投影片 1
advertisement

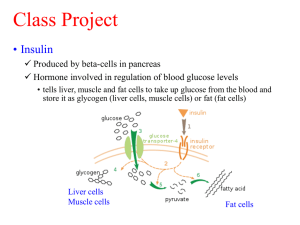
J. Biol. Chem. 266, pp. 8302-8311,1991 Purification and Partial Sequence Analysis of pp185, the Major Cellular Substrate of the Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase* Paul L. Rothenberg, William S. Lane, Avraham Karasik, Jonathan Backer, Morris White, & C. Ronald Kahn The Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA FaO hepatoma cells +/- insulin (1 mM), 1 min pp185 INR(b) (1) SDS(100oC) extraction/TCA ppt or (2) Liquid N2 quick-freezing Triton X-100 extraction IP by anti-PY antibody SDS-PAGE Western blot by anti-PY antibody Rats Liver +/- insulin (from portal vein) 1 min or various time points pp185 Tissue removed INR(b) SDS/TCA extraction IP by anti-PY antibody SDS-PAGE Western blot by anti-PY antibody Fat pads pp185 INR(b) TCA ppt/washed by organic solvent/ lypholized/0.1 M NaOH solubilized/ filtered with 0.45 mM membrane Rats insulin infusion (from portal vein) (0.5 min at 1 ml/min) Liver removed SDS/TCA extraction IP by anti-PY antibody SDS-PAGE Western blot by anti-PY antibody Half maximum stimulation ~1-5 x 10-8 M insulin Rats insulin infusion (from portal vein) (0.5 min at 1 ml/min) Liver removed SDS/TCA extraction IP by anti-PY antibody Eluted by pNPP Sup. + ppt. SDS-PAGE Western blot by anti-PY antibody & silver stained 50 Rats (starvation for 2-3 days) +/-insulin infusion (from portal vein) + insulin - (0.5 min at 1 ml/min) Liver removed SDS/TCA extraction IP by anti-PY antibody Eluted by pNPP Sup. + ppt. SDS-PAGE Transferred to NC membrane & trypsin digested RPC18 HPLC Amino acid sequencer CPS: carbamyl phosphate synthase as major contaminant in pp185 fraction IP: aPY WB: aPY - + aPY aPep80 - + aPep80 aPep80 - + aPep80 aPY Production of anti-peptide 80 Ab - + (insulin) Rats insulin infusion (from portal vein) (0.5 min at 1 ml/min) Liver removed SDS/TCA extraction IP by anti-PY or anti-pep 80 antibody SDS-PAGE Western blot by anti-PY or anti-pep 80 antibody Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73-7. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Sun XJ, Rothenberg P, Kahn CR, Backer JM, Araki E, Wilden PA, Cahill DA, Goldstein BJ, White MF. Joslin Diabetes Center, Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA IRS-1 cloning strategy: (1)Two cDNA libraries (2)Screened by 32P-oligonucleotide probes made from peptide 80 and 138 (3)Picked up positive clones and sequence determination (C18, C19 & P2-2) (4)Screened further by probes derived from C18 & P2-2 (14 clones were obtained) (5)Sequencing and overlapping DNA sequences of 14 clones IRS-1 cDNA: (1) Hydrophilic protein, 131 kDa (2) 9 tryptic peptides in DNA sequence (3) No SH2/SH3 domains (4) Contain ATP-binding domain (GXGXXG) (5) No protein kinase activity (6) mRNA 9.5 kb 6 YMXM motif 3 YXXM motif 1 EYYE motif Synthetic YMXM-containing peptide can be phosphorylated by purified INSR, Km~50 mM CHO/IR cells CHO/IRS-1 CHO/Neo metabolic 32P-labelling +/- insulin (100 nM, 1 min) cell extractes IP by PY-Ab SDS-PAGE/autoradiography IRS-1 expressed in CHO cells as 185 kDa PY-containing protein CHO/IR or CHO/IRF960 or CHO/IRD960 cells metabolic 32P-labelling +/- insulin (100 nM, 1 min) cell extractes IP by PY-Ab or IRS-1 Ab SDS-PAGE/autoradiography cut out 32P-labelled pp185 and IRS-1 Phosphoamino acid analysis Y960: the aa required for insulin signaling CHO/IR cells +/- insulin (100 nM, 10 min) cell extractes IP by IR Ab or PY Ab or IRS-1 Ab PI3 kinase assay in the IPP Role of IRS-1 in insulin-mediated signal transduction