UnitIMuscles
advertisement

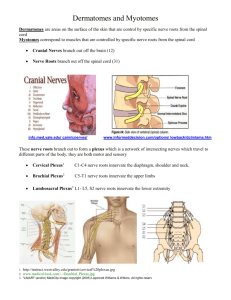
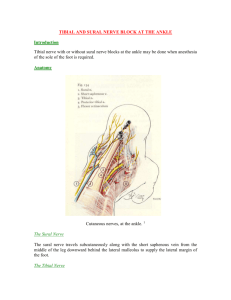
Erector spinae o All originate from a broad tendon that attaches inferiorly to the posterior part of the iliac crest, the posterior aspect of the sacrum, the sacroiliac ligaments, and the sacral and inferior lumbar spinous processes o Innervated by posterior rami of spinal nerves o Extend vertebral column and head; as back is flexed, control movement by gradually lengthening their fibers o Laterally flex vertebral column o Iliocostalis Inserts lumborum, thoracis, cervicis Fibers run superiorly to angles of lower ribs and cervical transverse processes o Longissimus Inserts thoracis, cervicis, capitis Fibers run superiorly to ribs between tubercles and angles to transverse processes in thoracic and cervical regions, and to mastoid process of temporal bone o Spinalis Inserts thoracis, cervicis, capitis Fibers run superiorly to spinous processes in the upper thoracic region and to cranium Superficial posterior axioappendicular muscles o Trapezius Attaches from medial third of superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament and spinous processes to lateral third of clavicle, acromnion, and spine of scapula Innervated by the spinal accessory nerve (XI) with motor fibers and C3, C4 spinal nerves with pain and proprioceptive fibers Elevates, depresses, and retracts scapula; also rotates glenoid cavity superiorly o Latissimus dorsi Attaches from spinous processes of inferior 6 thoracic vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inferior 3 or 4 ribs to the floor of intertubercular groove of humerus Innervated by thoracodorsal nerve (C6,C7,C8) Extends, adducts and medially rotates humerus; raises body towards arms during climbing Deep posterior axioappendicular muscles o Levator scapulae Attaches from posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae to the medial border of scapula superior to root of spine Innervated by dorsal scapular and cervical nerves (C3-C5) Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula o Rhomboid minor/major Minor: Attaches from nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7 and T1 vertebrae to the smooth triangular are at medial end of scapular spine Major: attaches from spinous processes of T2-T5 vertebrae to the medial border of scapula from level of spine to inferior angle Innervated by dorsal scapular nerve Retracts scapula and rotates it to depress glenoid cavity; fix scapula to thoracic wall Scapulohumeral muscles o Deltoid Divided into unipennate anterior and posterior parts, and a multipennate middle part Abducts the arm, but cannot initiate abduction; it can however act as a shunt muscle resisting inferior displacement of the head of the humerus (carrying suitcase) Anterior (assists pectoralis major in flexing) and posterior (assists latissimus dorsi in extension) parts are used to swing arms during walking TEST: abduct arm against resistance starting at 15 degrees Supplied by axillary nerve Attaches to lateral third of clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula proximally and the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus distally o Teres Major Adducts and medially rotates the arm Can help extend arm from flexed position and stabilize humeral head in glenoid cavity TEST: abducted arm is adducted against resistance Supplied by lower subscapular nerve Attaches to the dorsal surface of inferior angle of scapula proximally and the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of humerus distally o Rotator Cuff Muscles Supraspinatus Abducts the first 15 degrees of the arm TEST: abduct the arm from the fully adducted position Supplied by suprascapular nerve Attaches to the supraspinous fossa of scapula proximally and the superior facet of the greater tubercle of humerus Infraspinatus Occupies medial ¾ of infraspinous fossa and is partly covered by deltoid and trapezius Stabilizes glenohumeral joint and is a powerful lateral rotator of the humerus Supplied by suprascapular nerve Attaches to the infraspinous fossa of scapula proximally and the middle facet of the greater tubercle of humerus Teres Minor Completely hidden by deltoid and not delineated from infraspinatus Works with infraspinatus to laterally rotate the arm and assists in its adduction Supplied by axillary nerve Attaches to the upper portion of lateral border of scapula proximally and the lower facet of the greater tubercle of humerus Subscapularis Primary medial rotator of arm and assists in adduction Supplied by upper/lower subscapular nerves Attaches to the subscapular fossa of the scapula proximally and the lesser tubercle distally Muscles of arm o Biceps brachii Two heads arise proximally from tendinous attachments to processes of the scapula (long head: supraglenoid tubercle; short head: coracoid process); uniting just distal to middle of the arm; and forming a single biceps brachii tendon that attaches to the radial tuberosity of the radius When elbow is extended it acts as a simple flexor of the forearm When elbow is fixed close to 90 degrees and forearm is supinated biceps produce flexion When forearm is pronated the biceps is the most powerful supinator of the forearm Innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve o Brachialis Attaches proximally to lower anterior surface of humerus and distally to coronoid process of ulna and ulnar tuberosity Lies deep to biceps Main flexor of forearm Innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve o Coracobrachialis Attaches proximally to the coracoid process and distally to the middle third of medial surface of humerus Flexes and adducts Innervated by musculoscutaneous nerve o Triceps Attached proximally: long head: infraglenoid tubercle; lateral head: superior to radial groove of humerus; medial head: inferior to radial groove. Distally attached to posterior surface of olecranon process of ulna Primarily involved in extending forearm Long head stabilizes the adducted glenohumeral joint; resisting inferior displacement Medial head is active as an extensor at all speeds Lateral head is the strongest but is recruited into activity primarily against resistance innervated by the radial nerve Muscles of forearm o Superficial layer Pronator teres Attaches from coronoid process (ulnar head) and medial epicondyle (humeral head) to middle of convexity of lateral surface of radius Pronates and flexes forearm at elbow Median nerve Flexor carpi radialis Attaches from medial epicondyle of humerus to base of 2nd metacarpal Flexes and abducts hand at wrist Median nerve Palmaris longus Attaches from medial epicondyle of humerus to distal half of flexor retinaculum and apex of palmar aponeurosis Flexes hand at wrist and tenses palmar aponeurosis Median nerve Flexor carpi ulnaris Attaches from medial epicondyle (humeral head) and olecranon and posterior border (ulnar head) to pisiform, hook of hamate and 5th metacarpal Flexes and adducts hand at wrist Ulnar nerve o Intermediate layer Flexor digitorum superficialis Attaches from medial epicondyle (humeroulnar head) and superior half of anterior border (radial head) to shafts of middle phalanges of medial four fingers Flexes middle phalanges at proximal interphalangeal joints of middle four fingers; flexes hand and forearm Median nerve o Deep layer Flexor digitorum profundus Attaches from anteromedial surface of ulna and interosseus membrane to bases of distal phalanges of fingers Flexes distal interphalangeal joints and hand Ulnar and median nerve Flexor pollicis longus Attaches from anterior surface of radius, interosseus membrane and coronoid process to base of distal phalanx of thumb Flexes phalanges of thumb Median nerve Pronator quadrus Attaches from anterior surface of distal ulna to anterior surface of distal radius Pronates forearm Median nerve Muscles of posterior forearm (all radial nerve) o Brachioradialis Attaches from lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus to base of radial styloid process Flexes forearm (maximal when forearm is in midpronated position) o Extensor carpi radialis longus Attaches from lateral supraepicondylar ridge of humerus to dorsal aspect of base of 2nd metacarpal Extends and abducts hand o Extensor carpi radialis brevis Attaches from lateral epicondyle to dorsal aspect of base of 3rd metacarpal Extends and abducts hand o Extensor digitorum Attaches from lateral epicondyle to extensor expansions of medial four fingers Extends medial four fingers primarily at metacarpophalangeal joints; secondarily at interphalangeal joints o Extensor digiti minimi Attaches from lateral epicondyle to extensor expansion of 5th finger Extends little finger o Extensor carpi ulnaris Attaches from lateral epicondyle and posterior surface of ulna to base of fifth metacarpal Extends and adducts hand o Supinator Attaches from lateral epicondyle, radial collateral and annular ligaments, supinator fossa and crest of ulna to lateral side of upper part of radius Supinates forearm o Abductor pollicis longus Attaches from interosseus membrane, middle third of posterior surfaces of radius and ulna to lateral surface on base of first metacarpal Abducts thumb and hand o Extensor pollicis longus Attaches from interosseus membrane and middle third of posterior surface of ulna to base of distal phalanx of thumb Extends distal phalanx of thumb and abducts hand o Extensor pollicis brevis Attaches from interosseus membrane and posterior surface of middle third of radius to the base of proximal phalanx of thumb Extends proximal phalanx of thumb and abducts hand Muscles of hand o Thenar muscles Opponens pollicis Opposes thumb; draws 1st metacarpal medially to center of palm and rotates it medially Recurrent branch of medial nerve Abductor pollicis brevis Abducts thumb; helps oppose it Recurrent branch of medial nerve Flexor pollicis brevis Flexes thumb Recurrent branch of medial nerve Adductor pollicis Adducts thumb Deep branch of ulnar nerve o Hypothenar muscles Abductor digit minimi Abducts fifth finger Ulnar nerve Flexor digiti minimi brevis Flexes proximal phalanx of fifth finger Ulnar nerve Opponens digiti minimi Opposes little finger Ulnar nerve o Short muscles Lumbricals Flex metacarpophalangeal joints and extend interphalangeal joints Median nerve (1,2) and ulnar nerve (3,4) Dorsal interossei Abduct fingers from axial line; flex metacarpophalangeal joints; extend interphalangeal joints’ Ulnar nerve Palmar interossei Adduct 2nd, 4th, 5th fingers towards axial line; assist lumbricals in flexing metacarpophalangeal joints and extending interphalangeal joints