Waves powerpoint - Think Geography

Coasts
Waves
How do you get waves like this ?
6R Giant Wave surfing.dv
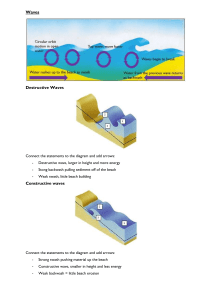
How are waves created?
Wind blows
Friction
Surface of the sea starts to move
What do you think affects the size of waves?
http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/geog/coastline/enhanced/
So wave size depends on:
1) Strength of wind
2) The fetch (the distance that a wave has travelled) http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/coastal/coastalpr ocessesrev1.shtml
What happens as the wave approaches the coast?
(Read and see Waugh p300 Figure 18.1)
Why does a wave break?
What is swash and backwash?
http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/geog/coastline/enhanced/ http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/coastal/coastalprocessesrev1.shtml
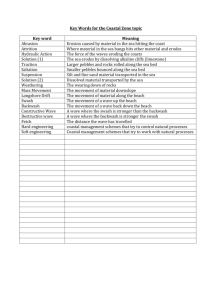
Destructive Waves
•They have a strong backwash compared to the their swash
•They are high in relation to the length of wave
•They are frequent waves (break at a rate of around 15 a min)
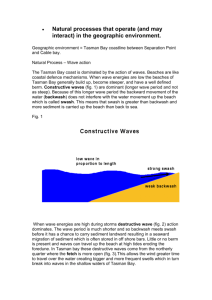
Constructive Waves
•They have a weak backwash compared to the their swash
•They are long in in relation to the height
•They are less frequent gentle waves (break at a rate of around 6-9 a min)
Sort the following facts. Are they about constructive or destructive waves?
• Weak swash & strong backwash
• Operate in calm weather
• Limited energy
• Steep beach angle
• High wave height (5-6 metres)
• Build up sediment on beaches
• Remove sediment from beaches
• Gentle sloping beaches
• Strong swash & weak backwash
• Cause erosion
• Break frequently (~15 per minute)
• Beach increases in size
• Low wave height (about 1 metre high)
• Much energy
• Operate in storm conditions
• Break less frequently (~7 per minute)