AP® Biology Scoring Guidelines Question 9 Interdependence in
advertisement

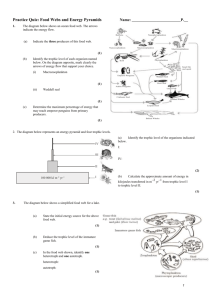
AP® BIOLOGY SCORING GUIDELINES Question 9 Interdependence in nature is illustrated by the transfer of energy through trophic levels. The diagram below depicts the transfer of energy in a food web of an arctic lake located in Alaska. (a) Choosing organisms from FOUR different trophic levels of this food web as examples, explain how energy is obtained at each trophic level. (3 point maximum) * Must include both example and how energy is obtained to earn point Examples correlated to proper trophic level Energy Obtained T.L #0 - (Detritivores) - Snails - larvae of Chironomids Larvae of Caddis Flies T.L #1 - (Producers/autotrophs) Phytoplankton - Algae Aquatic plants - Dead terrestrial plant T.L #2 - (First order or primary consumers) Zooplankton - Snails - Larvae of Chironomids - Larvae of Caddis Flies T.L #3 - (Second order consumers) Grayling - SculpinLake Trout T.L #4 - (Third order consumers) Lake trout Producers obtain energy by photosynthesis Consumers obtain energy by digestion or assimilation (must link to specific consumer or level) (b) Describe the efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels and discuss how the amount of energy available at each trophic level affects the structure of the ecosystem.(4 point maximum) *One point must be earned from Efficiency and Ecosystem Structure to earn 4 point max. Efficiency 10% rule or overall inefficient why inefficient (e.g. cellular respiration, never eaten, wastes, heat, metabolism) thermodynamics - increase in entropy primary - net - gross productivity life history - energy value varies per life stage Ecosystem Structure number of level thus indicated as 4-5 maximum pyramid of energy pyramid of biomass pyramid of numbers standing crop effect as related to phytoplankton and zooplankton AP® BIOLOGY SCORING GUIDELINES Question 9 (continued) (c) If the cells in the dead terrestrial plant material that washed into the lake contained a commercially produced toxin, what would be the likely effects of this toxin on this food web? Explain. (4 point maximum) * 1 point for each effect.... but must link one secondary effect to earn a .............. (Maximum = 4) * 1 point for each correct interdependent pathway as a secondary effect (NOTE) this list is not exhaustive EFFECT and SECONDARY EFFECT(S) Death of Snails/Larvae Death of snails and larvae lead to death of upper levels Death of trout leads to increase of sculpin and grayling Magnification/accumulation Death of grayling leads to overgrowth of zooplankton Death of sculpin leads to increase feeding of trout on grayling Sub-lethal effect grayling Eutrophication - tied to effect (1 point maximum) - for any of the following: Reason for why toxin is persistent, e.g. lipid soluble, eggshell effect, DDT, indigestible Biodegradable "left side" not immediately effected "Mutagenic" - explanation must be included "Create" pathway to phytoplankton (e.g. water soluble)