WATER AS A SOLVENT
advertisement

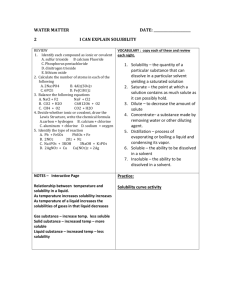
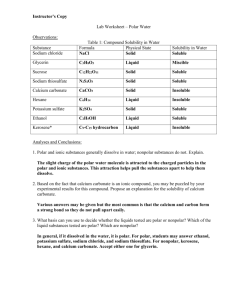
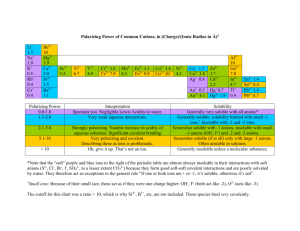
MODULE 3 12 WORKSHEET WORKSHEET WATER AS A SOLVENT Syllabus reference 8.4.3 1 Classify each of the following statements as true or false. For the statements that are false rewrite them so they are true. a Covalent molecular substances are very soluble in water. FALSE b MOST covalent molecular substances are INsoluble in water. Most ionic substances are soluble in water. TRUE c Another name for water solutions is aqueous solutions. TRUE d Water bound in an ionic substance is called water of binding. FALSE e Water is a non-polar solvent. FALSE f Water is a POLAR solvent. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is soluble in water. FALSE g Water bound in an ionic substance is called water of CRYSTALLISATION. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is INSOLUBLE in water. All large molecules will dissolve in water. FALSE MOST large molecules THAT ARE HIGHLY STRUCTURED will NOT dissolve in water. h Silicon dioxide will not dissolve in water because of the strong covalent lattice structure of the compound. TRUE i The low solubility of oxygen gas (O2) in water is due to weak dipole–dipole forces between solute and solvent. FALSE The low solubility of oxygen gas (O2) in water is due to weak DISPERSION forces between solute and solvent. j Sucrose dissolves well in water because it can form hydrogen bonds with water. TRUE Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 12 2 The solubility of substances depends on the nature of the bonding in the solute compared to that in the solvent. This is often generalised as ‘like dissolves like’. Explain what is meant by this generalisation. Polar substances will dissolve in polar solvents and do not dissolve in non-polar solvents while non-polar substances will dissolve on non-polar solvents but do not dissolve in polar ones. 3 Complete the following table. SUBSTANCE BONDING TYPE SOLUBILITY IN WATER SOLUBILITY IN HEXANE ionic soluble insoluble Glucose (C6H12O6) molecular covalent with O–H groups, hydrogen bonding soluble insoluble Iodine (solid) molecular covalent, non-polar insoluble soluble Silicon molecular covalent, non-polar insoluble soluble metallic insoluble insoluble Cellulose molecular covalent with O–H groups, hydrogen bonding soluble insoluble Hydrogen chloride molecular covalent, polar soluble insoluble Sodium chloride Zinc Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 12