Phys194_Syllabus
advertisement

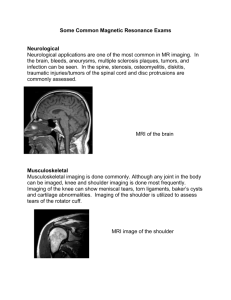
Phys194 Basic Principles of Medical Imaging Syllabus Part I. X-Ray Based Imaging (3 weeks) I-1. What is x-ray? Electromagnetic waves; photon; structure of atoms. I-2. Interactions between x-ray and matter Absorption and scattering of x-rays; fluorescence; ionization. I-3. Dosage and safety Damages caused by x-rays; safety measures. I-4. Use of contrast media The purpose of using a contrast medium; examples. I-5. Computed tomography (CT) Scans Planar, cross-sectional and 3D imaging; CT configurations. Part II. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) (2 weeks) II-1. What can we see with MRI? Bones vs. soft tissues; x-rays vs. MRI; examples. II-2. How MRI works A simplified explanation. II-3. Contrast MRI How it works; contrast media. II-4. How safe MRI is? Magnetic force; allergy and toxicity of contrast media. Part III. Ultrasound Imaging (2 weeks) III-1. What is ultrasound? Sound waves; interaction with human body. III-2. Imaging from echoes How it works; imaging quality and safety issues. III-3. Seeing the blood flow with ultrasound The Doppler effect; speed and flow rate of blood flow. Part IV. Nuclear Medicine (2 weeks) IV-1. SPECT and PET scans Why PET (or SPECT) scan? IV-2. What is going on in the nucleus? Radioactivity; How PET and SPECT work. Part V. Specialized Imaging (2 weeks) V-1. x-ray angiography How it works; examples. V-2. Functional MRI (fMRI) Blood-oxygen-level dependence (BOLD) in brain function and MRI signal. V-3. Image fusion Combination of different images; examples. V-4. Imaging for treatments and operations Imaging guided intervention, treatment, and operation. Part VI. Comparing Different Imaging Technologies (2 weeks) VI-1. Limitations, risks, pros and cons Diagnostic purpose; quality of image; side effects; cost. VI-2. A few application examples Broken bones; cancer; tapeworms; blood clots, etc.. VI-3. Typical questions Which imaging means should be used? How safe is that? Some uncommon but important questions.