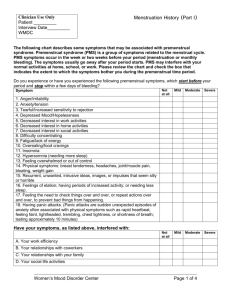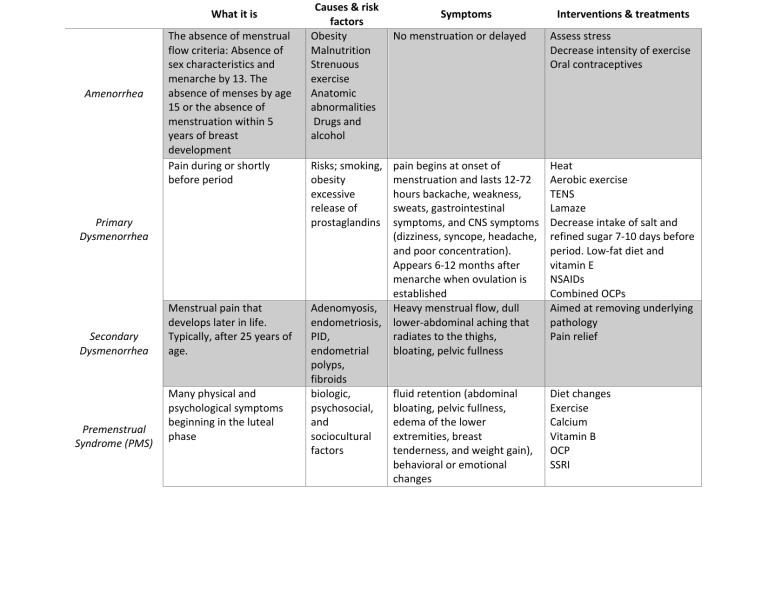
What it is Amenorrhea The absence of menstrual flow criteria: Absence of sex characteristics and menarche by 13. The absence of menses by age 15 or the absence of menstruation within 5 years of breast development Pain during or shortly before period Primary Dysmenorrhea Secondary Dysmenorrhea Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) Menstrual pain that develops later in life. Typically, after 25 years of age. Many physical and psychological symptoms beginning in the luteal phase Causes & risk factors Obesity Malnutrition Strenuous exercise Anatomic abnormalities Drugs and alcohol Risks; smoking, obesity excessive release of prostaglandins Symptoms No menstruation or delayed pain begins at onset of menstruation and lasts 12-72 hours backache, weakness, sweats, gastrointestinal symptoms, and CNS symptoms (dizziness, syncope, headache, and poor concentration). Appears 6-12 months after menarche when ovulation is established Adenomyosis, Heavy menstrual flow, dull endometriosis, lower-abdominal aching that PID, radiates to the thighs, endometrial bloating, pelvic fullness polyps, fibroids biologic, fluid retention (abdominal psychosocial, bloating, pelvic fullness, and edema of the lower sociocultural extremities, breast factors tenderness, and weight gain), behavioral or emotional changes Interventions & treatments Assess stress Decrease intensity of exercise Oral contraceptives Heat Aerobic exercise TENS Lamaze Decrease intake of salt and refined sugar 7-10 days before period. Low-fat diet and vitamin E NSAIDs Combined OCPs Aimed at removing underlying pathology Pain relief Diet changes Exercise Calcium Vitamin B OCP SSRI Premenstrual more severe variant of PMS biologic, Dysphoric psychosocial, Disorder (PMDD). and sociocultural factors Endometriosis Presence and growth of endometrial tissue outside of the uterus marked irritability, dysphoria, mood lability, anxiety, fatigue, appetite changes, and a sense of feeling overwhelmed Same as PMS pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, and dyspareunia (painful intercourse). Women may also have chronic noncyclic pelvic pain, pelvic heaviness, or pain radiating into the thighs. Many women report bowel symptoms such as diarrhea, pain with defecation, and constipation caused by avoiding defecation because of the pain. GnRH agonists androgen derivatives androgenic synthetic steroid total abdominal hysterectomy (TAH) with bilateral salpingectomy and oophorectomy (BSO) laser therapy