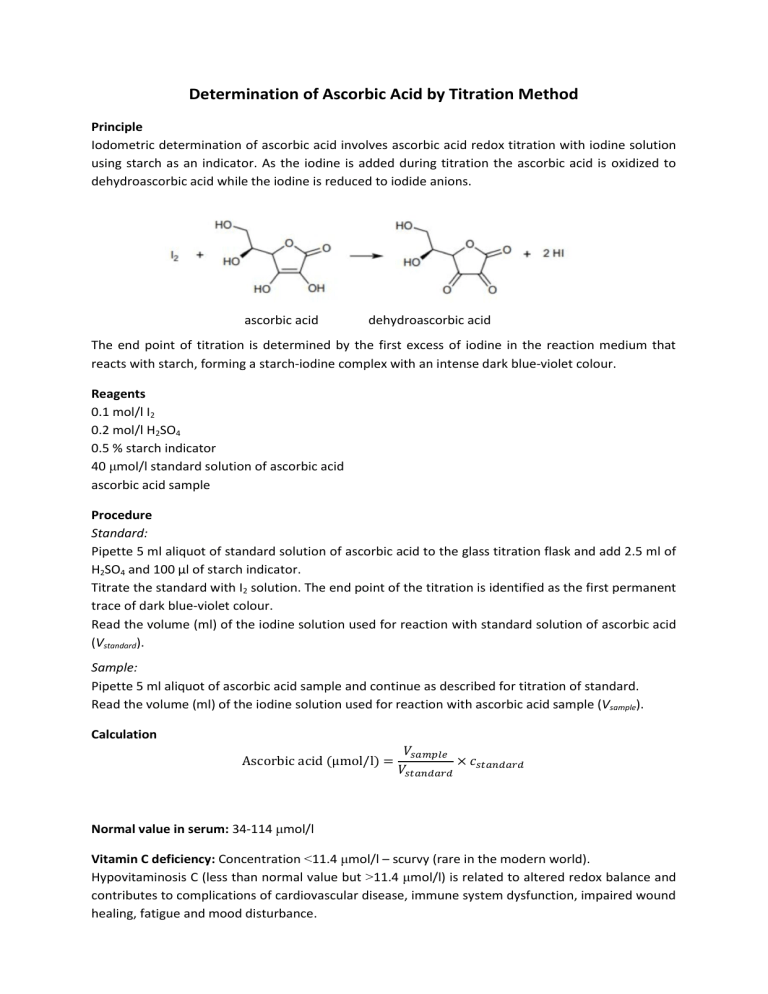
Determination of Ascorbic Acid by Titration Method Principle Iodometric determination of ascorbic acid involves ascorbic acid redox titration with iodine solution using starch as an indicator. As the iodine is added during titration the ascorbic acid is oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid while the iodine is reduced to iodide anions. ascorbic acid dehydroascorbic acid The end point of titration is determined by the first excess of iodine in the reaction medium that reacts with starch, forming a starch-iodine complex with an intense dark blue-violet colour. Reagents 0.1 mol/l I2 0.2 mol/l H2SO4 0.5 % starch indicator 40 μmol/l standard solution of ascorbic acid ascorbic acid sample Procedure Standard: Pipette 5 ml aliquot of standard solution of ascorbic acid to the glass titration flask and add 2.5 ml of H2SO4 and 100 µl of starch indicator. Titrate the standard with I2 solution. The end point of the titration is identified as the first permanent trace of dark blue-violet colour. Read the volume (ml) of the iodine solution used for reaction with standard solution of ascorbic acid (Vstandard). Sample: Pipette 5 ml aliquot of ascorbic acid sample and continue as described for titration of standard. Read the volume (ml) of the iodine solution used for reaction with ascorbic acid sample (Vsample). Calculation Ascorbic acid (μmol/l) = 𝑉𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 × 𝑐𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑉𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 Normal value in serum: 34-114 μmol/l Vitamin C deficiency: Concentration <11.4 μmol/l – scurvy (rare in the modern world). Hypovitaminosis C (less than normal value but >11.4 μmol/l) is related to altered redox balance and contributes to complications of cardiovascular disease, immune system dysfunction, impaired wound healing, fatigue and mood disturbance.