ProteomicsWorkshop2014
advertisement

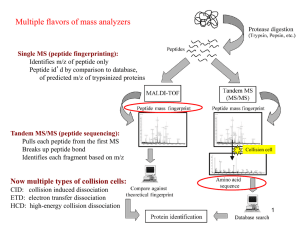
Targeted Proteomics Kelly Stecker Sussman Lab Outline • What is MRM/SRM/Targeted mass spec • Quantification using peptide standards • Selecting standard peptides and building methods • Practical notes and suggestions. MRM/SRM/Targeted proteomics MRM: Multiple Reaction Monitoring SRM: Selective/Selected Reaction Monitoring Specifically monitoring or ‘targeting’ one or more peptides Shotgun/untargeted proteomics: Coomassie stained gel Targeted proteomics: Western blot 1 2 3 MRM/SRM/Targeted proteomics MRM: Multiple Reaction Monitoring SRM: Selective/Selected Reaction Monitoring Specifically monitoring or ‘targeting’ one or more peptides Shotgun/untargeted proteomics: Coomassie stained gel -Indiscriminately identifies most abundant proteins -No prior knowledge required for protein detection -Information obtained for a large number of proteins Targeted proteomics: Western blot 1 2 3 -Selectively targets one protein -Requires prior knowledge of protein mass/sequence -Limited number of proteins can be assays at once (<150) -Improved sensitivity! -Higher throughput! Peptides are targeted using a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (QQQ) Triple quads contain 3 quadrupoles in series that are programed to selectively stabilize your ion of interest. Quadrupoles act as a mass filter. Ion Source Detector The DC and RF voltages are tuned to stabilize particular m/z ranges www.waters.com SRM analysis uses 2 stages of mass filtering Q1 q2 Q3 Ion Source Detector Fragmentation Q1: Peptide mass is selected (parent ion) q2: peptide is fragmented via collision induced dissociation Q3: Peptide fragment is selected (fragment ion) • Parent ion to fragment ion mass change is called a “transition” • Usually ≥ 3 transitions are monitored for each peptide of interest SRM analysis uses 2 stages of mass filtering q2 Q1 Q3 At1g01690.1 MSDALSAIPAAVHRNLSDKLYEKRKNAAL MLENIVKNLTSSGDHDKISKVIEMLIKEFA KSPQANHR NLTSSGDHDISK AQYLEQ IVPPVINSFSDQDSRVRYYACEALY SGDHDISK Three transitions (aka 3 pieces of data identifying this peptide) NLTSSGDHDISK SGDHDISK NLTSSGDHDISK DHDISK NLTSSGDHDISK NLTSS Basic workflow for SRM analysis Extract proteins Digest into peptides Chromatographic separation of peptides (C18 column) ESI MS analysis Q1 Parent ion selection q2 Fragmentation Q3 Fragment ion selection Ion Intensity Electrospray Ionization Time Peptides are quantified using stable isotope labeled peptide standards Endogenous: NLTSSGDHDISK Standard: NLTSSGDHDIS[K+08] Q1 mass Q3 fragment Q3 mass 637.67 y7 771.38 641.67 y7 779.38 Peptide A Intensity Peptide Standard Endogenous Endogenous Single transition m/z Standard Intensity Extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) Time Peptide B Peptides are quantified using stable isotope labeled peptide standards Endogenous: NLTSSGDHDISK Standard: NLTSSGDHDIS[K+08] m/z Intensity Extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) Time Overlay: Std & Endog. Intensity Endogenous Q3 fragment Q3 mass 637.67 y7 771.38 641.67 y7 779.38 Peptide A Single transition Peptide Standard Q1 mass Peptide B Peptides can be multiplexed in a single targeted MS run Standard peptides Endogenous peptides Standards peptides Endogenous peptides Peptide standards are spiked in during sample processing Extract proteins * * * * * Digest into peptides * * Chromatographic separation of peptides (C18 column) * ** * * * * * * ESI Single transition MS analysis Parent ion selection q2 Fragmentation Q3 Fragment ion selection Intensity Q1 Peptide Std. Endogenous m/z Intensity Electrospray Ionization Time Quantitation is achieved by measuring area under XIC curve Endog Area Std. Area = signal intensity normalized to peptide standard Awesome freeware exists for analyzing SRM data MacCoss Lab https://skyline.gs.washington.edu/ Vendor specific software also exists: MultiQuant from ABSciex How to select peptides for SRM analysis Considerations 1. Feasibility of chemical synthesis -Peptide length (≤ 20 A.A., or ≤ 24 A.A.) -PTMs? 3. Biological considerations -Is the peptide unique to 1 protein -Likelihood of trypsin misscleavage 4. PRESENCE OF EMERPICAL MS DATA! -Has your protein been detected by MS? -Software for predicting proteotypic behavior” of peptides is “Not so good”-Dr. MacCoss Poor performing Number of peptides 2. Physiochemical properties -Hydrophobicity -Chemically modified residues (Met, Cys) Good performing Hydrophobicity bins (SSR Calc) Picotti et. al. 2013 Nature Vol 494, pp 266-270 Examples of endogenous peptide detection success rate Sussman Lab data: -Lab mate working with rat blood proteins: • In silico selection ~20% • Empirical data ~80% Success rate for peptide detection depending on selection source -Targeting specific Arabidopsis protein: 11 tryptic peptides selected from in silico prediction, 2 endogenous peptides detected after SCX fractionation AND extended LC gradient. • In silico selection ~18% -Arabidopsis phosphopeptides: 65 peptides selected from discovery shotgun proteomics data, 61 endogenous peptides detected. • Empirical data ~93% NOTE: Isobaric tags may influence peptide behavior. Keep this in mind when viewing discovery data from iTRAQ or TMT experiments. In general, good quality MS1 spectra is a good indicator of SRM peptide performance. Huttenhain et al. Sci Transl Med 11 July 2012: Vol. 4, Issue 142, p. 142ra94 Commercial options for peptide synthesis Sigma-Aldrich • PEPscreen Peptide libraries • AQUA peptides Thermo Scientific • PEPotec Pros Cons Guaranteed 7-day turn around Cheap (around $60/peptide) Length restriction (~20 amino acids) Minimum order requirement (24) More PTMs available No minimum order size >95% pure Expensive ($200-$300/peptide) Slow production (months) Pros Cons Cheap! (around $40/peptide) Minimum order requirement (4) Peptides arrive resuspended http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/custom-oligos/custom-peptides/product-highlights/pepscreen-peptides.html http://www.piercenet.com/info/pepotec-srm-custom-peptide-libraries Note: all prices are for heavy labeled peptides and are approximate Developing SRM methods What you need to know -Peptide parent mass and charge state -Fragment peptide masses and charge states -Highly recommend building SRM methods by first starting with peptide standards Resources MacCoss Lab https://skyline.gs.washington.edu/ http://prospector.ucsf.edu/prospector/mshome.htm Developing SRM methods Step 0: Successfully resolubilize lyophilized peptide standards. Recommend stepwise resuspension. Step 1: Determine strongest transitions for each peptide (start with 5/peptide; method can be trimmed down to 3/peptide later on). If your instrument has an ion trap, this process is easier. Step 2: Optimize collision energy (CE). This must be performed for every single transitions. Step 3: Determine retention time of peptide. Using scheduled SRM methods significantly improves multiplexing capability. Step 4: Look for endogenous peptides. Determine necessary pre-fractionation steps. Why I like targeted MS: improved peptide detection Untargeted discovery data Detection overlap between samples 1400 Identificaitons 1200 Both Exps Single Exp Detection overlap between injection replicates Inj1 Offline SCX fraction + 4 hour LC-MS runs Inj2 1000 800 306 600 460 185 No SCX fraction, 90min LC-MS runs 400 200 0 Protein Peptide PICC pS124 Intensity, cps PEN3 pS40 Intensity, cps Untargeted Quantitation Unfractionate SCX fraction d PEN3 pS40 Intensity PICC pS124 Intensity Comparison between MS methods Time Time Targeted SRM Quantitation Standard Endogenous peptide peptide Log2 (treated/control) 3 fold Cold FC JA Flg22 H2O2 ABA KCl NaCl Mann. + 1.2 fold +/3 fold - AT5G56980 pS61 MSL9 pS124 EIF4A1 pT145 JAZ12 pS97 AHA1 pT948 AHA2 pT947 CPK5 pS552* ERD14 pS59 YAK1 pY284 AHA3 pT882 AHA3 pT948 CAX4 pS38 PIP3B pS274 AHA4 pT959 PIP2F pS283 AMT1 pS488 AT5G53420 pS204 NIA1 pS537 NPC4 pT158 DaySleeper pS155 TRP1 pS214 PP2C-g pS347 RPS6 pS240 WDL1 pS6 ZAC pS155 AREB3 pS43 ABF2 pS86* HSFB2B pS222 SnRK2.2 pS177 SnRK2.3 pS176 SnRK2.6.1 pS175 CPK9 pS78 PEN3 pS40 ADH1 pS229 CPK9 pT37 PEPC1 pS11 AHA2 pS899 Remorin pT58 SIP1 pS11 PICC pS124 Ox-reductase pS29 FAC1 pS203 PIP2F pS286 PLC2 pS280 GC5 pS793 V-ATPase pS241 SAY1 pS313 COP related pS24 MAP4Kα1 pS478 VCS pS692 bZIP30 pS176 MyoB1 pS825 PB1domain pS218 RAF18 pS671 TUA3 pT349* TUA4 pT349* SnRK2.4 pS158* Vac14 pS624 Reliable peptide detection means proteins can be reproducibly analyzed across many different samples ABA responsive block Osmoticspecific block Heat map of 5 min phosphorylation response of 60 peptides under 9 treatment conditions Stecker et al. Plant Physiology 165.3 (2014): 1171-1187. Log2 (treated/control) 3 fold Cold FC JA Flg22 H2O2 ABA KCl NaCl Mann. + 1.2 fold +/3 fold - AT5G56980 pS61 MSL9 pS124 EIF4A1 pT145 JAZ12 pS97 AHA1 pT948 AHA2 pT947 CPK5 pS552* ERD14 pS59 YAK1 pY284 AHA3 pT882 AHA3 pT948 CAX4 pS38 PIP3B pS274 AHA4 pT959 PIP2F pS283 AMT1 pS488 AT5G53420 pS204 NIA1 pS537 NPC4 pT158 DaySleeper pS155 TRP1 pS214 PP2C-g pS347 RPS6 pS240 WDL1 pS6 ZAC pS155 AREB3 pS43 ABF2 pS86* HSFB2B pS222 SnRK2.2 pS177 SnRK2.3 pS176 SnRK2.6.1 pS175 CPK9 pS78 PEN3 pS40 ADH1 pS229 CPK9 pT37 PEPC1 pS11 AHA2 pS899 Remorin pT58 SIP1 pS11 PICC pS124 Ox-reductase pS29 FAC1 pS203 PIP2F pS286 PLC2 pS280 GC5 pS793 V-ATPase pS241 SAY1 pS313 COP related pS24 MAP4Kα1 pS478 VCS pS692 bZIP30 pS176 MyoB1 pS825 PB1domain pS218 RAF18 pS671 TUA3 pT349* TUA4 pT349* SnRK2.4 pS158* Vac14 pS624 Reliable peptide detection means proteins can be reproducibly analyzed across many different samples 20%CV Median ABA Cold C1 8.5% 5.7% 12.9% 12.8% 6.8% C2 C3 FC Flg H2O2 JA KCl Mann NaCl 5.8% 6.9% 6.5% 7.6% 10% 6.4% 9.3% CV= Standard Deviation Average Cold FC JA Flg22 H2O2 ABA KCl NaCl Mann. + 1.2 fold +/3 fold - AT5G56980 pS61 MSL9 pS124 EIF4A1 pT145 JAZ12 pS97 AHA1 pT948 AHA2 pT947 CPK5 pS552* ERD14 pS59 YAK1 pY284 AHA3 pT882 AHA3 pT948 CAX4 pS38 PIP3B pS274 AHA4 pT959 PIP2F pS283 AMT1 pS488 AT5G53420 pS204 NIA1 pS537 NPC4 pT158 DaySleeper pS155 TRP1 pS214 PP2C-g pS347 RPS6 pS240 WDL1 pS6 ZAC pS155 AREB3 pS43 ABF2 pS86* HSFB2B pS222 SnRK2.2 pS177 SnRK2.3 pS176 SnRK2.6.1 pS175 CPK9 pS78 PEN3 pS40 ADH1 pS229 CPK9 pT37 PEPC1 pS11 AHA2 pS899 Remorin pT58 SIP1 pS11 PICC pS124 Ox-reductase pS29 FAC1 pS203 PIP2F pS286 PLC2 pS280 GC5 pS793 V-ATPase pS241 SAY1 pS313 COP related pS24 MAP4Kα1 pS478 VCS pS692 bZIP30 pS176 MyoB1 pS825 PB1domain pS218 RAF18 pS671 TUA3 pT349* TUA4 pT349* SnRK2.4 pS158* Vac14 pS624 Reliable peptide detection means proteins can be reproducibly analyzed across many different samples P-value Log2 (treated/control) 3 fold +/- 1.25 fold change +/- 1.5 fold change 0.05 Students T-Test: 3 control samples, 3 treated samples Practical sample handling comments Three biological replicates per treatment Homogenization, protein extraction Spike in isotopically labeled peptide standards, trypsin digest, TiO2 phosphopeptide enrichment It is difficult to correct for differential sample handling before standard peptides are spiked in! 90 min LC-MS analysis using Triple Quadrupole (QQQ) Q1 Q2 Parent ion selection Q3 Fragmentatio n Fragment ion selection Intensity Quantification of endogenous/standard extracted ion chromatograms Standard Endogenou s m/z Intensity Process all samples and controls in the SAME batch! -Extract proteins on the same day -Spike standards on the same day from the same aliquot Targeted Proteomics Time Useful references • “A complete mass-spectrometric map of the yeast proteome applied to quantitative trait analysis.” Paola Picotti, (lots of authors) Reudi Aebersold (2013) Nature • “Selected reaction monitoring–based proteomics: workflows, potential, pitfalls and future directions.” Paola Picotti & Ruedi Aebersold (2012) Nature Methods • “Selected reaction monitoring for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial.” Vinzenz Lange, Paola Picotti, Bruno Domon and Ruedi Aebersold (2008) Molecular Systems Biology 4:222 Arabidopsis SRM data from our lab • Stecker KE et al. "Phosphoproteomic Analyses Reveal Early Signaling Events in the Osmotic Stress Response." Plant Physiology 165.3 (2014): 1171-1187. • Su SH et al. "Deletion of a tandem gene family in Arabidopsis: increased MEKK2 abundance triggers autoimmunity when the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 signaling cascade is disrupted." The Plant Cell Online 25.5 (2013): 1895-1910.