Homework assignment topics 43-50 Georgina Salas Topics 43
advertisement

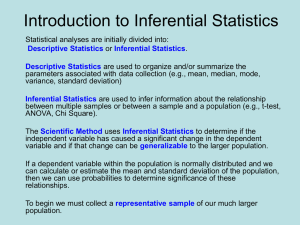
Homework assignment topics 43-50 Georgina Salas Topics 43-50 EDCI Intro to Research 6300.62 Dr. A.J. Herrera Topic 43 1. Which branch of statics ("inferential" or "descriptive") helps researchers to summarize data so they can be easily comprehended? Descriptive statistics helps researchers to summarize data. 2. According to Table 1 in this topic, how many participants had a score of 19? 9 participants had a score of 19. 3. What is the name of the statistics that describes how many participants per 100 have a certain characteristic? Percentages is the name of the statistics. 4. Which branch of statistics helps researchers to draw inferences about the effects of sampling errors on their results? Inferential statistics helps researchers to draw inferences about the effects of sampling errors. 5. If a researcher tests a random sample instead of all members of a population, is it likely that the sample results will be the same as the results the researcher would have obtained by testing the population? No it would not. 6. Is a margin of error a "descriptive" or an "inferential" statistic? It is an inferential statistic. 7. Are significance tests associated with "descriptive" or " inferential" statistics? It is associated with inferential statistics. 8. By studying populations, do researchers obtain "statistics" or "parameters"? Researchers obtain parameters. 9. By studying samples, do researchers obtain "statistics" or "parameters"? Researchers obtain statistics. Topic 44 1. How many explanations were there for the differences between psychologists and engineers in the example in this topic? There were 3. 2. What does the null hypothesis say about sampling error? It says the observed difference was created by sampling error. 3. Does the term sampling error refer to "random errors" or to "bias"? Sampling error refers only to random errors, not errors created by bias. 4. The null hypothesis says the true difference equals what numerical value? It equals to zero. 5. Significance tests are designed to determine the probabilities regarding the truth of what hypothesis? Tests are designed to determine the probabilities of null hypothesis. 6. The expression p<.05 stands for what words? It stands for probability. 7. Do researchers reject the null hypothesis when the probability of its truth is "high" or when the probability is "low"? Researchers reject the null hypothesis when the probability is low. 8. What do researchers do if the probability is greater than .05? Researchers determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. 9. What is an alternative way saying a researcher has rejected the null hypothesis? An alternative way is statistically significant. 10. Are null hypotheses more likely to be explicitly stated in a "journal article" or in a "dissertation"? Null hypotheses are likely to be explicitly stated in dissertations. Topic 45 1. If a researcher asks participants to name the country in which they were born, the researcher is using which scale of measurement? The researcher is using nominal. 2. Which two scales of measurement have equal distances among the scores they yield? The two scales are interval and ratio. 3. If a researcher assigns a teacher to rank students according to their oral-language skills, the researcher is using which scale of measurement? The researcher is using ordinal. 4. Which scale of measurement has an absolute zero? The scale of measurement is ratio. 5. Which scale of measurement is at the lowest level? The scale of measurement is nominal. 6. Objective, multiple-choice achievement tests are usually assumed to measure at what level? They are assumed to measure at interval. 7. If a researcher measures in such a way that he or she finds out which participant is the most honest, which is the next most honest, and so on (without measuring to determine how much honesty each one has), the researcher is measuring with what scale of measurement? The researcher is measuring with ordinal. 8. The number of minutes of overtime work that employees perform is an example of which scale of measurement? It is an example of ratio. 9. Weight measured in pounds is an example of which scale of measurement? It is an example of ratio. Topic 46 1. If 600 individuals in a population f 1,000 are Democrats, what is the corresponding percentage of Democrats? The corresponding percentage of Democrats is 60.0%. 2. When reporting a percentage, is it a good idea to also report the underlying number of cases? Yes it is a good idea. 3. Do researchers use "univariate" or "bivariate" analyses to examine relationships between two nominal variables? Researchers use bivariate. 4. Percentages for different groups are expressed on a common scale with what base? They are expressed on a common scale of 100. 5. What is the base for a proportion? The base for a proportion is 1. 6. Are "percentages" or "proportions" easier for most individuals to comprehend? Percentages are easier for most individuals to comprehend. 7. When consumers of research encounter proportions in research reports, it is a good idea to do what? It is a good idea to convert them to percentages. Topic 47 1. When researchers study a sample, are the results called the "true results" or the "observed results"? The results are called observed results. 2. According to the null hypothesis, what created the differences in Table 1 in this topic? Random sampling errors created the differences. 3. What is the name of the test of the null hypothesis used in this topic? The name of the test is chi-square. 4. According to this topic, should the typical consumer try to interpret the value of df? No they should not. 5. What is the symbol for probability? The symbol is p. 6. If a researcher found that a chi-square test of a difference yielded a p of less than 5 in 100, on the basis of conventional wisdom, what should the researcher conclude about the null hypothesis? The researcher should reject it. 7. Does "p<.05" or "p>.05" usually lead a researcher to declare a difference statistically significant? p>.05 leads a researcher to declare a difference. 8. If a researcher fails to reject a null hypothesis, is the difference in question statistically significant? No it does not. 9. If a researcher has a statistically significant result, should the null hypothesis remain on the list of viable explanations for an observed difference? Yes it should. Topic 48 1. Which type of analysis classifies participants in terms of two variables in order to examine the relationship between the two variables? The type of analysis is bivariate analysis. 2. What decision should researchers make about the null hypothesis if a chi-square test leads to the conclusion that the observed differences are unlikely to be due to random errors? The decision should be to reject the null hypothesis. 3. If p=.05 for a chi-square test, chances are how many in 100 that the null hypothesis is true? The chances are 5. 4. When a researcher uses the .01 level, what are the odds of making a Type I error? The odds are 1 in 100. 5. What is the name of the error researchers make when they fail to reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is an incorrect hypothesis? The name of the error is called Type II error. 6. What is the name of the error researchers make when they reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is a correct hypothesis? The name of the error is called Type I error. 7. Why is random sampling desirable even though it creates errors? It is desirable because it is free from bias. Topic 49 1. According to Figure 1, about how many participants has a score of 16? 60 participants 2. In Figure 1, are the frequencies on the "vertical" or the "horizontal" axis? The frequencies are one the vertical. 3. What is the name of the curve that is symmetrical? The name of the curve is normal curve. 4. If a distribution has some extreme scores on the right (but not on the left), it is said to have what type of skew? It is said to have a positive skew. 5. If a distribution skewed to the left, does it have a "positive" or a "negative" skew? It has a negative skew. 6. In most populations, income has what type of skew? Income has positive skew. 7. Does a distribution with a tail to the right have a "positive" or a "negative" skew? It has a positive skew. Topic 50 1. Which average is defined as the most frequently occurring score? Mean is defined as the most frequently occurring score. 2. Which average is defined as the balance point in a distribution? Mean is the balance point in a distribution. 3. Which average is defined as the middle score? Median is defined as the middle score. 4. What is the formal definition of the mean? The formal definition is value around which the deviations sum to zero. 5. How is the mean calculated? The mean is calculated by adding up all scores and divide by the number of scores. 6. Should the mean be used for highly skewed distributions? No it should not. 7. Should the median be used for highly skewed distributions? Yes it should. 8. Which one of the three averages is very seldom used in formal reports of research? Mode is seldom used in formal reports of research. 9. What is the synonym for the term averages? The synonym is measures of central tendency.