Urethral Catheterization
(your opportunity to be a hero)
Darren Desantis
Eric Saltel
Outline
catheterization
– contra/indications, complications, catheters,
procedures
difficult catheterization
suprapubic cystotomy
Indications for Catheterization
Drain bladder
– Unconsious - OR/Intubated
– Retention - Neurogenic bladder, Obstruction, Clots
Monitor output
– Trauma
– Medical (CHF, RF, sepsis)
Urine specimen
Diagnostic studies
– Residual
– Radiographic contrast studies
– Renal function (24 h)
– Urodynamics
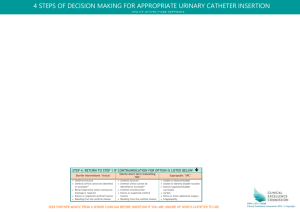
Contraindications
Traumatic urethral injury
– Mechanism (90% will have pelvic #)
– Blood at meatus
– High riding prostate
Retrograde Urethrogram
Duration
Intermittent / In & Out
– CIC- usually colonized
Indwelling
– 4% colonization / day
Complications of Catheterization
Short Term
Trauma
False passage
Hematuria
UTI
Long Term
colonization
urethral sloughing
malignancy
stones
hematuria
obstruction
stricture
Catheters
Size
– French size = circumference in millimeters
– French: 10 Fr circumference = 3.14 mm diameter
Material
– Latex
– Silicone (silastic)
– Teflon
Types
Way
– 1 vs 2 vs 3 way
Design
–
–
–
–
Foley
Coude (Tieman)
Malecot
Council
- Couvaliere
Holes:
– hematuria
– 6 eyed
Catheters
Equipment
Foley trays
– Gloves, drapes, bottle, gauze, lubricant
– prep, syringe w/ water
Collection bag
2% xylocaine (Urojet)
Catheter
+ extra set of hands
Procedure (male)
Sterile technique
Lubricant in urethra and on catheter
“Penis up to the sky”
=
Procedure
“Penis to the sky”
No force needed
– not an orthopedic procedure
DO NOT INFLATE UNTIL URINE SEEN
Inflate with hub at meatus in males
Procedure
Procedure
How do you know when you are in the bladder?
1. Urine
2. Hub of catheter at tip of penis
3. Balloon inflates easily
4. Patient should not have pain when inflating
balloon
5. When catheter pulled back (after balloon inflated)
an end-point is felt.
6. Catheter can slide in and out
7. Catheter can irrigate easily (in = out)
Important Misc.
Lubricant is your friend
Pull the penis up
Antibiotics
– Infected: short course
– SBE prophylaxis (not indicated unless infected)
– traumatic
Latex allergy
Water (not saline)
Reduce foreskin (paraphimosis)
Difficult catheterization
Difficult catheterization
History – attempts, PMHx, surgery, LUTS
P/E- abdomen, genitals
Instrumentation
1. Why?
2. Where?
3. Options?
WHY Difficult catheterization?
Females
Exposure
– lots of hands
Female hypospadius
– Tieman run along finger
Urethral stenosis
– Introital mass
WHERE Difficult catheterization
Males
meatus
urethral stricture
sphincter
prostate (BPH/Cancer)
bladder neck
Difficult Catheterization
Lubricant and proper technique
Catheter
– Size (go larger not smaller)
– Type eg. Coude (Tieman)
Filiforms and Followers
Stylet
Flexible Cystoscope and Guide Wire
Suprapubic Tube
WHERE is Difficulty ?
Males
Meatus- dilatation ( sounds, snap), lubricant
urethral stricture - f + f, scope, SP
Sphincter- lubricant, relaxation
prostate (BPH/Cancer)- f+f, scope, SP
bladder neck- stylet, f+f, scope, SP
Suprapubic Cystostomy
Should be familiar to all surgeons
Percutaneous approach
Different from OR formal procedure
– 24-32 Fr malecot cut down
Suprapubic Tube
Indications
– unable to catheterize per urethra
– Traumatic urethral disruption
– Full bladder
Contraindications
– empty bladder
– known Bladder cancer
– Fem-fem bypass
– extensive scarring (relative)
– clot hematuria (relative)
Suprapubic Tubes
U/S guided
“MacGyver”
– Cystocentesis: 22 G spinal needle
– Seldinger- Central line, femoral art line
SP Kits ( 10 – 16 Fr)
– Balloon
– Malecot
– Pigtail
SP Equipment
sterile procedure tray
SP kit
22 G spinal needle, local anesthetic, scapel
blade, 3 x 10cc Syringes, nonabsorb. suture
drainage bag
SP Procedure
Landmarks
– Check groins and abdo for scars (Bypass)
– Midline, 2 fingerbreaths above symphasis
– Percuss bladder
Local anesthetic
– Infiltrate skin, then perpendicular to skin, aspirate as
you go beyond fascia (point posterior - not inferior)
22 G spinal with syringe- to sacrum (perp) and
aspirate
– Mark depth of bladder with a hemostat on the needle
…SP Procedure
if no urine, try superior approach
set up SP with trocar and syringe
aspirate until same distance plus 1 cm
remove trocar
malecot / inflate balloon/ tie pigtail
secure with nonabsorbable suture
SP Tube Complications
Bleeding
– urinary (bladder/prostate) or extraurinary
Catheter Obstruction
– irrigate routine + prn
– ensure not displaced
Adjacent organs i.e. bowel
– use 22 G spinal needle
SP DEMONSTRATION
Summary
Find the Foley
Love the Lube
Pull the Penis up
Think of where obstruction is
SP tube
– Contraindications
– 22 Gauge needle
To bring to session