COASTAL LANDFORMS
advertisement

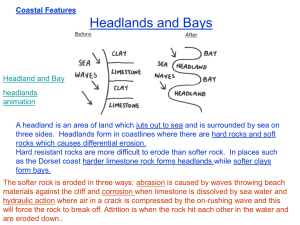
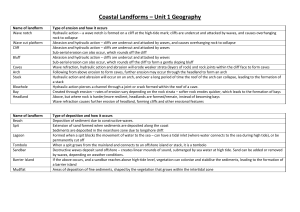
COASTAL LANDFORMS FEATURES OF SEA EROSION AND DEPOSITION WAVES Size and type of wave will depend on the FETCH and wind speed. Destructive waves – BACKWASH is stronger than the SWASH. Destructive waves form features of erosion. Constructive waves – SWASH is stronger than the backwash. Constructive waves form features of deposition. EROSIONAL PROCESSES Hydraulic Action – power of wave carries away any loose material. Abrasion – Waves use their load to break rock down into smaller fragments. Solution – water dissolves soft rock. Compressed Air- tiny little explosions within cracks due to trapped air. Erosion rates depend on: Rock Type Degree of exposure Amount of protective interference by man Wave Type Slope of shoreline Features of sea erosion Bay and Headland Cave / Arch / Stack Sea Cliff Formation of bay and headland Bands of hard and soft rock eroded at different rates – Differential Erosion. Processes at work : hydraulic action / abrasion / solution / compressed air. Hard rock stands out as headlands and soft rock retreats inland to form bays. Wave refraction occurs as bays retreat so headlands receive more high energy waves. Example – Howth Head and Dublin Bay. Formation of cave, arch, stack. Waves attack weak areas of exposed rock. Processes at work????? Cave cut into base of cliff/ deepened by abrasion. Cave extends through to other side of headland forming an arch. Erosion and gravity cause roof of cave to collapse forming a stack. Continuous erosion creates a sea stump. Example – Old Head Of Kinsale, Co. Cork. Formation of Sea Cliff. Destructive waves attack coast. Processes at work ???? Notch carved out and enlarged. Upper slope unsupported/ undermining occurs. Due to erosion, weathering and gravity, slope collapses forming a steep face. Cliff retreats and increases in height. Rock left at base of retreating cliff is a wave cut platform. The bigger the platform – the less rate of erosion. Example – Cliffs of Moher, Co. Clare. SEA CLIFFS Marine Transportation Longshore Drift – movement of material along the coast in a zig-zag pattern. Swash moves material up the beach. Backwash moves sediment back into the sea. Formation of a Beach. Formed by constructive waves. Weak backwash allows material to build up higher up the shore and finer material is left closer to shoreline. Beach forms between high and low water marks. Sections of beach include sandy area/ shingle area and storm beach. Example – Skerries. Formation of Sand Spit. Long ridge of sand and shingle deposited along entrance to sheltered bay. Constructive waves and longshore drift. Waves hit obstacle/ lose power / deposit load. Builds up above sea level across entrance to bay. Wave refraction may cause spit to curve inwards towards bay= Recurved spit. Example – Portmarnock, Dublin. Formation of a Tombolo. Island connects to mainland due to deposition. Constructive waves and longshore drift. Wave refraction at island causes currents to converge / deposit load. Example – Howth to Sutton.