Moving from Quality Control to Quality Assurance (Proactive Compliance!) Guy Wingate,
advertisement

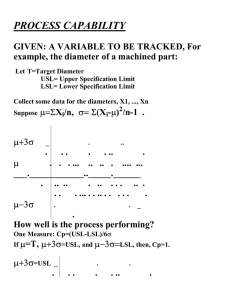
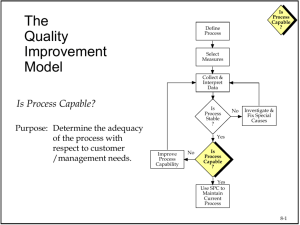
Moving from Quality Control to Quality Assurance (Proactive Compliance!) Guy Wingate, VP & Compliance Officer Global Manufacturing & Supply, GlaxoSmithKline Disclaimer • The views and opinions expressed in the following PowerPoint slides are those of the individual presenter and should not be attributed to GlaxoSmithKline • These PowerPoint slides are the intellectual property of the individual presenter and are protected under the copyright laws of the United States of America and other countries. All rights reserved. The ISPE logo is a registered trademark. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Slide 2 2 Our Collective Challenge Oxford English Dictionary: Proactive - creating or controlling a situation rather than just responding to it after it has happened Compliance – in accordance with rules or standards In other words as it applies to many of us... Assuring sustained higher performance (often during a period of significant change) with no nasty surprises Slide 3 Contents • • • • • • Current Controls Framework Step Change Performance Challenge Key Elements of Holistic Control Framework Ghosts in the Machine Management Accountability Summary Slide 4 Everything we do is to ensure they can do more, feel better, live longer Simplified Supply Chain Drug Substance Predictable Performance Product Quality ‘QC’ Checks Robust Manufacture Finished Products Secure Supply Assured Stability ‘QC Checks’ Slide 6 Mature Control Framework? Examples of Established Industry Controls – Quality Management System aligned to cGMP/ICH – Independent & Experienced Quality Organisation – Tiered Quality Governance for Escalation and Review – Validation & Incident Review Processes – Science-Based Risk Assessments – Regular Training & Communication – Supplier Quality Audits Examples Applied to Automation – GAMP5 Guidance – Independent & Experienced Validation Professionals – Tiered Quality Governance for Escalation and Review – Validation & Incident Review Processes – Science-Based Risk Assessments – Regular Training & Communication – Supplier Quality Audits – Highly dependable integrated systems? Slide 7 Step Change Challenge SemiConductor Pharma Red Zone Highlights the need for reliable KPIs and performance data Slide 8 Key Elements of Holistic Control Framework Governance & Management Systems & Processes Mindset & Behaviours Supporting Elements • QbD Technology • Procedures • Organisation • Facility/Systems Investment • Risk Management Nurture & Refresh • Company values to be in evidence as part of decision making processes • SpeakUp culture to raise concerns in the right and respectful way • Incentives support improved sustained performance Slide 9 d S Chart: Content rmity 4 3 Mfg….. Batch 2 1 Mfg….. Discrete Units 0.99 0.95 0.85 0.70 0.50 0.30 0.15 0.05 0.01 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 Capability Plot Within SD: 3.330; Cp: 1.502; Cpk: 1.495 Overall SD: 3.519; Pp: 1.421; Ppk: 1.415 LSL: 85.00; Nom.: 100.0; USL: 115.0 Within Overall Spec. Limits 80 “Population of Many” Quality assessed by 90 95 100 105 110 115 sampling Capability post Histogram manufacture 85 LSL -3.*S Nominal +3.*S “Population of One” Quality assessed on-line for every tablet 120 Process Capabi l i ty Report Drop Vol ume: Mean of 150 Drops (Speci fi cati on Li mi ts +/- 3% of Overal l Mean) LSL 350 USL 150 -3.s Process Data +3.s USL LSL Targ et USL 125 100 75 85% 50 Tablet N= 520 PpK =1.4 300 Droplet N= 606 PpK =16 250 115% 25 0 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 100 102 104 106 108 110 112 114 116 118 200 150 Frequency 0 QbD Technology (Example) Normal Probability Plot 85% Sample Mean Samples Sample N Total N StDev(Within) StDev(Actual) Actual Capab PPK 100 Slide 10 50 115% Lower 95% CL PPL PPU PP 0 Level Capability Exp. Actual Performance 7.36E6 7.34E6 7.32E6 7.28E6 7.3E6 7.26E6 0 7.24E6 PPM < LSL 7.22E6 7.18E6 Exp. Within Performance 7.2E6 7.16E6 7.14E6 7.12E6 7.08E6 7.1E6 0 7.06E6 PPM < LSL 7.04E6 7.02E6 6.98E6 7E6 6.96E6 6.94E6 Observed Performance Potential Cap CPK CPL PPM < LSL 0 PPM > USL 0 PPM > USL 0 PPM > USL 0 CP PPM Total 0 PPM Total 0 PPM Total 0 CPM CPU People – Helping Hands Training Mandated and optional training Clear work practices Allowance for personal judgement Competency test Q&A opportunity Capability Human Error Technical know-how Data robustness? Leadership and effective teams Real root cause identified Personal Style (consistency and motivation) Understand impact of local culture, mindset and behaviour Link to development plan and succession planning Solution shared as part of company production system Slide 11 Facilities/Systems Investment • • • • • Equipment maintenance budgets Calibration schedule adherence Refurbish/refresh to keep up with current expectations New equipment, facility and IT investment and validation Plan for healthy levels of depreciation Risk Management • • • • • Eliminate risks at root cause rather than symptom Avoid silo thinking, see bigger picture Reduce risks in timely manner to acceptable level Verify mitigation is effective and locked-down Recognise CA & PA management as separate process Slide 12 Ghost in the Machine – Culture QUALITY QUALITY Ideally , we want to keep all 3 elements in harmony COST ...but when we need to prioritise, its only possible to have TWO. SUPPLY If Cost & Supply are allowed to dominate then Quality can be viewed as something that can be fixed later Slide 13 Embracing a Culture of Quality Aspiration Execution – – – – – – – – – – Quality for All Transformational Change Right First Time Sustainable Improvement Preventive Solutions Enterprise Thinking Visibility of True Situation Tackle Root Cause Meaningful KPIs Science/Risk Based Decisions Foundation – No compromise to fundamentals – SpeakUp Culture (Disclosure) – Visible commitment to do the right thing Slide 14 Ghost in the Machine - Hidden Factory Foundation cGMP Processes Incident Reviews Deviation Process Effective ROOT Cause Analysis CAPA Process Mandated Standard Work Verification cGMP Change Control 1. Deviation Management 2. Root Cause Analysis 3. Corrective & Preventative Action 4. Escalation & Incident Review 5. Quality Governance 6. Risk Management 7. Change Control 8. Total Disclosure 9. Auditing 10. cGMP Training Slide 15 Being Brilliant at the Basics • Deviation Management – ensuring transparency and prioritised management • Root Cause Analysis – getting to the real root cause quickly and efficiently • CAPA – corrective action and preventative action • Management engagement – alongside team, understanding the issues and ensuring resolution • Effective governance – driving improvement Slide 16 Ghost in the Machine – Inspection Readiness “To Be” “As Is” Preparations for Specific Inspection Inspection Ready Preparations for Specific Inspection Inherent Audit Readiness Inherent Audit Readiness Slide 17 Assurance Pyramid Independent oversight of the control environment including ethical decision-making, behaviours and risk management. 4 External Audits and Reviews 3 Internal Auditing 2 Management Owned Monitoring 1 Self Assessment Slide 18 Management Accountability FDA looking closer at the root causes of cGMP failures… – May reflect management inattention – Deliberate decisions to defer investment in modern production facilities – Corporate disregard for the Quality Dept. DOJ also looking at role of senior managers in cGMP failures… – Do we have the right people? (capability and attitude – employees, contractors, suppliers) – Do people have the right incentives to see, report and fix problems? – Are people satisfied and engaged? – Do policies and procedures acknowledge how real people work and what they are capable of? – Do managers have personal visibility into what people are actually doing? – Is there a supportive organisational culture that recognises the patient at the end of the supply chain? [1] Janet Woodcock (Head of CDER FDA), FDA/ISPE Conference held 4th June 2012 [2] Maame Ewusi-Mensah Frimpong, (Deputy Assistant Attorney General for DOJ's Consumer Protection Branch), Pharmaceutical Compliance Congress held 29th January 2013 Slide 19 Summary – Proactive Compliance • Tone from the Top – holistic approach to compliance; never compromise the fundamentals • Remember quality is perishable so avoid nasty surprises... maintain a sustainable control framework with everyone playing their role in ensuring Quality • Trusting and open environment needed to report issues with obligation to resolve them Slide 20 Everything we do is to ensure they can do more, feel better, live longer Questions?