Radiology
advertisement

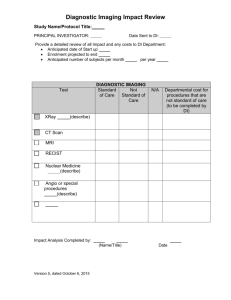
THE SYLLABUS OF RADIODIAGNOSIS FOREWORD Applicable Students: Six-year system oversea students in the department of clinical medicine. Class Hours: It takes 64 hours to study this course. The study of theory consists of 32 hours and the laboratory practical take up 32 hours. Course Introduction and Objectives The teaching contents are divided into three grades: First grade content is to be mastered and to be learned by heart; it is of the greatest importance and it is the key point of teaching; the second grade is for students to be familiar with, the teaching files in this grade will be presented only in part in lectures, thus some files are to be self studied; the third grade contents help the student to form a knowledge base, such as the state of art Radiology, to catch up with the rapid development of modern imaging technology; as well as the comparison of the several imaging modalities on the basis of their advantages and limitations. TEACHING HOURS DISTRIBUTION No. Contents Lecture Practice Chapter 1 Overview 2 4 Chapter 2 Respiratory system 6 4 Chapter 3 Circulation system 2 4 Chapter 4 Digestive system 5 4 Chapter 5 Urinary system 4 4 Chapter 6 Musculoskeletal system 5 4 Chapter 7 Neuroimaging 4 4 Chapter 8 Interventional radiology 4 4 Total 32 32 285 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW AND PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING [Objectives] 1. Get familiar with the general aspect of Diagnostic Radiology, including its history, present status, and prospect. 2. Realize the content object of the Course of Diagnostic Radiology. 3. Master the basic knowledge of Diagnostic Radiology. 4. Identify four types of fundamental radiographic densities on plain films. 5. Master and understand the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of various modalities of imaging examination including traditional diagnostic radiology and modern imaging examinations. 6. Choose optimal radiographic contrast agent and manage their adverse reaction. COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Introduction and definition of Diagnostic Radiology. 2. Historical perspectives. (1) Examination techniques of traditional diagnostic radiology (2) Modern imaging techniques 3. The nature and production of X-rays (1) Definition of X-rays (2) Production of X-rays (3) Physical effects of X-rays 4. Fundamental radiographic densities on plain films. 286 5. Modalities of Diagnostic Radiology examination. (1) Plain film radiography (2) Fluoroscopy (3) Conventional tomography (4) Contrast radiographic examination (5) Computed tomography (CT) (6) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 6. The radiographic contrast agent and management of their adverse reaction Practice 1. Help the students to be familiar with the courses of routine imaging examination, including X-ray, CT, and MRI in the radiology department. 2. Help the students to be familiar with various types of images of diagnostic radiology including plain X-ray films, contrast radiography, CT and MRI. CHAPTER 2: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM [Objectives] 1. Master the imaging technology (X-ray, CT and MRI) and normal imaging anatomy in respiratory system 2. Understand the basic features in diseases of the following common diseases: Pulmonary Sequestration, Bronchogenic Cysts, Inflammatory Disorders (Pneumonia, Lung Abscess, Tuberculosis, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Emphysema, Bronchiectasis, Neoplasms of the Lung Hamartoma, Bronchial Carcinoma, Pulmonary Metastases), Sarcoidosis, Disease Of The Mediastinum (Intrathoracic Thyroid, Thymoma, Teratoma, Malignant Lymphorna, Aortic 287 Aneurysm, Dissecting Aneurysms), Disease Of the Pleura (Pleural Effusion, Pneumothorax, Pleural Thickening and Fibrothorax, Pleural Mesothelioma), Pulmonary Thromboembonsm, Thoracic Trauma (Bone Fractures, Pneumothorax and Hemothorax, Pulmonary Contusion, Pulmonary Laceration) COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Imaging Technology and Imaging Anatomy (1) Imaging Technology (2) Imaging Anatomy 2. The basis features in chest diseases (1) Exudation and consolidation (2) Proliferative lesion (3) Fibrosis (4) Calcification (5) Cavitation (6) Mass 3. Imaging appearance of diseases in respiratory system (1) Malformation (2) Inflammatory disorders (3) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (4) Neoplasms of the lung (5) Disease of the mediastinum (6) Disease of the pleura (7) Pulmonary thromboembolism 288 (8) Thoracic Trauma Practice 1. The routine imaging examinations (X-ray, CT and MRI) of respiratory system in radiological department 2. Discuss some clinical cases of respiratory system in class or in radiological department CHAPTER 3: CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM [Objectives] 1. Master the imaging technology (X-ray, CT and MRI), normal imaging anatomy, and basic features in diseases of cardio-vascular system 2. Understand the imaging appearance, diagnosis and differential diagnosis of rheumatic heart disease (mitral stenosis), hypertensive heart disease, COR pulmonale, pericarditis, and congenital heart disease COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Imaging Technology and Imaging Anatomy (1) Plain film (2) Computed tomography (CT) (3) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 2. Imaging appearance of diseases in central nervous system (1) Rheumatic heart disease (2) Hypertensive heart disease (3) COR pulmonale 289 (4) Pericarditis (5) Congenital heart disease Practice 1. Show the students the routine imaging examinations (X-ray, CT and MRI) of cardio-vascular system in radiological department. 2. Show the students the clinical cases of cardio-vascular system in class or radiological department. CHAPTER 4: GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM [Objectives] 1. Master the image technology (X-ray, CT and MRI) in gastrointestinal system 2. Get familiar with the normal imaging anatomy in gastrointestinal system 3. Understand the radiological appearance of common diseases in gastrointestinal system, included diseases of esophagus, stomach and duodenum, small bowel, colon, liver, gallbladder and biliary system, pancreas and spleen. 4. Understand the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of gastric ulcers, gastric cancer, colon carcinoma, hepatic tumors and pancreatitis. COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Imaging techniques and anatomy (1) Abdominal plain film (2) Double contrast examination (3) Computed tomography (4) Ultrasonography 290 (5) Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging (6) Nuclear medicine 2. Principles of interpretation (1) Types of pathology (2) Elements of the double-contrast image (3) Protrusions (4) The barium pool (5) Radiologic-histologic correlation of GI tract 3. Imaging appearance of diseases in gastrointestinal system (1) Esophagus (2) Stomach and duodenum (3) Small bowel (4) Colon (5) Liver (6) Gallbladder and biliary system (7) Pancreas (8) Spleen Practice 1. Show the students the routine imaging examinations (X-ray, CT and MRI) of gastrointestinal system in radiological department. 2. Show the students the clinical cases of gastrointestinal system in class or radiological department. CHAPTER 5: URINARY SYSTEM 291 [Objectives] 1. Master the image technology (X-ray, CT and MRI) of urinary system 2. Be familiar with the normal imaging anatomy of urinary system 3. Understand the image appearance of congenital abnormalities, calculus, infections, and masses. 4. Understand the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of urolithiasis, tuberculosis, masses (including renal cyst and tumors) COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Imaging Technology and Imaging Anatomy (1) Plain film (K.U.B, I.V.P) (2) Computed tomography (CT) (3) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 2. Imaging appearance of diseases in urinary tract (1) Congenital abnormalities (2) Obstructive lesions (3) Infections (4) Masses: cysts and tumors (5) Vascular lesions (6) Traumatic lesions (7) Extrinsic compression (8) Renal transplantation Practice 1. Show the students the routine imaging examinations (X-ray, CT and MRI) of 292 urinary tract in radiological department. 2. Show the students the clinical cases of urinary tract in class and radiological department. CHAPTER 6: MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING [Objectives] 1. Understand the structure and growth of bones and joints 2. Master the basic X-ray features in diseases of bones and joints 3. Get familiar with the image appearance and the diagnosis of fracture, skeletal infection and bone tumors COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. The structure and growth of bones and joints 2. Basic X-ray features in diseases of bones and joints (1) Changes of bones (2) Changes of joints (3) Changes of soft tissues 3. Fracture 4. Skeletal infection (1) Pyogenic osteomyelitis and septic arthritis (2) Skeletal tuberculosis 5. Bone Tumors (1) Giant cell tumors of bone (2) Osteosarcoma 293 (3) Metastatic Tumors in Bone Practice Show the students the clinical cases of musculoskeletal system in class CHAPTER 7: NEUROLOGICAL IMAGING [Objectives] 1. Be familiar with the imaging technology (X-ray, CT and MRI) and normal imaging anatomy in central nervous system 2. Understand the imaging appearance, the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of cerebral vascular diseases, brain tumors, brain trauma, demyelization diseases and infection COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Imaging Technology and Imaging Anatomy (1) Plain skull film (2) Computed tomography (CT) (3) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 2. Imaging appearance of diseases in central nervous system (1) Cerebral Vascular Diseases (2) Brain tumors (3) Brain trauma (4) Demyelinating Diseases: Multiple Sclerosis (5) Infection: Cerebritis and Abscess Practice 294 1. Show the students the routine imaging examinations (X-ray, CT and MRI) of central nervous system in radiological department 2. Show the students the clinical cases of central nervous system in class or radiological department CHAPTER 8: INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY [Objectives] 1. Be familiar with the general concepts of the diagnostic and therapeutic procedure in interventional radiology 2. Understand the appliances, their clinical application and therapeutic procedures in interventional radiology COURSE CONTENTS Theory 1. Essential knowledge of interventional radiology (1) History of interventional radiology (2) The application using interventional radiology (3) Categorization of intervention examination (4) Puncture approach 2. Interventional therapy (1) Embolotherapy method and indication (2) PTA (3) Filter release (4) Tumor embolism and chemotherapy Practice 295 1. Show the students the routine DSA examinations equipment sample and machine furnish. 2. Show the students the clinical cases of interventional therapy in class and radiological department. REFERENCES 1. Clinical Radiology: The Essential, 2nd Edition, Richard H. Daffner, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Pennsylvania USA,1999 2. Radiology, 2nd Edition, Taveras JM, Ferrucci JT. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Pennsylvania USA, 2002 3. Body CT with MRI Correlation, 2nd Edition. Lee SS, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Pennsylvania USA , 2004 4. CT of the Heart: Principles and Applications Schoepf UJ, Humana Press Inc., 2005 5. Essential of Skeletal Radiology, 2nd Edition, Yochum Terry R., Rowe Lindsay J. Williams & Wilkins,1996 6. Diagnostic Neuradiology, Osborn Anne G. Mosby-Year Book, Inc. St. Louis, 1994 296