Thermal stability of polyphenols - IQ
P21
Lina Glittmann
Juan Sesma Martín
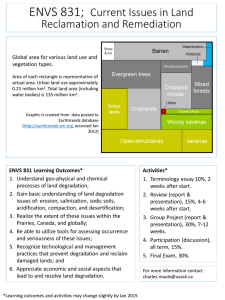
Definition
Polyphenols are a group of chemicals found in plants characterized by the presence of more than one phenol group per molecule.
Properties
Polyphenols have beneficial properties for human
Drying
Dehydration
Enzymatic reaction
t>80°C reduction of phenolic compounds
Leaching
Begin of thermal degradation
- forming of monomers
- reaction among molecules
- hydrolysis
- oxidation
without thermal treatment amount to enzymatical reactions
Epimerization frequency stabilisation
High Polimerization degree degradation presence of gallate groups heat sensitivity
Biological activity degradation through enzymes
Hydrolysis Stabilization
Prevent thermal degradation of more sensible compounds polymeric
Temperature around 30-55 ̊C
Copigmentation effect
Oxidation to quinins
Interaction with proteins
Degradation instantly in the first 10min zero order
Velocity constant k increasing with T k iso values as a function of temperature in extra-virgin oil
Time for complete disappearance of total polyphenols
Changes in
Phenolic profil
Chemical-
Physical-
Biological Properties
Inactivation of enzyms necessary

![Pre-workshop questionnaire for CEDRA Workshop [ ], [ ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010861335_1-6acdefcd9c672b666e2e207b48b7be0a-300x300.png)