Diverticulitis
advertisement
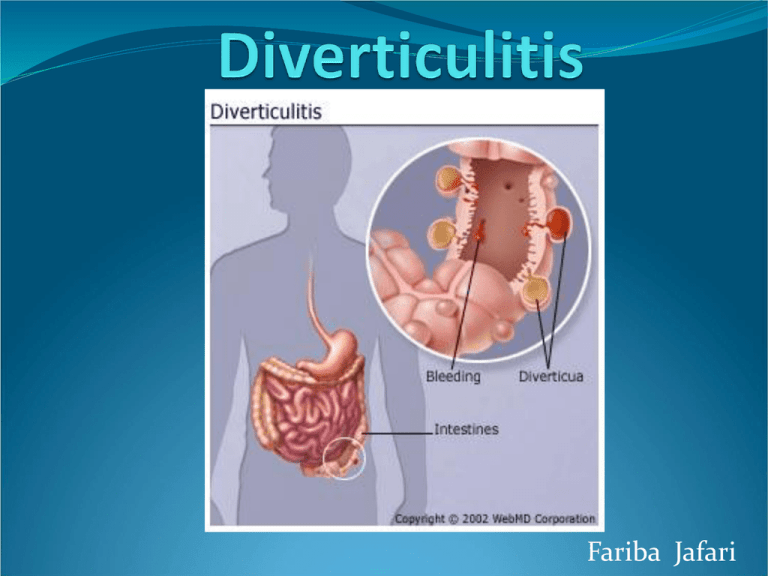
Fariba Jafari Definition • Outpouchings of the colon • Located at sites where blood vessels enter the colonic wall • Inflamed as a result of obstruction by feces or hardened mucus or of mucosal erosion localized perforation= diverticulitis Associated Risk Factors Decreased physical activity Intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) Smoking Constipation from any cause • Incidence increases with age. • Diet has been associated with the emergence of this disease. • Low-residue diet constipation lead to increased intraluminal pressure in the large bowel • High pressure zones or areas of segmentation may develop (sigmoid colon), and diverticula begin to protrude at these locations • Microperforation of thin walled diverticulum widespread contamination with fecal organisms may ensue Saint’s triad Cholelithiasis, diverticulitis, and hiatal hernia frequently occur together. Characteristic Findings Abdominal pain LLQ tenderness Irregular bowel habits Fever Physical Examination Uncomplicated: LLQ tenderness, possible mass, bleeding (uncommon), localized inflammation, Complicated: mass, evidence of fistula, ambdominal distention, abdominal tenderness, marked in cases of free perforation, hypotension; bleeding 2 courses Mild: outpatient basis. Liquid diet, oral antibiotics If not: hospitalize patient. NPO. IV antibiotics. CT with contrast. What now? Symptoms resolve: colonoscopy or contrast study Recur: surgical treatment Surgical • 20% of patients with diverticulitis require surgical treatment. Obstruction Perform diagnostic imaging Small bowel: highgrade, low-grade Large bowel: cecal distention Abscess Perform diagnostic imaging Small abscess Large abscess Fistula Signaled by fecaluria and pneumaturia Diagnostic imagingbladder air Treat medically Resect colon and fistula in one-stage procedure Free Perforation SURGICAL TREATMENT!! Hinchey Stage III & IV To the WEB Bleeding (lower GI) Massive Transfusions Angiography If + superselective embolization If - observe patient, RBC scanning. Moderate Observe patient Colonoscopy