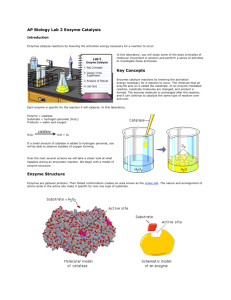
enzymes
advertisement
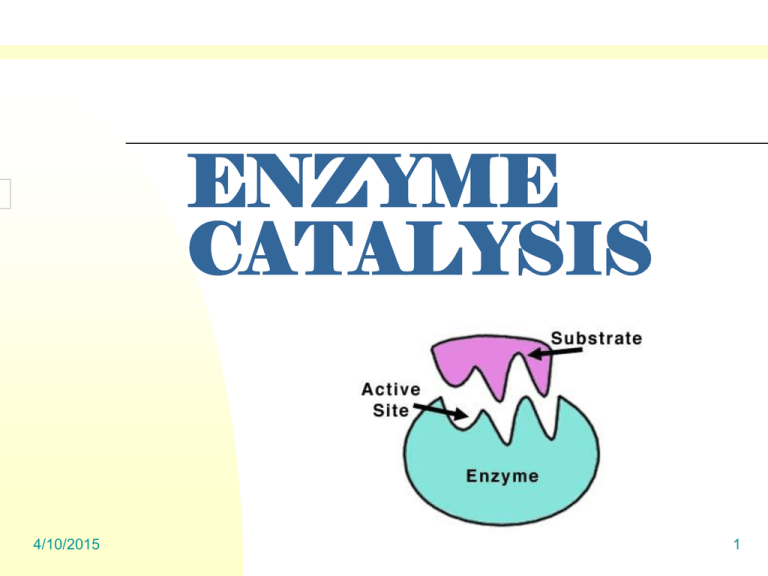
ENZYME CATALYSIS 4/10/2015 1 ENZYMES Globular Proteins Active Site One Substrate only Induced Fit: Changes occur when meet with substrate 4/10/2015 2 ENZYME CATALYSIS Enzymes Catalysis - ↓ Activation Energy - Faster Reaction without change of form. 4/10/2015 Factors affecting change: pH, temperature 3 BEFORE THE LAB Find out rate - enzyme catalasesubstrate → product Hydrogen peroxide = substrate amount of hydrogen peroxide remain after reaction → titration with KMnO4 Titration - add KMnO - color 4 change until target color 4/10/2015 4 LAB 1. Add 10ml of H₂O₂to each of 7 beakers. 2. Add 1ml of catalase to the first beaker at 0 second. 3. Observe the reaction until the time labeled on the beaker. 4. Stop the reaction by adding 10ml of H2SO4 5. Repeat the process for other remaining beakers. 4/10/2015 5 TITRATION 1. Remove a 5ml sample for titration and move the sample to a clean flask. 2. Record initial burette reading. 3. Add KMnO4 (purple) until faint brown color persists (it is the endpoint of process.) 4. Record final burette reading. 5. Calculate the ml of KMnO4 used to reach the endpoint. 6. Repeat the process for other remaining beakers. 4/10/2015 6 * KMnO4 to the flask mix - lose color - all peroxide reacted with KMnO4 → additional KMnO4 light brown or pinkish * KMnO4 ↑ - peroxide ↑ We calculate the rate of a reaction by measuring or observing the disappearance of substrate or the appearance of product. This lab figured out the rate at which the enzyme catalase converts substrate to product by observing the disappearance of substrate. 4/10/2015 7 Bibliography 1.LabBench http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labb ench/lab2/active.html 2. Drug Strategies to Target HIV http://www.chemistry.wustl.edu/~edudev/LabTu torials/HIV/DrugStrategies.html 4/10/2015 8