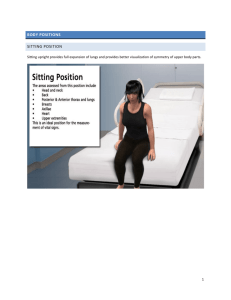
Med-Surg Glossary anemia reduction in the number and volume of red blood cells, the amount of hemoglobin, or the volume of packed red cells aneurysm sac formed by the dilation of the wall of an artery, a vein, or the heart angiography radiographic visualization of blood vessels after injection of radiopaque contrast material anorexia loss of appetite aphasia loss or impairment of the ability to communicate through speech, written language, or signs, resulting from brain disease or trauma apraxia complete or partial inability to perform purposeful movements in the absence of sensory or motor impairment ascites fluid in the peritoneal cavity ataxia impairment of the ability to coordinate voluntary muscle movement aura sensations that occur before a paroxysmal attack, such as a seizure or migraine headache auscultation physical assessment technique by which the examiner listens (usually with a stethoscope) for sounds coming from the heart, lungs, abdomen, or other organs autoimmune disorder disorder in which the body launches an immunologic response against itself bruit abnormal sound heard over peripheral vessels on auscultation that indicates turbulent blood flow cardiac output volume of blood ejected from the heart per minute constipation decreased passage of stools; stools are characteristically hard and dry crepitation grating sound produced by bone rubbing against bone decerebrate posturing associated with a lesion of the upper brain stem or severe bilateral lesions in the cerebrum; the patient typically lies with legs extended, head retracted, arms adducted and extended, wrists pronated, and the fingers, ankles, and toes flexed decorticate posturing associated with a lesion of the frontal lobes, cerebral peduncles, or internal capsule; the patient lies with arms adducted and flexed, wrists and fingers flexed on the chest, legs stiffly extended and internally rotated, and feet plantar flexed diarrhea rapid movement of fecal material through the intestines that causes poor absorption of water and nutrients; stools are watery and frequent disease pathologic condition that occurs when the body can’t maintain homeostasis distal farthest away dysmenorrhea painful menstruation dyspepsia gastric discomfort, such as fullness, heartburn, bloating, and nausea, that occurs after eating dysphagia difficulty swallowing dysphasia impairment of speech involving failure to arrange words in their proper order, usually resulting from injury to the speech area in the cerebral cortex dyspnea difficult, labored breathing ecchymosis bruise embolism sudden obstruction of a blood vessel by foreign substances or a blood clot exacerbation increase in the severity of a disease fasciculation involuntary twitching or contraction of the muscle Fowler’s position patient positioning with head of bed raised, knees slightly flexed hematuria blood in the urine hemoglobin iron-containing pigment in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues hemoptysis expectoration of bloody sputum hemorrhage escape of blood from a ruptured vessel hirsutism excessive hair growth or unusual distribution of hair hormone chemical substance produced in the body that has a specific regulatory effect on the activity of specific cells or organs hypertension high arterial blood pressure hypotension abnormally low blood pressure hypoxia reduction of oxygen in body tissues to below normal levels idiopathic disease with no known cause inspection critical observation of the patient during which the examiner may use sight, hearing, or smell to make informed observations insulin hormone secreted into the blood by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas; promotes the storage of glucose, among other functions ischemia decreased blood supply to a body organ or tissue jugular vein distention distended neck veins that may indicate increased central venous pressure lateral recumbent position patient positioning lying on the left side with the right thigh and knee drawn up lethargy slowed responses, sluggish speech, and slowed mental and motor processes in a person oriented to time, place, and person lichenification thickening and hardening of the epidermis lithotomy position lying on the back with the hips and knees flexed and the thighs abducted and externally rotated lymphadenopathy enlargement of the lymph nodes melena passage of black, tarry stools murmur abnormal sound heard on auscultation of the heart; caused by abnormal blood flow through a valve necrosis tissue death nocturia excessive urination at night oliguria urine output of less than 30 ml/hour orthopnea respiratory distress that’s relieved by sitting upright palpation physical assessment technique by which the examiner uses the sense of touch to feel pulsations and vibrations or to locate body structures and assess their texture, size, consistency, mobility, and tenderness pathogen disease producing agent or microorganism percussion physical assessment technique by which the examiner taps on the skin surface with his fingers to assess the size, border, and consistency of internal organs and to detect and evaluate fluid in a body cavity peristalsis intestinal contractions, or waves, that propel food toward the stomach and into and through the intestine petechiae multiple, small, hemorrhagic areas on the skin plasma liquid part of the blood that carries antibodies and nutrients to tissues and carries wastes away from tissues platelet disk-shaped structure in blood that plays a crucial role in blood coagulation polydipsia excessive thirst polyphagia consuming abnormally large amounts of food polyuria excessive production of urine prone position lying face down proximal nearest to pruritus severe itching ptosis drooping of the eyelid renal colic flank pain that radiates to the groin reverse Trendelenburg’s position lying flat with the head higher than the body or legs subluxation partial dislocation of a joint supine position lying flat on the back thrombosis the development of a thrombus (blood clot) tophi clusters of urate crystals surrounded by inflamed tissue; occur in gout Trendelenburg’s position lying flat with the head lower than the body or legs vasopressor drug that stimulates contraction of the muscular tissue of the capillaries and arteries virus microscopic, infectious parasite that contains genetic material and needs a host cell to replicate