Organic Molecule Foldable
advertisement

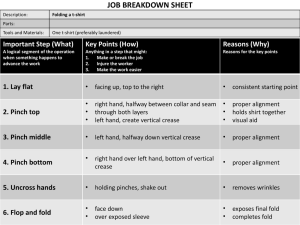
Organic Molecule Foldable 1. Fold a piece of 11 x 17 paper in half the “hamburger” way and crease. Fold 1. 2. 3. Fold a piece of 11 x 17 paper in half the “hamburger” way and crease. Unfold the paper. Then fold each end into the middle crease. Fold Fold 1. 2. Fold a piece of 11 x 17 paper in half the “hamburger” way and crease. Unfold the paper. 3. Then fold each end into the middle crease. 4. 5. Unfold the paper back flat Divide the right fold into thirds with a straight line. 6. Divide the left side fold in half with a straight line. Draw Draw Draw 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Fold a piece of 11 x 17 paper in half the “hamburger” way and crease. Unfold the paper. Then fold each end into the middle crease. Unfold the paper back flat Divide the right fold into thirds with a straight line. Divide the left side paper in half with a straight line 7. 8. Cut the left line to the first fold on the left Cut the right lines to the first fold on the right Cut Cut Cut • Fold the flaps in and label each as follows :: • Left side flaps = Carbohydrates and Lipids • Right side flaps = Carbon, Proteins and Nucleic Acids Fold Fold Categories • • • • • Carbohydrates (left side) pg. 46-47 Lipids (left side) pg. 47, pg. 204 Carbon (top right side) pg. 45, diagram pg. 34 Proteins (right middle side) pgs. 48-49 Nucleic Acids (bottom right) pg. 48, pg. 344-45 For the flap labeled Carbon: • In Chapter 2 section 3, read the section “The Chemistry of Carbon” • list at least 4 major points about Carbon • draw the Carbon Atom showing protons, electrons and neutrons in their correct locations • For the macromolecules, look up the information in your book and put it behind the “flap” for each organic molecule: 1) Name the Subunit(s) or building block(s) and draw a picture showing the chemical structure of it (them). 2) Function, description and example of that organic molecule 3) Name and picture of an example of the organic macromolecule (one of the polymer forms)