Lewis et al: Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assessment and
advertisement

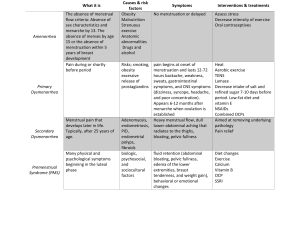
Lewis et al: Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems, 7th edition Key Points Chapter 54: Nursing Management: Female Reproductive Problems PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a common disorder of physical and psychologic symptoms during the last few days of the menstrual cycle and before onset of menstruation. PMS is thought to have a biologic trigger with compounding psychosocial factors. Physical symptoms include breast discomfort, abdominal bloating, sensation of weight gain, episodes of binge eating, and headache. Anxiety, depression, irritability, and mood swings are some of the emotional symptoms. No single treatment is available to relieve symptoms. The goal is to reduce symptom severity. DYSMENORRHEA Dysmenorrhea is abdominal cramping pain or discomfort associated with menstrual flow. o Primary dysmenorrhea is caused by an excess of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) and/or an increased sensitivity to it. o Secondary dysmenorrhea is acquired after adolescence; pelvic causes include endometriosis, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, and uterine fibroids. Treatment for primary dysmenorrhea includes heat, exercise, and drug therapy. For secondary dysmenorrhea, it depends on the cause. Abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding is a common gynecologic concern and is caused by dysfunction of hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, infection, and stressful changes in lifestyle. Treatment varies depending on the cause but can include drug therapy and surgery. MENOPAUSE Menopause is the physiologic cessation of menses associated with declining ovarian function. It is usually considered complete after 1 year of amenorrhea. Ovarian changes start the cascade of events that result in menopause. Premenopausal symptoms include hot flashes, irregular vaginal bleeding, fat redistribution, and a tendency to gain weight. Treatment might include hormone replacement, drug therapy, and alternative therapies. INFECTION AND INFLAMMATION OF VAGINA, CERVIX, AND VULVA Infection and inflammation of vagina, cervix, and vulva commonly occur when natural defenses of the acid vaginal secretions (maintained by sufficient estrogen levels) and presence of Lactobacillus are disrupted. Copyright © 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Key Points 54-2 Abnormal vaginal discharge and reddened vulvar lesions are often noted with itching and dysuria. Treatment includes antibiotics and antifungal preparations. LEIOMYOMAS Leiomyomas (uterine fibroids) are benign smooth-muscle tumors that occur within the uterus. Symptoms may include abnormal uterine bleeding, and pain. Treatment depends on size of tumor and may include surgery. UTERINE PROLAPSE Uterine prolapse is the downward displacement of uterus into the vaginal canal. Symptoms are dyspareunia, dragging or heavy pelvic feeling, backache, and bowel or bladder problems if cystocele or rectocele is also present. Therapy depends on degree of prolapse and can include strengthening exercises, and a pessary. Copyright © 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.