Diffusion and Osmosis PowerPoint
advertisement

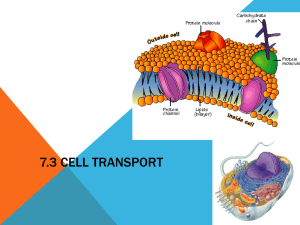
Diffusion and Osmosis Importance of Water Living things are composed of more than 50 percent water and depend on water to survive. You can live for weeks without food but only a few days without water. Why is water so important? All the chemical reactions in living things take place in water solutions. 2. Organisms use water to transport materials through their bodies. Plants use water to move minerals and sugars between roots and leaves. 3. The large percentage of water in living things acts like an insulator. The water in a cell helps keep its temperature constant, which allows life-sustaining chemical reactions to take place. 1. Cell Membrane Cells take in food, and oxygen, from their environment and release waste material. A cell has a membrane around it that works like a window screen. Selectively Permeable A cell’s membrane is selectively permeable. -Allows some things to enter or leave the cell while keeping other things outside or inside the cell. – Cell membranes will allow small molecules like O2, H20 and , CO2, to pass through. – Cell membranes will not allow larger molecules like Sucrose, and Starch. to pass through. Passive Transport How things move through a cell membrane depends on the size of the particles, the path taken through the membrane, and whether or not energy is used. The movement of substances through the cell membrane without the input of energy is called passive transport. 3 Types of Passive Transport 1. 2. 3. Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion 1. Diffusion Molecules in solids, liquids, and gases move constantly. This random movement of molecules from one area where there are more of them into another area where there are fewer of them is called diffusion. Example: Food Coloring and Water Equilibrium Molecules of a substance will continue to move from area into another until the relative number of these molecules is equal in the two areas. When this occurs, equilibrium is reached and diffusion stops. 2. Osmosis Water molecules move by diffusion into and out of cells. Osmosis is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semipermeable membrane to a region of low water concentration. Osmosis If the area surrounding the cell has a lower concentration of water molecules than inside the cell, the cell will lose water by osmosis. If the area surrounding the cell has a higher concentration of water molecules than inside the cell, the cell will gain water by osmosis. Example:Carrots Why do carrots in salt water become limp? When there is a lower concentration of water molecules surrounding the carrot cells, water is lost from inside the cells. The cell membrane comes away from its cell wall. The loss of water reduces pressure against the cell wall, and carrot cell becomes limp. Why do carrots stay crisp in pure water? When there is a higher concentration of water surrounding the carrot cells than inside the cell, water moves into the cells. The cells would fill with water. Their cell membranes press against their cell walls. Pressure increases and the cells become firm. 3rd Type of Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion • Some substances pass easily through the cell membrane by diffusion. • Other substances are so large that they can enter and leave the cell only with the help of molecules in the cell membrane called transport proteins. Glucose, Calcium, Potassium • This process, a type of passive transport, is known as facilitated diffusion. Facilitated Diffusion is a process of passive transport in which molecules diffuse across membranes, with the help of transport proteins. Re-Cap Passive Transport: The movement of substances through the cell membrane without the input of energy Types of Passive Transport: 1. Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. O2 and CO2 2. Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a region of high water concentration through a semipermeable membrane to a region of low water concentration. 3. Facilitated Diffusion is the transport of substances through the cell membrane with the help of proteins Active Transport • Sometimes a substance is needed inside the cell even though the amount of that substance inside the cell is already greater than the amount outside the cell. • Active transport is the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy. Two Types of Active Transport 1. Endocytosis 2. Exocytosis 1. Endocytosis • Large protein molecules and bacteria, can be transported into a cell when they are surrounded by the cell membrane. • This process of taking substances into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane is called endocytosis Endocytosis • Some one-celled organisms take in food this way. • The cell membrane surrounds and engulfs a particle wraps around the particle and forms vesticle. (storage and transport structures) 2. Exocytosis • The contents of a vesicle can be released by a cell using the process called exocytosis. • Exocytosis occurs in the opposite way that endocytosis does. • Exocytosis occurs when a vesicle’s membrane fuses with a cell’s membrane, and the contents are released.