File
advertisement

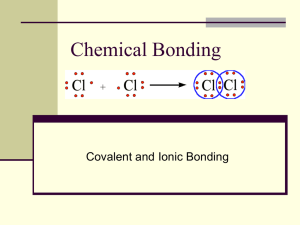
Intramolecular forces describe bonds that hold atoms together to create molecules and compounds • Bonding between atoms is a result of the atoms competing for electrons to get full valence shells • Bonding between atoms can occur by two atoms sharing electrons to form covalent bonds, or by transferring and accepting electrons to form ionic bonds Ionic bond describes the force holding charged particles together in ionic compounds Na loses an e- Cl Na+ Cl- gains an e- Na+-Cl- Ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged atoms An ionic bond is formed by the ________________________ from a metal to a nonmetal • Metal atom always ________ or ______________ electron(s) to become a ___________________ • Nonmetal atom always __________ or __________ electron(s) to become a ___________________ • Ionic bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ion and the negative nonmetal ion • Electronegativity difference between the nonmetal and the metal atom in ionic bonds is usually 1.7 or greater Example of substances containing ionic bonds NaCl sodium chloride CaF2 calcium fluoride Fe2O3 iron oxide Covalent bond describes the force holding atoms of nonmetals together in covalent and molecular substances H Cl H-Cl Covalent bond forms between H and Cl atoms. A (-) between two nonmetal atoms represents two (a pair) shared electrons Covalent bonding occurs between two nonmetal atoms that are _________________ electrons • Electronegativity difference between the two nonmetals in a covalent bond is usually less than 1.7 • Electronegativity difference between 0 and 0.4 indicates a nonpolar covalent bond • Electronegativity difference between 0.5 and 1.6 indicates a polar covalent bon • Nonpolar covalent bond = equal sharing of electrons • Polar covalent bond = unequal sharing of electrons Examples of substances containing covalent bonds H2O water CO2 carbon dioxide SiC silicon carbide H2 diatomic hydrogen molecule There are four types of covalent bonding • Polar covalent bond – unequal sharing of electrons between two different nonmetal atoms (electronegativity difference 0.5 – 1.6; examples H2O, HCl, NH3) • Nonpolar covalent bond – equal sharing of electrons between two nonmetal atoms (sometimes the same atoms) (electronegativity difference 0 – 0.4; examples H2, N2) • Network covalent bond – formed between nonmetal atoms in network solid compounds; compounds formed by network bonding cannot exist as an individual molecule (examples C diamond, SiO2, SiC) • Coordinate covalent bond – formed when both shared electrons are provided by ONLY one of the atoms (H+ does not have an electron but bonds with a molecule such as NH3 ammonia or H2O that have a lone pair (two unbonded) electrons that they can share with a H+ in that doesn’t have any electron Examples NH4+ ammonium ion formed from NH3 and H+ H3O+ hydronium ion formed from H2O and H+ • Metallic bond – force that holds metal atoms together in metallic substances; positive ions immersed in sea of mobile valence electrons; mobile electrons allow for high electrical conductivity in metals Examples Ca Au Fe Electronegativity difference Type of substances containing bond Example formulas containing bond Positive ions in sea of electrons _________ Metallic substances Ag K Metal + nonmetal Transfer of electrons 1.7 or greater Ionic substances NaCl Li2O Covalent Nonmetals only Sharing of electrons Less than 1.7 Molecular substances HCl Polar covalent Two different nonmetals Unequal sharing 0.5 – 1.6 Polar and nonpolar substance H2O CH4 Nonpolar covalent Same nonmetal or nonmetal atoms with similar electronegativity Equal sharing of electrons 0 – 0.4 Nonpolar substances H2 O2 Coordinate covalent Two different nonmetals One atom provides both shared electrons _________ Polyatomic ions NH4+ H3O+ Network solid covalent Nonmetals only No discrete particies _________ Network solids C, SiC, SiO2 Bond Type Type of elements involved in bonding Bond Metallic metal atoms of the same element Ionic description Determining type of bonding between atoms To determine formula containing • Ionic bond LOOK for a formula or name containing a metal and a nonmetal • Covalent bond LOOK for a formula or name containing only nonmetal atoms • Polar covalent bonds LOOK for a formula or name containing two different nonmetals • Nonpolar covalent bonds LOOK for a diatomic formula • Metallic bond LOOK for a symbol of a metallic element • Both ionic and covalent bonds LOOK for a formula containing at least three different elements or a polyatomic ion