M. Woodin

Electrophysiology
the science and branch of physiology that pertains to the flow of ions in biological tissues and, in particular, to the electrical recording techniques that enable the measurement of this flow and the potential changes related to them
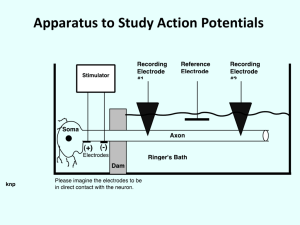
Intracellular Recording
Intracellular Recording: A recording electrode is inserted into a cell, so that the intracellular potential can be measured against the extracellular potential cell
The Nobel Prize in
Physiology or
Medicine 1963
Sir John
Carew
Eccles
Alan Lloyd
Hodgkin
Andrew
Fielding
Huxley
"for their discoveries concerning the ionic mechanisms involved in excitation and inhibition in the peripheral and central portions of the nerve cell membrane" http://nobelprize.org/medicine/laureates/1963/
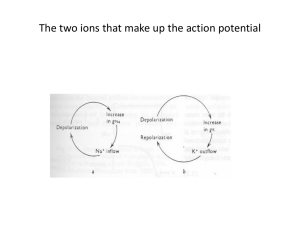
Membrane potentials in squid axons:
The first experiments examining how changes in ion concentrations affect the membrane potential were done on squid.
Why squid axons?
Voltage Clamp
Allows you to ‘clamp’ the membrane potential and record the ionic current
Normally, the voltage is ‘stepped; and the resulting current is measured
Difficulties with Voltage Clamp and sharp intracellular recordings?
E. Neher B. Sakmann
1991 Nobel Prize in Medicine
For the development of the Patch clamp
Small patch of membrane is sealed to the tip of a micropipette
The high resistance seal (called a gigaohm seal)ensures that currents flow through the amplifier rather than escaping through the rim of the patch
Recording Configurations
• Why select cellattached vs. wholecell recording?
Cell-attached recording
• Allows the recording from a single ion channel located in the area of the patch under the pipette
• As the ion channel opens or closes there will be an abrupt increase or decrease in the conductance of the patch of membrane
• Ion channels can be characterized by their conductance, their open time, and probability of channel opening (in addition to pharmacological inhibition and ion substitution)
Figure 4.6 Effect of Potential on Currents
Single spontaneously active K+ channel; 150 mM KCl on both sides
Channel current as a function of voltage; the slope of the line indicates the channel conductance; the ability of a channel to pass current
A linear IV curve indicates no voltage-dependent gating of the channel
Permeability = open channel
Conductance = permeability + ions
Equilibirum Potential for K+ Currents
[K + ] i
= 90mM [K + ] o
= 3mM; (B) with no electrical gradient K
(C) with 20mV applied to the cell the flow of K +
+ flows out out of the cell increases
(D) -50mV inside the cell reduces the current amplitude
Non-linear curve indicates the channel is voltage-dependent
What is the difference between
Patch Clamp and Voltage Clamp?
Can they be used simultaneously?
Recording Configurations
• Why select cellattached vs. wholecell recording?
• How do you decide what solution to include in your whole cell solution?
• Electrical access vs. dialysis?
Figure 7.1 Membrane Currents Produced by Depolarization
• Ion substitution experiments
Figure 7.3 Dependence of Early and Late Currents on Potential
How can we find synaptically connected neurons?
EPSPs
IPSPs
Figure 11.8 Reversal Potential for Synaptic Currents Measured by Voltage Clamp Recording
STDP
Fiumelli & Woodin 2007 Current Opinion in Neurobiology
Perforated Patch Clamp Recording