ANATOMY OF THE PELVIS
TYPICAL SI FUSION PATIENT…
SYMPTOMS:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Low back pain
Buttock and hip pain
Ipsilateral LE weakness
LE numbness and
tingling
Trouble sleeping
Leg instability
Problems sitting
SI JOINT AS A CAUSE OF PAIN:
25% of all low back pain is caused by Sacroiliac joint
disease.
The incidence of SI joint degeneration in post-lumbar
fusion surgery is 75% at 5 years post-op.
SI joint is a pain generator in low back pain of 43%
post- lumbar and lumbar-sacral fusion patients.
DIAGNOSIS…
• Clinical tests
• Imaging studies (x-ray.
CT scan, MRI)
• SI joint injections of a
local anesthetic
OTHER TREATMENT OPTIONS
• Physical therapy
• Chiropractic
manipulations
• Pain medication
• Injection therapy
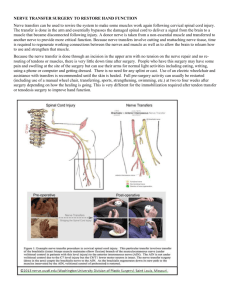
SI FUSION SURGERY
WHY DO WE MONITOR SI FUSIONS?
IATROGENIC NERVE INJURY RATES HAVE BEEN
REPORTED TO BE AS LOW AS 1% AND AS HIGH
AS 18%.
Lower Limb Dermatomes
Lower Limbs Myotomes
Movement
Nerve Root Segments
Hip flexion
L2/3
Hip extension
L4/5
Hip adduction
L2/3
Hip abduction
L4/5
Knee extension
L3/4
Knee flexion
L5/S1
Ankle Dorsiflexion
L4/5
Great toe
extension
Ankle
plantarflexion
L5
S1/2
SSEP
EMG
SE-EMG
SSEP
Stimulation:
Uppers: Ulnar
Nerve
Lowers: Posterior
Tibila Nerve
Low Freq
Filter (Hz)
High Freq
Filter (Hz)
Amp
(μV)
Typical
latencies
(ms)
Stim.
Intensity
(mA)
Stim
Duration
(ms)
Stim.
Rate
(Hz)
SEP median
nerve cortical
30
250-1000
0.5-5
17-23
20-35
0.2-0.5
1.3-4.7
SEP median
nerve subcortical
30
500-1000
0.5-3
11-16
20-35
0.2-0.5
1.3-4.7
SEP tibial
nerve cortical
30
250-1000
0.5-5
35-45
25-50
0.2-1
1.3-4.7
SEP tibial
nerve subcortical
30
500-1000
0-3
27-35
25-50
0.2-1
1.3-4.7
SSEP
Alarm Criteria:
- Amplitude decrease
of 50%
- Latency increase of
10%
EXAMPLES OF CHANGES
Patient had LUE amplitude decrease of greater than 50% due to a positional
issue.
EMG
Needle electrodes
used in the following
muscles:
• L5- Tibialis Anterior
• S1- Gastrocnemius
• S2- Anal Sphincter
FREE RUN EMG
Alarm Criteria:
• Any burst/firing
from nerves on the
side the surgeon is
working.
SE-EMG
Stimulation probe used
to stimulate either the
guide wire/pin or the
drill bit to insure a safe
distance between the
drill bit and the neural
structures.
SE-EMG
Alarm Criteria:
• Response <8 mA
with an absolute
minimum of 6
mA
IN THE CASE OF NERVE INJURY
•
•
•
•
LE numbness
LE weakness
Incontinence
Foot drop
QUESTIONS?
REFERENCES
-
"Minimally Invasive Sacroiliac Joint Surgery." MIS Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Surgery.
SI-BONE, n.d. Web. 08 Apr. 2013.
-
Moed, B.R. (2008). Monitoring neural function during pelvic surgery. In M.R.
Nuwer (Ed.), Intraoperative Monitoring of Neural Function Handbook of Clinical
Neurophysiology (vol. 8, pp. 752-763). Elsevier B. V.
-
Moore MD, M.R. (2012, January ). The Sacroiliac Joint: A Forgotten Pain
Generator. The SI-BONE Sentinel, 1-2.