Measure - Process Capability
advertisement

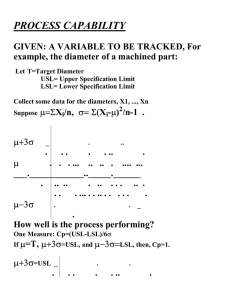
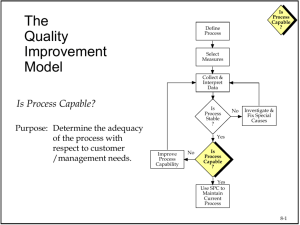
Measure Phase Process Capability Process Capability Welcome to Measure Process Discovery Six Sigma Statistics Measurement System Analysis Process Capability Continuous Capability Concept of Stability Attribute Capability Wrap Up & Action Items 2 Understanding Process Capability Process Capability: • The inherent ability of a process to meet the expectations of the customer without any additional efforts. • Provides insight as to whether the process has a : – – – – • Centering Issue (relative to specification limits) Variation Issue A combination of Centering and Variation Inappropriate specification limits Allows for a baseline metric for improvement. Are you capable? *Efforts: Time, Money, Manpower, Technology, and Manipulation 3 Capability as a Statistical Problem Our Statistical Problem: What is the probability of our process producing a defect ? Define a Practical Problem Create a Statistical Problem Correct the Statistical Problem Apply the Correction to the Practical Problem 4 Capability Analysis The Y’s (Outputs) Y = f(X) (Process Function) Verified ? Op i Op i + 1 Data for Y1…Yn X1 Y1 X2 Off-Line Correction Analysis Scrap Y2 X3 X4 Yes X5 No Y3 Correctable 10.16 10.11 10.16 10.05 10.11 10.33 10.05 10.44 10.33 9.86 10.44 10.07 9.86 10.29 10.07 10.36 10.29 10.36 Variation – “Voice of the Process” Frequency The X’s (Inputs) 9.87 10.16 9.99 9.87 10.11 10.12 9.99 10.05 10.43 10.12 10.33 10.21 10.43 10.44 10.01 10.21 9.86 10.15 10.01 10.07 10.44 10.15 10.29 10.03 10.44 10.36 10.33 10.03 10.15 10.33 10.15 9.80 9.90 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 ? Critical X(s): Requirements – “Voice of the Customer” Data - VOP 10.16 10.11 10.05 10.33 10.44 9.86 10.07 10.29 10.36 Any variable(s) which exerts an undue influence on the important outputs (CTQ’s) of a process Capability Analysis Numerically Compares the VOP to the VOC 5 9.87 9.99 10.12 10.43 10.21 10.01 10.15 10.44 10.03 10.33 10.15 USL = 10.44 LSL = 9.96 10.16 10.11 10.05 10.33 10.44 9.86 10.07 10.29 10.36 Defects -6 -5 Defects -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 +4 +5 +6 9.70 9.80 9.90 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 Percent Composition Process Output Categories Incapable LSL Average Off target LSL USL Average Target Target Capable and on target LSL Average Target 6 USL USL Problem Solving Options – Shift the Mean This involves finding the variables that will shift the process over to the target. This is usually the easiest option. USL LSL Shift 7 Problem Solving Options – Reduce Variation This is typically not so easy to accomplish and occurs often in Six Sigma projects. LSL USL 8 Problem Solving Options – Shift Mean & Reduce Variation This occurs often in Six Sigma projects. LSL USL Shift & Reduce 9 Problem Solving Options Obviously this implies making them wider, not narrower. Customers usually do not go for this option but if they do…it’s the easiest! USL LSL USL Move Spec 10 Capability Studies Capability Studies: • Are intended to be regular, periodic, estimations of a process’s ability to meet its requirements. • Can be conducted on both Discrete and Continuous Data. • Are most meaningful when conducted on stable, predictable processes. • Are commonly reported as Sigma Level which is optimal (short term) performance. • Require a thorough understanding of the following: – Customer’s or business’s specification limits – Nature of long-term vs. short-term data – Mean and Standard Deviation of the process – Assessment of the Normality of the data (Continuous Data only) – Procedure for determining Sigma level 11 Steps to Capability Select Output for Improvement #1 Verify Customer Requirements #2 Validate Specification Limits #3 Collect Sample Data #4 Determine Data Type (LT or ST) #5 Check data for normality #6 Calculate Z-Score, PPM, Yield, Capability Cp, Cpk, Pp, Ppk #7 12 Verifying the Specifications Questions to consider: • What is the source of the specifications? – – – – Customer requirements (VOC) Business requirements (target, benchmark) Compliance requirements (regulations) Design requirements (blueprint, system) • Are they current? Likely to change? • Are they understood and agreed upon? – Operational definitions – Deployed to the work force 13 Data Collection Capability Studies should include “all” observations (100% sampling) for a specified period. Long-term data: •Is collected across a broader inference space. •Monthly, quarterly; across multiple shifts, machines, operators, etc •Subject to both common and special causes of variation. •More representative of process performance over a period of time. •Typically consists of at least 100 – 200 data points. Short-term data: •Collected across a narrow inference space. •Daily, weekly; for one shift, machine, operator, etc. •Is potentially free of special cause variation. •Often reflects the optimal performance level. •Typically consists of 30 – 50 data points. Lot 1 Fill Quantity Lot 5 Lot 3 Lot 2 Short-term studies Lot 4 Long-term study 14 Baseline Performance Process Baseline: The average, long-term performance level of a process when all input variables are unconstrained. Long-term baseline 4 Short Term Performance ` 3 2 1 LSL TARGET USL 15 Components of Variation Even stable processes will drift and shift over time by as much as 1.5 Standard Deviations on the average. Long Term Overall Variation Short Term Between Group Variation Short Term Within Group Variation 16 Sum of the Squares Formulas = SS total + SS between SS within Precision (short-term capability) Shift x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 17 x x x x x Time Stability A Stable Process is consistent over time. Time Series Plots and Control Charts are the typical graphs used to determine stability. Tic toc… tic toc… 18 Measures of Capability Hope Cp and Pp: • What is Possible if your process is perfectly Centered • The Best your process can be • Process Potential (Entitlement) Reality Cpk and Ppk: • The Reality of your process performance • How the process is actually running • Process Capability relative to specification limits 19 Capability Formulas Six times the sample Standard Deviation Sample Mean Three times the sample Standard Deviation LSL – Lower specification limit USL – Upper specification limit 20 SigmaXL® Example Open worksheet “Camshaft”. Create a Normal Probability Plot and Descriptive Statistics of Suppliers 1 and 2. The P-values say the data is Normal since P >.05 21 SigmaXL® Example Create a Capability Analysis for both suppliers…. Assume long-term data. Note the subgroup size for this example is 5. LSL = 598 USL = 602 22 SigmaXL® Example Supplier 1 23 SigmaXL® Example Supplier 2 24 SigmaXL® Example SigmaXL® has a calculator to allow you to quickly find the sigma level for a process. SigmsXL>Templates and Calculators> Basic Process Capability Templates>Process Sigma Level - Continuous 25 Supplier 1 SigmaXL® Example For long term sigma level use the long term StDev. For short term use the short term StDev. 26 SigmaXL® Example Supplier 2 Long Term 27 Continuous Variable Caveats Capability indices assume Normally Distributed data. Always perform a Normality test before assessing Capability. 28 Capability Steps Select Output for Improvement #1 We can follow the steps for calculating capability for Continuous Data until we reach the question about data Normality… Verify Customer Requirements #2 Validate Specification Limits #3 Collect Sample Data #4 Determine Data Type (LT or ST) #5 Check data for Normality #6 Calculate Z-Score, PPM, Yield, Capability Cp, Cpk, Pp, Ppk #7 29 Attribute Capability Steps Select Output for Improvement #1 Notice the difference when we come to step 5… Verify Customer Requirements #2 Validate Specification Limits #3 Collect Sample Data #4 Calculate DPU #5 Find Z-Score #6 Convert Z-Score to Cp & Cpk #7 30 Z Scores Z Score is a measure of the distance in Standard Deviations of a sample from the Mean. The Z Score effectively transforms the actual data into standard normal units. By referring to a standard Z table you can estimate the area under the Normal curve. – Given an average of 50 with a Standard Deviation of 3 what is the proportion beyond the upper spec limit of 54? 50 54 31 Z Table 32 Attribute Capability Attribute data is always long-term in the shifted condition since it requires so many samples to get a good estimate with reasonable confidence. Short-term Capability is typically reported, so a shifting method will be employed to estimate short-term Capability. You Want to Estimate : Your Data Is : ZST ZLT ZST ZLT Short Term Capability Long Term Capability Short Term Capability Long Term Capability Subtract 1.5 Add 1.5 33 Sigma Level Short-Term DPMO Long-Term DPMO 1 158655.3 691462.5 2 22750.1 308537.5 3 1350.0 66807.2 4 31.7 6209.7 5 0.3 232.7 6 0.0 3.4 Attribute Capability By viewing these formulas you can see there is a relationship between them. If we divide our Z short-term by 3 we can determine our Cpk and if we divide our Z long-term by 3 we can determine our Ppk. 34 Attribute Capability Example A customer service group is interested in estimating the Capability of their call center. A total of 20,000 calls came in during the month but 2,500 of them “dropped” before they were answered (the caller hung up). Results of the call center data set: Samples = 20,000 Defects = 2,666 They hung up….! 35 Attribute Capability Example 1. 2. 3. 4. Calculate DPU Look up DPU value on the Z-Table Find Z-Score Convert Z Score to Cpk, Ppk Example: Look up ZLT ZLT = 1.11 Convert ZLT to ZST = 1.11+1.5 = 2.61 36 Attribute Capability 1. 2. 3. 4. Calculate DPU Look up DPU value on the Z-Table Find Z Score Convert Z Score to Cpk, Ppk Example: Look up ZLT ZLT = 1.11 Convert ZLT to ZST = 1.11+1.5 = 2.61 2 37 .87 Summary At this point, you should be able to: • Estimate Capability for Continuous Data • Estimate Capability for Attribute Data • Describe the impact of Non-normal Data on the analysis presented in this module for Continuous Capability 38 Open Source Six Sigma offers extensive White Label Solutions for Corporate Deployments & Training Providers. Turn Key eLearning: Your own LSS eLearning system and content to train your Employees or Clients. Partner Program: Solutions designed for Consultants & Training Providers. Use the best materials in the industry as your own. Enterprise Licensing: Content Solutions for internal Corporate Lean Six Sigma Initiatives. Learn more about these programs at: http://www.opensourcesixsigma.com/