1) How do you do a urethrogram +/- cystogram
advertisement

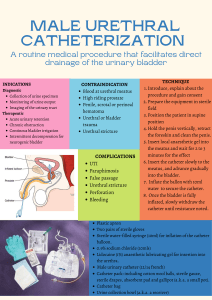
Emergency 1 – March 2013 – Ivo Dukic, Arie Parnham, Mr DA Jones HOW DO YOU DO URETHROGRAM +/- CYSTOGRAM? Urethrogram I would make sure any trauma patient had been stabilized and treated in accordance with ATLS guidelines as the majority (86%) of urethral injuries secondary to trauma are associated with additional injuries (Mundy & Andrich 2011) I would explain the procedure to the patient and position them on an appropriate X-ray table (A&E or X-ray Department). I would position the patient in a 30° right lateral position with the right leg flexed at the knee and hip if possible (alternatively the C-arm could be rotated to give a more lateral view in trauma patients). Using an ANTT, I would place a 12Fr. Foley catheter in the fossa navicularis and inflate the balloon with 2mls of water. If a catheter was already in place a 6-8 Fr catheter could be placed alongside and urethrogram performed if there was a possible urethral injury and per urethral bleeding (Mundy & Andrich 2011). I would take a scout/plain film. I would slowly inject 20- 30mls of a non-ionic contrast agent (Omnipaque) and screen as I was injecting and take at least 2 films to be archived. I would perform a post drainage film to look for small tears. Cystogram 70-97% of bladder injuries caused by blunt trauma are associated have associated pelvic fractures. 90% are caused by motor vehicle accidents. Insert catheter into bladder with ANTT Fill with at least 350mls of diluted non-inonic contrast agent (Niopam / Omnipaque). Oblique and post drainage films compulsory. (10% of bladder perforations seen on post drainage films)