SCID Screening: A New York State of Mind
advertisement

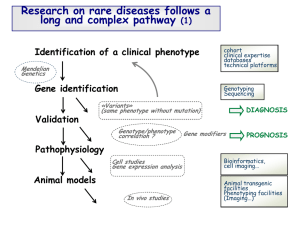
New York Newborn Screening Program - DNA Jason Isabelle June 4-5, 2012 Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Caused by diverse mutations in several different genes resulting in a combined immune deficiency X-Linked/Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Prevalence: ~1:40,000-100,000 3-7 affected newborns in NY each year Extreme lack of T lymphocyte differentiation and function Severally impaired humoral/cellular immunity Often fatal within the first year of life Prepared by Jason Isabelle-NYSNSP X-linked SCID Mutations in the gene encoding the common gamma chain of IL-2,4,7, & 9 cytokine+ receptors Autosomal Recessive SCID Adenosine deaminase deficiency Jak3 tyrosine kinase deficiency RAG1,2 IL-7R (α chain) CD-45 David Vetter: X-linked SCID Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) Donor marrow is depleted of T cells (Prevents GVHD) Allows for half-matched donor Climbing to a 90% success rate if administered <3 months of age Enzyme replacement therapy ADA deficient SCID Gene Therapy X-linked or ADA deficient SCID By-products of T cell receptor gene rearrangements during T cell maturation in the thymus TRECs do not replicate during mitosis Episomal DNA that gets diluted by cell divisions TREC levels in peripheral blood reflect T cell production in the thymus Low/No TRECs = Low/No T cell production by the thymus Created from the sequential rearrangements of the TCR α/δ locus 70% of thymocytes that express α/β TCR will form this specific TREC Signal joint region of this TREC is flanked by a conserved region Allows for universal primer design that will always detect this TREC Occurs late in maturation Likely to generate a functional and diverse T cell repertoire Hazenberg MD, Verschuren MCM,Hamann D, Miedema F, van Dongen JMJ (2001) T cell receptor excision circles as markers for recent thymic emigrants: basic aspects, technical approach, and guidelines for interpretation. J Mol Med 79:631640 Prepared by Jason Isabelle-NYSNSP Automated assay developed and validated 12/2009-9/2010 Submitted validation package to NYS Clinical Laboratory Evaluation Program (CLEP) for approval on 9/08/2010 CLEP and emergency regulation approved 9/27/2010 SCID screening started 9/29/2010 1st “True SCID” baby detected 12/27/2010 (NICHD Support) Presumptive Positive (Borderline) category added 1/25/2011 Commissioner of Health officially adds SCID to NSP panel 4/12/2011 CASM ‘Homebrew’ Extraction 4 Solutions 100μl Total Volume Tip Intensive Easily Scalable Low-Mid Throughput Average Yield: 4-5ng/μl RBC Lysis Solution Targets and destroys known PCR inhibitors ▪ Immunoglobulins, hemoglobin, etc Wash Solution Eliminate lysis by-products Buffer A Lyses of WBC’s and “scratches” fiber matrix Buffer B Neutralize pH and solubilize DNA Accommodate increased throughput Reduce repetitive stress injuries Address staffing shortages Increase reproducibility and consistency of results Many manual processes are difficult to automate Centrifugation, heating/cooling, vortexing, etc… Spot/Tip interactions 10….960….3,840….11,520 Labware Adjustments Liquid Type Editor Pipetting Template Volume Conditioning METHOD CREATION Each complete Liquid Handling System is capable of 1200 DNA extractions per 8 hour day. Each Cytomat has a capacity of 6048 Tips when fully loaded. Each Shaking Peltier Device can heat/cool from +4°C to +70°C . 10 μl Final Volume (8μl Reaction Mix/2μl DNA) RNaseP/TREC Multiplex 8-Point Standard Curve In Triplicate 2000,1000,500,250,125,62.5,31.2,15.6 Copies +SCID/-SCID Control In Triplicate ADA, IL7R alpha, X-Linked, Omenn’s Syndrome—0 Avg Cutoff: 200 Trecs/μl of Whole Blood Applied Biosystems Reporter/Quencher 5’ Nuclease Activity Probe Cleavage Sequence Specific Multiplex Capability 62bp amplicon Probe sequence spans signal joint 96 Well Extraction Plate to 384 Well Reaction Plate. Shaking-Heating-Multiplate Adapters Each 7900HT is capable of running 1500 samples per 8 hour day. QPCR TERMS Baseline Adjustment Threshold Adjustment Algorithm Settings Individual Trace Analysis Sample Passes Applied Biosystems 2nd most common form of SCID ~15% of all SCID cases Autosomal recessive inheritance Mutations in the ADA gene reduce or eliminate the activity of the enzyme adenosine deaminase Toxic buildup of deoxyadenosine ensues Massive reduction in lymphocyte population Affected newborns have options ADA RNaseP TREC TREC AMPLIFICATION PLOT RNASE P AMPLIFICATION PLOT ADA ADA Dried Blood Spot Specimen Multiplex PCR (TREC/RNaseP) TREC ≥ 200 and RNase P < WAL TREC values are copies/ul RNaseP values are Cq TREC< 200 Sample is retested in duplicate RNase P ≥ 35 SCREEN NEGATIVE Two of Three RNaseP WAL AND Two of Three TREC ≥ 200 OR Average of Three TREC ≥200 SCREEN NEGATIVE Two of Three RNaseP WAL AND Two of Three TREC < 200 AND Average of Three TREC >125<200 AND Gestation Age ≥37 AND Has never been a PP before PRESUMPTIVE POSITIVE Two of Three RNaseP WAL AND Two of Three TREC <200 AND Average of Three TREC <200 AND Gestation Age <37 REPEAT PREMATURE Two of Three RNaseP WAL AND Two of Three TREC ≤200 AND Gestation Age ≥37 AND Average of Three TREC ≤200 if a previous PP OR Average of Three TREC <150 if an initial Specimen REFERRAL Early detection benefits Adaptable screening methodology Prevalence Treatment Testing Funding Support The New York State Department of Health The Eunice Kennedy Shriver Institute for Child Health and Human Development Jeffrey Modell Foundation