Photosynthesis PP
advertisement

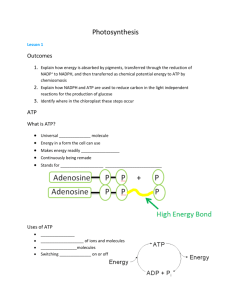
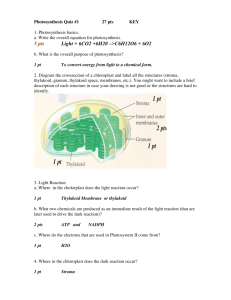
Photosynthesis General Formula • CO2 + H2O + light O2 + C6H12O6 • Photosynthesis is a endothermic reaction requiring an external source of energy to drive the production of organic molecules existing at a higher energy state than the reactants. • Entropy The Chloroplast • The chloroplast has two outer membranes and an inner most thylakoid membrane. • The thylakoid membrane form grana, and are the site of the light reactions (photo). • The thylakoid membrane segregates the part of the chloroplast space into the outer stroma and the inner thylakoid space. • The dark reactions occur in the stroma (synthesis). Light Absorption • Photosystems are complex protein molecules that have imbedded within them a variety of pigments. • Some of these pigments act as the light harvesting complex while others make up the reaction center. • The light harvesting pigments increase the range of wavelengths that the system can absorb (some pigments are protective as well). • The reaction center contains special chlorophyll a pigments that become oxidized, losing electrons to a primary electron acceptor. Oxygen Production or Photolysis • Within photosystem II, radiation is also used to split water into: 1) Electrons (e-) which replace those lost by Chlorophyll a (it becomes reduced again) 2) Hydrogen ions (H+) which build up inside the thylakoid, and 3) Oxygen (O2) which is lost through stomata to the atmosphere Electron Transport • In photosynthesis there are actually two paths for electrons lost by chlorophyll electrons. • The predominant path is a non-cyclic pathway where electrons pass from photosystem II though a series of more electronegative electron acceptors (specifically plastoquinone (Pq), the cytochrome complex, and plastocyanin (Pc)), eventually to be passed through photosystem I, an electron acceptor called ferredoxin (Fd) where they are passed to the final electron acceptor NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) creating NADPH. While this is occurring hydrogen ions are being actively transported inside the thylakoid space through the cytochrome complex. • In the non-cyclic pathway the electrons cycle between photosystem I and portions of the electron transport chain without the production of NADPH but with the generation of an H+ gradient. Electron Transport ATP Formation • • • Ions can’t diffuse through the lipid membrane of the thylakoid. During photosynthesis a H+ gradient is generated that is 1000 time more concentrated inside the thylakoid (pH or 5 versus 8) producing a source of potential energy. Inside the thlakoid membrane there are proteins called ATP synthase that use the movement of hydrogen ions to power particular conformational changes that result in the production of ATP. The Dark Reactions • • • The dark reactions are also called the light independent reaction or the Calvin-Benson Cycle. In these series of reactions NADPH and ATP from the light reactions provide the electrons (and H+) and energy, for converting CO2 in C6H12O6 and other organic molecules. The series of six reactions is categorized into three steps, carbon fixation, reduction, and the regeneration of RuBP.