File - Units 1 & 2 Geography

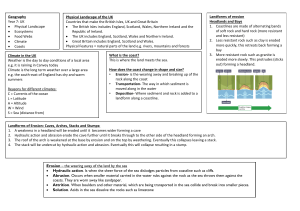
Name of landform
Wave notch
Wave cut platform
Cliff
Bluff
Caves
Arch
Stack
Blowhole
Bay
Headland
Name of landform
Beach
Spit
Lagoon
Tombolo
Sandbar
Barrier Island
Mudflat
Coastal Landforms – Unit 1 Geography
Type of erosion and how it occurs
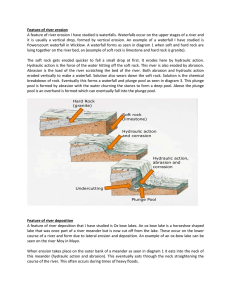
Hydraulic action – a wave notch is formed on a cliff at the high-tide mark; cliffs are undercut and attacked by waves, and causes overhanging rock to collapse
Abrasion and hydraulic action – cliffs are undercut and attacked by waves, and causes overhanging rock to collapse
Abrasion and hydraulic action – cliffs are undercut and attacked by waves
Sub-aerial erosion can also occur, which rounds off the cliff
Abrasion and hydraulic action – cliffs are undercut and attacked by waves
Sub-aerial erosion can also occur, which rounds off the cliff to form a gently sloping bluff
Wave refraction, hydraulic action and abrasion will erode weaker strata (layers of rock) and rock joints within the cliff face to form caves
Following from above erosion to form caves, further erosion may occur through the headland to form an arch
Hydraulic action and abrasion will occur on an arch, and over a long period of time the roof of the arch can collapse, leading to the formation of a stack
Hydraulic action pierces a channel through a joint or crack formed within the roof of a cave.
Created through erosion – rates of erosion vary depending on the rock strata – softer rock erodes quicker, which leads to the formation of bays
Above, but where rock is harder/more resilient, headlands are formed/remain, instead of becoming bays
Wave refraction causes further erosion of headland, forming cliffs and other erosional features
Type of deposition and how it occurs
Deposition of sediment due to constructive waves.
Extension of sand formed when sediments are deposited along the coast
Sediments are deposited in the nearshore zone due to longshore drift
Formed when a spit blocks the movement of water to the sea – can have a tidal inlet (where water connects to the sea during high tide), or be permanently cut off
When a spit grows from the mainland and connects to an offshore island or stack, it is a tombolo
Destructive waves deposit sand offshore – creates linear mounds of sound, submerged by sea water at high tide. Sand can be added or removed by waves, depending on weather conditions.
If the above occurs, and a sandbar reaches above high-tide level, vegetation can colonise and stabilise the sediments, leading to the formation of a barrier island
Areas of deposition of fine sediments, shaped by the vegetation that grows within the intertidal zone