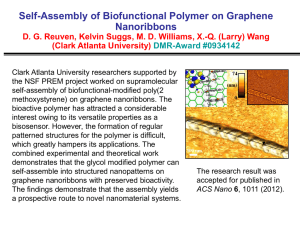
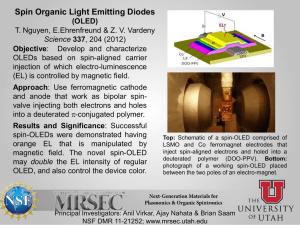
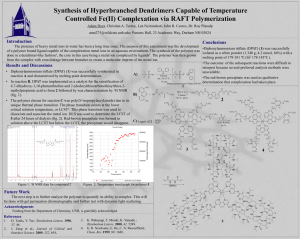
6: Hydrolytic and Biotic Degradation
advertisement

ADVANCED BIO-FRIENDLY POLYMERS Eva Papajová Mechanochemical degradation, degradation by O3, radiolytic degradation, burning Thermal degradation Thermooxidation Photodegradation Photooxidation Hydrolytic degradation Biodegradation Decomposition of polymer chain by reaction with water. in relation with ester bond of polyesters pH initiated pH < 7 (acid) pH > 7 (basic) Decomposition of polymer chain by reaction with water. RX + HOH → ROH + HX Ability of polymers to degrade by hydrolysis is given by difference in electronegativity of atoms in polymer chain or side groups. O R 1 X R 2 + H+ O H2O R 1 1 X + CX R 2 O R 1 R 2 + - OH H2O 1 R + C X 2 + R + R + XH + H XH + OH OH HO O R H2O O 2 R H2O R 1 2 - OH OH 5 polyanhydrides polyesters polyamides polyethers polyether urethanes polyurea polycarbonates Depends on repulsive interactions with ions availability of reacting bonds physical parameters (swelling, transport of ions along polymer chain) Water as a carrier of microorganisms for biodegradation of polymer material. degradation process resulting from the action of naturally occuring microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and algae microorganisms can use their enzymes for cleavage of the polymer chain at the specific location and use them as a source of energy structure of the polymer makes it biodegradable Enzymes responsible for the biodegradation process EXOGENEOUS CELLULAR ENZYMES 1st step ENDOCELLULAR ENZYMES 2nd step 1st STEP EXTRACELLULAR ENZYMES enzyme secreted by cell that works outside of that cell used for cleavage of long polymer chain in order to permeate through cell membrane Depolymerization (oligomers, dimers, monomers, ...) Cell Preliminary degradation (photodegradation, photooxidation, chemical degradation, etc.) enhances biodegradation process. Material changes - important mostly for characterization of the first step of biodegradation Mechanical properties (tensile or dynamic analysis) Molecular weight of polymer chains (size-exclusion chromatography) Degradation in crystalline or amorphous region (differential scanning calorimetry) Structure of polymer material (scanning electron microscopy, contact angle measurements) Changes in polymer structure (spectroscopy techniques – NMR, IR, MS) Enzymes responsible for the biodegradation process EXOGENEOUS CELLULAR ENZYMES 1st step ENDOCELLULAR ENZYMES 2nd step 2nd STEP ENDOCELLULAR ENZYMES enzyme works inside the cell in which it was produced carbon and energy sources are metabolized Mineralization Cell Products in presence of O2 CO2, H2O in absence of O2 CH4, CO2 Production of gasses - characteristic for mineralization process Devices for measuring composition of gasses (O2, CO2, CH4) Gas chromatography IR spectroscopy (CO2) Paramagnetic resonance (O2) Measurement of pressure (O2) Amount of absorbed gasses measured by titration technique (CO2) Biodegradation process is dependent on factors .... Polymer characteristics Flexibility Crystallinity Morphology Functional groups Crosslinking Molecular weight Copolymers Blend Tacticity Additives Exposure conditions Abiotic Temperature Moisture pH UV radiation Biotic Extracellular enzymes Hydrophobicity Biosurfactants accessability of water and microogranisms functional groups and additives as an active points for initiation of degradation Crystallinity of polymers Decreasing rate of degradation Poly(L-lactide) Lamella Increasing crystallinity Amorphous region Tsuji, H., Miyauchi, S. (2001) Polymer Degradation and Stability 71, 415. poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) O ( O (CH2)5 poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) CH3 C )n ( C poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) O C CH2 O ) m ( C CH2 poly(lactide) (PLA) O O (CH2)4 CH2 CH2 O 3.5:1 5:1 ( O CH3 O (CH2)2 3:1 C )n CH3 ( O CH O C )n 1:1 Hydrolytic degradation PCL < PHBV < PBS < PLA Biodegradation PCL > PHBV > PBS > PLA CH2 O )n Simulations (reactor) Analysis in the nature water, soil, compost or material from dump complexity of parameters defined conditions water, soil, compost, dump complexity of parameters variability of conditions Relevance of the information Laboratory analysis enzymes, individual and mixed cultures of microorganisms artificial conditions precisely defined conditions Biodegradable polymers starch poly(hydroxybutyrate) cellulose poly(lactide) pectin polycaprolactone gelatine medicinal sutures drug delivery systems orthopedic fixation devices replacing a bone cement industrial mulching foils plant pots silage foils packaging (bags, boxes) tooth brush handles others ... textile, electronics, houseware