Lower Gastrointestinal
advertisement

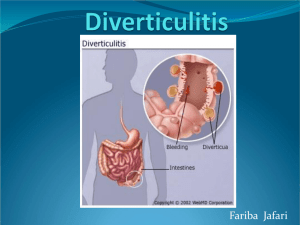
Lower Gastrointestinal 1. Describe the risk factors, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations of o Disorders of intestinal motility Diarrhea: What is the usual cause of acute diarrhea? What problem is the most important concern? What is often present in the etiology of Clostridium difficile? Constipation; when would you use a laxative, stool softener, bulk forming? Fecal incontinence/impaction: describe the stool in impaction; causes of incontinence; describe a bowel training program. Irritable Bowel syndrome; define; What is the relationship of o Structural and Obstructive Disorders hernia: inguinal, umbilical, incisional or ventral Do all hernias need to be repaired? How do you recognize an emotional problems to this syndrome? o incisional hernia? What is a strangulated hernia? How do you recognize it? What is the difference between diverticulitis and diverticulosis? What is the difference in the management? Diet? Medication? Use of laxatives? Acute abdominal pain; common symptoms; name five common causes; why would the patient have fluid volume deficit? What kind of surgery might be done? What orders would you anticipate on admission? Intestinal obstruction. What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction? When is surgery required? Bowel sounds are hyperactive, high-pitched, tinkling, rushing or growling at the onset of obstruction and may be absent later in obstruction. When a patient is admitted with possible bowel obstruction what orders would you anticipate? Anorectal Disorders hemorrhoids What causes hemorrhoids? How and why are hemorrhoids treated surgically? What is the conservative management? What is the criteria for discharge after a hemorroidectomy? How do you teach the patient to manage the pain? anorectal lesions: anal fissure, anorectal abscess, anorectal fistula, and pilonidal disease You mostly need to know the definitions of these. 2. Describe the collaborative management of the above, including diagnostic tests, o o o o o o o medications, and surgical management. stool specimen (occult blood, ova and parasites; culture) sigmoidoscopy proctoscopy colonoscopy serum electrolytes, osmolality, ABG biopsy CBC with diff; ESR o small bowel series: UGI with small bowel follow through and barium enema. o Why is a colostomy done on a patient with diverticulitis? When is it closed? 3. Identify necessary information for administration of medications in lower GI disorders. o Absorbents and protectants o Opium and opium derivatives: What is Lomotil? What is the protocol for administration? o Anticholinergics o Why would you not give Donnagel to a patient with prostatic hypertrophy? Laxatives and cathartics What advice would you give a person about the daily use of Milk of Magnesia? Why do you give mineral oil at bedtime? Why is obstruction a contraindication to osmotic laxatives? o Antibiotics 4. Use the nursing process to plan for the nursing care of patients with the above disorders. o Dietary management: low fat, high residue, high fiber, clear liquids What diet is best to prevent diverticulitis? o Risk for infection Why would you give Flagyl and a broad spectrum antibiotic to a patient with diverticulitis? o o Risk for fluid volume deficit Diarrhea What is the significance of assessing this patient for Fluid volume deficit? 5. o Risk for impaired skin integrity o Pain o Anxiety o Impaired Tissue Integrity Describe health promotion and home care strategies for patients with the above disorders. What would you teach a person with diverticulitis about straining at stool? Why? A person with hemorrhoids? What do you teach a patient about coughing after a hernia operation? 6. Discuss outcome measures used in evaluating goal attainment and revisions in the nursing care plan.