printout - photosynthesis
advertisement

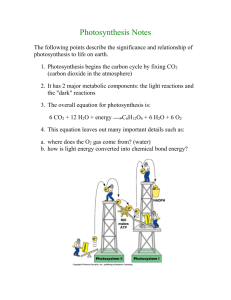
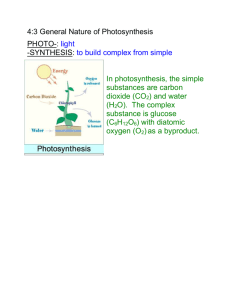
Definitions for Photosynthesis: Autotroph: An organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds; also called a producer. an organism that produces its own nutrients from inorganic substances or from the environment instead of consuming other organisms Heterotrophs: An organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer. Organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their byproducts and that cannot synthesize organic compounds from inorganic materials Photosynthesis: A process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches. Chloroplast: An organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy Chlorophyll: green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis Light Reactions: The steps in photosynthesis that occur on the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast and that convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH, evolving oxygen in the process. The initial reactions in photosynthesis, which are triggered by the absorption of light by photosystems I and II and include the passage of electrons along the electron transport chains, the production of NADPH and oxygen gas, and the synthesis of ATP through chemiosmosis Calvin Cycle: a biochemical pathway of photosynthesis in which carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using ATP. The Calvin Cycle is the second of two major stages in photosynthesis (following the light reactions), involving atmospheric CO2 fixation and reduction of the fixed carbon into carbohydrate. NADP+: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, an acceptor that temporarily stores energized electrons produced during the light reactions. Carbon Fixation: The incorporation of carbon from carbon dioxide into an organic compound by an autotrophic organism. The synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide, such as in photosynthesis Wavelength: The distance between crests of waves, such as those of the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic Spectrum: all of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, the entire frequency range of electromagnetic waves. Visible Light: That portion of the electromagnetic spectrum detected as various colors by the human eye, ranging in wavelength from about 380 nm to about 750 nm. Photons: A quantum, or discrete amount, of light energy. Spectrometer: Instrument that measures index of light reflection. Chlorophyll a: A blue-black plant pigment having a blue-green alcohol solution Chlorophyll b: A dark-green plant pigment having a brilliant green alcohol solution Carotenoid: Yellow and orange plant pigments that aid in photosynthesis. Primary Electron Acceptor: A specialized molecule sharing the reaction center with the pair of reaction-center chlorophyll a molecules; it accepts an electron from one of these two chlorophylls Photosystem: a cluster of chlorophyll and other molecules in a thylakoid that help to harvest light energy during photosynthesis Photosystem I: The photosystem that makes use of light to transfer electron 3 particularly from plastocyanin to ferredoxin, and whose reaction center chlorophyll is P700. Photosystem II : The photosystem that absorbs light for use to drive the oxidation of water and the reduction of plastoquinone, and whose reaction center chlorophyll is P680. Thylakoid: A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy. Grana: A stack of thylakoids inside the chloroplast. Stroma: The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water Pigment: a colored chemical compound that absorbs light, producing color Electron Transport Chain: A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. Chemiosmosis: in chloroplasts and mitochondria, a process in which the movement of protons down their concentration gradient across a membrane is coupled to the synthesis of ATP Biochemical Pathway: a series of chemical reactions that convert one biological material into another Stoma: A series of chemical reactions in which the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction Phototropism: a plant growth movement that occurs in response to the direction of a source of light Thigmotropism: a response of an organism or part of an organism to touch, such as the coiling of a vine around an object