Photosynthesis
advertisement

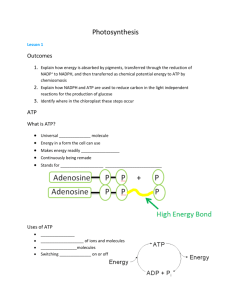
PHOTOSYNTHESIS The Dark and Light Reactions ENERGY IS ESSENTIAL TO ALL LIVING THINGS. All energy on earth originates in nuclear reactions in the sun. PRODUCERS PLANTS AND OTHER ORGANISMS CAPABLE OF CARRYING OUT PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6C02+ 6H20+ energy C6H1206 + 602 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 PHOTOSYNTHESIS TAKES PLACE IN THE CHLOROPLAST LIGHT REACTIONS: OCCUR ON THE THYLAKOID MEMBRANES •convert light and water into chemical energy •produce O2 as a waste product HOW LIGHT WORKS Visible radiation drives the light reactions Light is a type of energy called electromagnetic energy. Different pigments embedded in thylakoid membranes DIFFERENT PIGMENTS ABSORB LIGHT OF DIFFERENT WAVELENGTHS. The wavelengths absorbed by the light harvesting pigments are mainly in the blue and red range This is why most plants appear green The light harvesting pigments of chloroplasts are 1. chlorophyll a: absorbs in blue and red 2. chlorophyll b: absorbs in blue and orange 3. carotenoids: absorbs mainly blue-green range Having all these different pigments broadens the range of visible light that is usable for photosynthesis. Only chlorophyll a passes electrons to the electron transport chain and thus is directly involved in the light reactions. The other pigments convey the light energy to chlorophyll a. THE LIGHT REACTIONS Photosystems I and II STEP 1: Pigments in photsystems II absorb light Energy from the light is absorbed by electrons (increasing energy level) High-energy electrons are passed on to the electron transport chain H2O molecules provide new electrons to the chlorophyll to replace the ones that were lost Enzymes on the inner surface of the thylakoid membrane break up each H2O molecule into 2 high-energy electrons Oxygen is released into the air as oxygen gas 2 H+ ions are released inside the thylakoid membrane STEP 2: High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain from photosystem II to photosystem I b.Energy is used from the electrons to transport the H+ from the stroma into the inner thylakoid STEP 3: Pigments in photosystem I use energy from light to reenergize the electrons b.NADP+ picks up high-energy electrons on the outer surface of the thylakoid membrane plus a H+ ion and becomes NADPH STEP 4: H+ ions released during water-splitting and electron transport the inside of the thylakoid membrane becomes positively charged and the outside negatively charged b.The difference in charges provides the energy to make ATP STEP 5: H+ ions CANNOT directly cross the membrane b.ATP synthase (protein) allows H+ ions to pass through it c.As H+ ions pass through this protein, the protein rotates and ATP synthase binds to ADP and a phosphate group – producing ATP Water splits into H+ ions electrons and Oxygen PHOTOLYSIS: the splitting of water Electrons WATER H+ ions Oxygen PHOTOSYNTHESIS: THE DARK REACTIONS ATP + NADPH2 + CO2C6H12O6 DARK REACTIONS: OCCUR IN THE STROMA Carbon dioxide is split, providing carbon to make sugars. The ultimate product is glucose. While this system depends on the products from the light reactions, it does not directly require light energy. CARBON FIXATION 3 CO2 molecules attach to 3, 5 carbon sugars (RuBP) A 6 carbon sugar is formed and O2 is released This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco. This 6 carbon sugar rearranges and splits into 2, 3 carbon sugars (PGA) REDUCTION 6 ATP contribute phosphate groups 8 NADPH drop off electrons These are used to make the high energy compound G3P REGENERATION 1 G3P is used to form glucose The others are used to regenerate the original 5 carbon sugar 9 ATP and 6 NADPH are used per turn of the calvin cycle These are regenerated by Light Reactions 2 G3P = Glucose