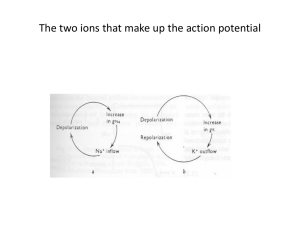
2014 Midterm + Answers
advertisement

NAME _______________________ BIO 360 - MIDTERM FALL 2014 This is a closed book, no notes exam. PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH SHEET. Read each question carefully and answer as well as you can. Each is worth 10 points for a total of 100 points. Please do not exceed the space provided. 1. Give four advantages of electrical synapses over chemical synapses. A. Faster, no synaptic delay B. Bidirectional transmission C. Signal amplification through synchronous recruitment of multiple post-synaptic cells D. More reliable (fails less frequently) 2. Define permeability and conductance. What is the difference between the two? Give a physiological example where permeability is high when conductance is zero. Permeability: property of membrane or channel allow substances to pass in or out of cell Conductance: the reciprocal of electrical resistance and a measure of permeability to one or more ion species Example: at ENa the permeability of Na+ is high while the conductance is zero because there is not net flow of Na+ at ENa. 3. The cell below is stimulated to produce an action potential at point A. What happens when it reaches point B (circle the best answer): A. Goes to point C B. Returns to point A C. Stops at point B D. Goes to point D E. Goes to points C and D F. Goes to Point D and returns to point A G. Goes to points C and D and returns to Point A Explain your answer: When initiated, the AP will travel along any active membrane (containing voltage dependent channels) that is not in the refractory state. Hence the AP will travel antidromically (backwards) from Point A to Point B. At Point B, the AP will activate membranes in both directions and the AP will travel to both Points C and D. 1 NAME _______________________ 4. A depolarizing voltage clamp pulse is delivered to an axon being held at -70mv and the inward Na and outward K currents are recorded. If you want to eliminate the Na current and record only the outward K current, name three ways of accomplishing this aim. Assume you have control over the external solution and the voltage of the clamp pulse. Make certain that your procedures make the Na current zero. 1. Block Na channels with TTX 2. Voltage clamp to ENa 3. Make [Na]out equal to [Na]in 5. In which cells do you find saltatory conduction of the action potential? In which cells do you find continuous conduction of the action potential? Which is faster saltatory or continuous conduction and why? Saltatory conduction occurs in myelinated cells. Continuous conduction occurs in unmyelinated cells. Saltatory conduction is faster than continuous conduction because the myelin sheath decreases capacitance and thus causes a decrease in the time constant Tau (RmCm). One consequence of a decrease in Tau is that the rising phase of the action potential will be steeper and the action potential will reach its peak more quickly, resulting in a fast conduction velocity of the action potential down the axon. 6. Why is the Na/K ATPase pump considered electrogenic? What are the short- (min) & long-term (hrs) effects on the resting potential if the Na/K ATPase pump is blocked? a) Na/K ATPase pumps 3 Na+ ions out of the cell for every 2 K+ ions it transports into the cell. Hence every cycle makes the inside slightly more negative than the outside. The Na/K ATPase pump makes the cell about 10 mV more negative than without it. b) The resting potential rises immediately to -60 mV due to the electrogenic nature of the pump, after which it will slowly rise to 0 mV as the Na and K gradients break down. 7. Assuming that the EK+ in a normal neuron is -90mV, what would be the new value of EK+ if: a) the intracellular concentration of K+ was reduced to 10% of its original value? b) the extracellular concentration of Na+ was increased 10 fold? c) ligand-gated Cl- channels were activated. a) The new EK+ would be -32 mv, 58 mV more positive than the initial EK+. b) EK+ would remain unchanged at -90mV since Na+ is not a component of the Nernst potential equation for K+. c) EK+ would remain unchanged at -90mV since Cl- is not a component of the Nernst potential equation for K+. 2 NAME _______________________ 8. Matching pairs: choose the one best answer from column B (insert a number) that most closely matches the phrase in column A. You may only use an answer once. COLUMN A A. resting membrane potential B. less negative membrane potential C. threshold D. increase in charge separation across membrane E. action potential F. no net ionic flux G. membrane conductance H. voltage clamp I. resting channels J. passive potential YOUR ANSWER 7 COLUMN B 4 1. transient reversal of membrane potential 2. ion channels 10 5 3. dendrite 4. depolarization 1 8 2 9 6 3 5. hyperpolarization 6.non gated ion channels 7. charge separation across membrane 8. steady state 9. negative feedback system 10. regenerative activation of voltage dependent Na+ channels 9. A family of patch clamp recordings of 3 channels from a neuron looks like this: What do you conclude about this channel? Explain your conclusions. This is a voltage dependent K+ channel. The channel is voltage dependent because it is open only at more depolarizing voltages (it is closed at -70 mV and -60 mV and open at 30 mV and 0 mV). The conclusion that it is a K+ channel is based on the observation that the current is outward and its amplitude increases at the voltage step increases. This increase in current amplitude occurs when the driving force increases (driving force = Vm - Eion) and the only ion which would cause an increase in outward current flow as the voltage becomes more positive is K+. 3 NAME _______________________ 10. You are studying a pair of neurons in the octopus brain that are monosynaptically (i.e., directly) connected to each other. You have inserted stimulating and recording intracellular electrodes into each of the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic cells. Depolarization of the pre-synaptic cell produces hyperpolarization in the post-synaptic cell with a synaptic delay of 1 ms. Depolarization of the post-synaptic cell produces a smaller depolarization in the pre-synaptic cell without any delay. Provide a plausible explanation for this result and devise an experiment that would test your answer. There are two synaptic interactions here: 1) there is a chemical synapse from PRE to POST that releases an inhibitory transmitter; and 2) there is a rectifying electrical synapse from POST to PRE. An experiment that would test this hypothesis is to lower extracellular [Ca2+] which would decrease the IPSP from PRE to POST without affecting the electrical synapse from POST to PRE. 4