Solid Liquid and Gas Notes
advertisement

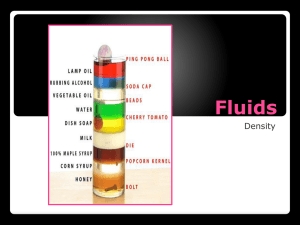
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Notes Read the paragraph at the top of the screen, then add the notes at the bottom of the screen to your notebook. WRITE THE BLACK TEXT INTO YOUR NOTEBOOK WRITE THE GLOSSARY WORDS (G) IN THE BACK OF YOUR NOTEBOOK Press F5 on your keyboard to view the slide show. Press the space bar or arrows to advance the slide. Your everyday world is full of substances that can be classified as solids, liquids, or gases. (Write the black text in your notebook and fill in the blanks) Substances can be classified as ________, ____________, or ________________. Solids, liquids, and gases may be elements, compounds, or mixtures. Gold is an element. Water is a compound that you’ve seen as both a liquid and solid. Air is a mixture of gases. Add to your glossary (G): Element – made of the same type of atoms. Compound – different atoms chemically bonded together to make a new substance. Mixture – a composition of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together that can be separated. What would happen if you picked up a solid object and moved it around the room. Would the comb, or book, or table change shape or size? Would a book get bigger if you put it inside an aquarium? Would a comb become flatter if you set it on a table? Of course not!! Solids G: Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Draw this diagram in your notebook. The particles in a solid are packed tightly together and vibrate (wiggle) slightly. Solids are rigid because they can’t overcome the attractive forces locking them in place. In many solids, the particles form a regular repeating pattern. These patterns create crystals. Solids that are made up of crystals are called crystalline solids. Salt, sugar, and snow are examples of crystalline solids. When a crystalline solid is melted, it melts at a specific temperature. A solid that is made up of repeating patterns, or crystals, is called a __________ ______. Quartz Amorphous solids have particles that are not arranged in in a regular pattern. Examples include plastics, rubber, and glass. Amorphous solids do not melt at distinct temperatures. Instead, it may become softer and softer or change into other substances. A solid that becomes softer and softer as it is heated and made of particles not in a regular pattern is called an __________ ______. Quartz Glass If you pour a can of pop from the can into a cup. The shape of the liquid will change, but the volume will stay the same. If you spill the pop on the floor, it will spread out into a big shallow puddle. G: Liquids have a definite volume but no shape of their own. They take the shape of the container. Draw this diagram into your notebook. Liquid particles are free to move. The particles move around, but stay in contact. Liquids can easily be poured. Properties of Liquids • Surface Tension is an attraction between molecules of a liquid that brings the molecules on the surface closer together. • The high surface tension of water, for instance, enables many small creatures, such as the water strider, to walk safely on its surface. Surface tension is an ____________ between molecules of liquid that allows many _________ ____________ to _________ safely on the surface. Properties of Liquids Viscosity – a liquid’s resistance to flowing. High viscosity (molasses) is really thick and low viscosity (water) is really thin. A liquid’s resistance to flowing is call ____________. Examples of viscosity (try to come up with your own): High: ______________________ Medium: ______________________ Low: _________________________ If you put gas into a closed container, the gas particles will either spread out or be squeezed together as they fill the container. G: Gases have no definite shape and no definite volume. Draw this diagram into your notebook. Gas particles spread apart, filling the space available. Gas particles move VERY fast in all directions and are not connected. Write and answer the following questions in your notebook: 1. Think about the properties of sand – it will take the shape of the container and can be poured. Is sand a solid or a liquid? Explain your answer. 2. Copy the Venn diagram and use it to compare solids, liquids, and gases. MAKING MEANING CONFERENCE Think about the properties of sand – it will take the shape of the container and can be poured. Is sand a solid or a liquid? Defend each argument. When you pour sand, is that a chemical or physical change? Explain your answer. SOLID CRYSTALLINE: SNOWFLAKES & SALT AMORPHOUS: GLASS & RUBBER HOLDS SHAPE SHAPE OF BOTTOM OF CONTAINER SHATTER DEFINITE VOLUME SHAPE OF ENTIRE CONTAINER VIBRATION SPLATTER NO DEFINITE VISCOSITY & SURFACE SHAPE TENSION LIQUID SCATTER GAS SOLID CRYSTALLINE: SNOWFLAKES & SALT AMORPHOUS: GLASS & RUBBER HOLDS SHAPE SHAPE OF BOTTOM OF CONTAINER SHATTER DEFINITE VOLUME SHAPE OF ENTIRE CONTAINER VIBRATION SPLATTER NO DEFINITE VISCOSITY & SURFACE SHAPE TENSION LIQUID SCATTER GAS Great Job! Have fun playing the review games at this site. Click on to address below and play the games, view the videos, etc . . . http://www.neok12.com/States-of-Matter.htm