2) What are the implications of a posterior urethral injury
advertisement
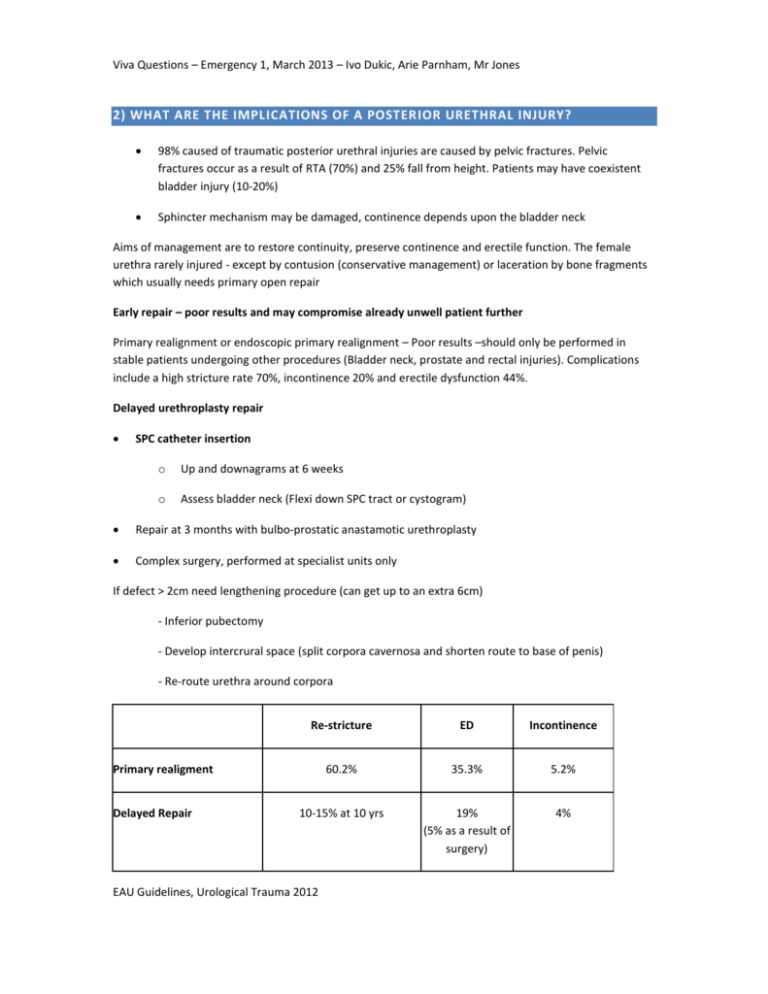
Viva Questions – Emergency 1, March 2013 – Ivo Dukic, Arie Parnham, Mr Jones 2) WHAT ARE THE IMPLICATIONS OF A POSTER IOR URETHRAL INJURY? 98% caused of traumatic posterior urethral injuries are caused by pelvic fractures. Pelvic fractures occur as a result of RTA (70%) and 25% fall from height. Patients may have coexistent bladder injury (10-20%) Sphincter mechanism may be damaged, continence depends upon the bladder neck Aims of management are to restore continuity, preserve continence and erectile function. The female urethra rarely injured - except by contusion (conservative management) or laceration by bone fragments which usually needs primary open repair Early repair – poor results and may compromise already unwell patient further Primary realignment or endoscopic primary realignment – Poor results –should only be performed in stable patients undergoing other procedures (Bladder neck, prostate and rectal injuries). Complications include a high stricture rate 70%, incontinence 20% and erectile dysfunction 44%. Delayed urethroplasty repair SPC catheter insertion o Up and downagrams at 6 weeks o Assess bladder neck (Flexi down SPC tract or cystogram) Repair at 3 months with bulbo-prostatic anastamotic urethroplasty Complex surgery, performed at specialist units only If defect > 2cm need lengthening procedure (can get up to an extra 6cm) - Inferior pubectomy - Develop intercrural space (split corpora cavernosa and shorten route to base of penis) - Re-route urethra around corpora Re-stricture ED Incontinence 60.2% 35.3% 5.2% 10-15% at 10 yrs 19% (5% as a result of surgery) 4% Primary realigment Delayed Repair EAU Guidelines, Urological Trauma 2012